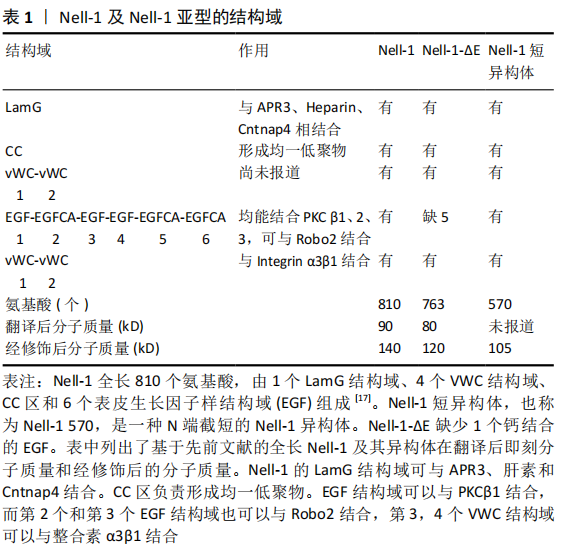
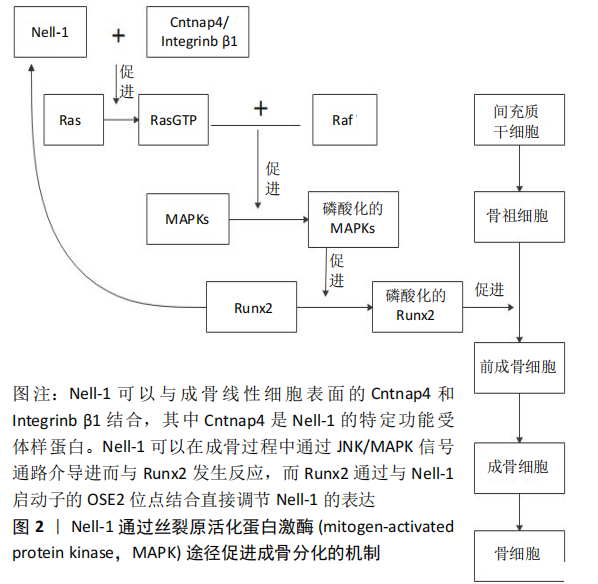
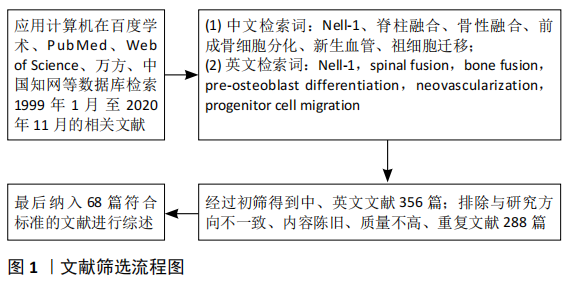
[1] BUCHBINDER R, VAN TULDER M, ÖBERG B, et al. Low back pain: a call for action. Lancet. 2018;391(10137):2384-2388.
[2] CHUN DS, BAKER KC, HSU WK. Lumbar pseudarthrosis: a review of current diagnosis and treatment. Neurosurg Focus. 2015;39(4):E10.
[3] MAKINO T, KAITO T, FUJIWARA H, et al. Risk Factors for Poor Patient-Reported Quality of Life Outcomes After Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion: An Analysis of 2-Year Follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017; 42(19):1502-1510.
[4] OLABISI R. Cell-based therapies for spinal fusion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;760:148-173.
[5] NAKAO S, MINAMIDE A, KAWAKAMI M, et al. The influence of alendronate on spine fusion in an osteoporotic animal model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(18):1446-1452.
[6] PINHEIRO AL, SANTOS NR, OLIVEIRA PC, et al. The efficacy of the use of IR laser phototherapy associated to biphasic ceramic graft and guided bone regeneration on surgical fractures treated with wire osteosynthesis: a comparative laser fluorescence and Raman spectral study on rabbits.Lasers Med Sci. 2013;28(3):815-822.
[7] MULCONREY DS, BRIDWELL KH, FLYNN J, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein (RhBMP-2) as a substitute for iliac crest bone graft in multilevel adult spinal deformity surgery: minimum two-year evaluation of fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(20):2153-2159.
[8] BODEN SD. Overview of the biology of lumbar spine fusion and principles for selecting a bone graft substitute. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(16 Suppl 1):S26-31.
[9] ZHANG X, TING K, BESSETTE CM, et al. Nell-1, a key functional mediator of Runx2, partially rescues calvarial defects in Runx2(+/-) mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(4):777-791.
[10] YUAN W, JAMES AW, ASATRIAN G, et al. NELL-1 based demineralized bone graft promotes rat spine fusion as compared to commercially available BMP-2 product. J Orthop Sci. 2013;18(4):646-657.
[11] LEE S, ZHANG X, SHEN J, et al. Brief Report: Human Perivascular Stem Cells and Nel-Like Protein-1 Synergistically Enhance Spinal Fusion in Osteoporotic Rats. Stem Cells. 2015;33(10):3158-3163.
[12] FAHMY-GARCIA S, VAN DRIEL M, WITTE-BUOMA J, et al. NELL-1, HMGB1, and CCN2 Enhance Migration and Vasculogenesis, But Not Osteogenic Differentiation Compared to BMP2. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(3-4):207-218.
[13] PAKVASA M, ALVERDY A, MOSTAFA S, et al. Neural EGF-like protein 1 (NELL-1): Signaling crosstalk in mesenchymal stem cells and applications in regenerative medicine. Genes Dis. 2017;4(3):127-137.
[14] QI H, KIM JK, HA P, et al. Inactivation of Nell-1 in Chondrocytes Significantly Impedes Appendicular Skeletogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2019;34(3):533-546.
[15] TING K, VASTARDIS H, MULLIKEN JB, et al. Human NELL-1 expressed in unilateral coronal synostosis. J Bone Miner Res. 1999;14(1):80-89.
[16] BOKUI N, OTANI T, IGARASHI K, et al. Involvement of MAPK signaling molecules and Runx2 in the NELL1-induced osteoblastic differentiation. FEBS Lett. 2008;582(2):365-371.
[17] ZHANG X, ZARA J, SIU RK, et al. The role of NELL-1, a growth factor associated with craniosynostosis, in promoting bone regeneration. J Dent Res. 2010;89(9):865-878.
[18] KURODA S, TANIZAWA K. Involvement of epidermal growth factor-like domain of NELL proteins in the novel protein-protein interaction with protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999;265(3):752-757.
[19] ZOU X, SHEN J, CHEN F, et al. NELL-1 binds to APR3 affecting human osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. FEBS Lett. 2011;585(15): 2410-2418.
[20] NAKAMURA Y, HASEBE A, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Oligomerization-induced conformational change in the C-terminal region of Nel-like molecule 1 (NELL1) protein is necessary for the efficient mediation of murine MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion and spreading. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(14):9781-9794.
[21] YAMAMOTO N, KASHIWAGI M, ISHIHARA M, et al. Robo2 contains a cryptic binding site for neural EGFL-like (NELL) protein 1/2. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(12):4693-4703.
[22] LI C, ZHENG Z, HA P, et al. Neurexin Superfamily Cell Membrane Receptor Contactin-Associated Protein Like-4 (Cntnap4) Is Involved in Neural EGFL-Like 1 (Nell-1)-Responsive Osteogenesis. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(10):1813-1825.
[23] MEYERS CA, SUN Z, CHANG L, et al. Age dependent effects of NELL-1 isoforms on bone marrow stromal cells. J Orthop. 2019;16(2):175-178.
[24] ZHAO H, QIN X, ZHANG Q, et al. Nell-1-ΔE, a novel transcript of Nell-1, inhibits cell migration by interacting with enolase-1. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(7):5725-5733.
[25] HIRSCH BP, UNNANUNTANA A, CUNNINGHAM ME, et al. The effect of therapies for osteoporosis on spine fusion: a systematic review. Spine J. 2013;13(2):190-199.
[26] BLONDER J, XIAO Z, VEENSTRA TD. Proteomic profiling of differentiating osteoblasts. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2006;3(5):483-496.
[27] SIU RK, LU SS, LI W, et al. Nell-1 protein promotes bone formation in a sheep spinal fusion model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(7-8):1123-1135.
[28] JAMES AW, SHEN J, TSUEI R, et al. NELL-1 induces Sca-1+ mesenchymal progenitor cell expansion in models of bone maintenance and repair. JCI Insight. 2017;2(12):e92573.
[29] TRUONG T, ZHANG X, PATHMANATHAN D, et al. Craniosynostosis-associated gene nell-1 is regulated by runx2. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(1):7-18.
[30] KWAK J, ZARA JN, CHIANG M, et al. NELL-1 injection maintains long-bone quantity and quality in an ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic senile rat model. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(3-4):426-436.
[31] PARK SB, PARK SH, KIM NH, et al. BMP-2 induced early bone formation in spine fusion using rat ovariectomy osteoporosis model. Spine J. 2013;13(10):1273-1280.
[32] ZHANG J, CHEN Y, XU J, et al. Tissue engineering using 3D printed nano-bioactive glass loaded with NELL1 gene for repairing alveolar bone defects. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(4):213-220.
[33] PANG S, SHEN J, LIU Y, et al. Proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells induced by a short isoform of NELL-1. Stem Cells. 2015;33(3):904-915.
[34] ASKARINAM A, JAMES AW, ZARA JN, et al. Human perivascular stem cells show enhanced osteogenesis and vasculogenesis with Nel-like molecule I protein. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(11-12):1386-1397.
[35] LIU L, LAM WMR, NAIDU M, et al. Synergistic Effect of NELL-1 and an Ultra-Low Dose of BMP-2 on Spinal Fusion. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019; 25(23-24):1677-1689.
[36] CHIBA H, SAWADA N, ONO T, et al. Establishment and characterization of a simian virus 40-immortalized osteoblastic cell line from normal human bone. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993;84(3):290-297.
[37] TAKIGAWA M. CCN2: a master regulator of the genesis of bone and cartilage. J Cell Commun Signal. 2013;7(3):191-201.
[38] COWAN CM, JIANG X, HSU T, et al. Synergistic effects of Nell-1 and BMP-2 on the osteogenic differentiation of myoblasts. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(6):918-930.
[39] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZARA JN, et al. BMP2-induced inflammation can be suppressed by the osteoinductive growth factor NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(21-22):2390-2401.
[40] AGHALOO T, COWAN CM, ZHANG X, et al. The effect of NELL1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 on calvarial bone regeneration. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(2):300-308.
[41] ZHU S, SONG D, JIANG X, et al. Combined effects of recombinant human BMP-2 and Nell-1 on bone regeneration in rapid distraction osteogenesis of rabbit tibia. Injury. 2011;42(12):1467-1473.
[42] SHEN J, JAMES AW, ZHANG X, et al. Novel Wnt Regulator NEL-Like Molecule-1 Antagonizes Adipogenesis and Augments Osteogenesis Induced by Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2. Am J Pathol.2016;186(2):419-434.
[43] PAN HC, LEE S, TING K, et al. Cyst-Like Osteolytic Formations in Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 (rhBMP-2) Augmented Sheep Spinal Fusion. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(7):1485-1495.
[44] JAMES AW, SHEN J, ZHANG X, et al. NELL-1 in the treatment of osteoporotic bone loss. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7362.
[45] JAMES AW, PAN A, CHIANG M, et al. new function of Nell-1 protein in repressing adipogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;411(1):126-131.
[46] CARRARA M, FUSCHI P, IVAN C, et al. Circular RNAs: Methodological challenges and perspectives in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(11):5176-5187.
[47] CAI H, LI Y, NIRINGIYUMUKIZA JD, et al. Circular RNA involvement in aging: An emerging player with great potential. Mech Ageing Dev. 2019;178:16-24.
[48] E S, COSTA MC, KURC S, et al. The circulating non-coding RNA landscape for biomarker research: lessons and prospects from cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(7):1085-1099.
[49] LI LJ, ZHU ZW, ZHAO W, et al. Circular RNA expression profile and potential function of hsa_circ_0045272 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology. 2018;155(1):137-149.
[50] CHEN D, MA W, KE Z, et al. CircRNA hsa_circ_100395 regulates miR-1228/TCF21 pathway to inhibit lung cancer progression. Cell Cycle. 2018;17(16):2080-2090.
[51] HE JH, HAN ZP, ZHOU JB, et al. MiR-145 affected the circular RNA expression in prostate cancer LNCaP cells. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(11):9168-9177.
[52] HUANG X, CEN X, ZHANG B, et al. The roles of circRFWD2 and circINO80 during NELL-1-induced osteogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(12):8432-8441.
[53] FATICA A, BOZZONI I. Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet. 2014;15(1):7-21.
[54] WU R, RUAN J, SUN Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS2 facilitates adipose-derived stem cells (ASCs) osteogenic differentiation through miR-665/IL6 axis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):348.
[55] XIAO Y, YAN X, YANG Y, et al. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA HOTAIRM1 variant 1 contributes to osteoarthritis via regulating miR-125b/BMPR2 axis and activating JNK/MAPK/ERK pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1569-1577.
[56] GAO X, GE J, LI W, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes osteogenic differentiation to relieve osteolysis via Wnt/β-catenin activation. Cell Biosci. 2018;8:19.
[57] PAN JX. LncRNA H19 promotes atherosclerosis by regulating MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(2):322-328.
[58] HU K, JIANG W, SUN H, et al. Long noncoding RNA ZBED3-AS1 induces the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and enhances bone regeneration by repressing IL-1β via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(10):17863-17875.
[59] XIA K, CEN X, YU L, et al. Long noncoding RNA expression profiles during the NEL-like 1 protein-induced osteogenic differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(9):6010-6022.
[60] TANJAYA J, LORD EL, WANG C, et al. The Effects of Systemic Therapy of PEGylated NEL-Like Protein 1 (NELL-1) on Fracture Healing in Mice. Am J Pathol. 2018;188(3):715-727.
[61] FAN M, JIANG WX, WANG AY, et al. Combined effects of NEL-like type 1 gene and zoledronate in preventing collapse of the femoral head. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2013;35(5):553-560.
[62] JAMES AW, LACHAUD G, SHEN J, et al. A Review of the Clinical Side Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016;22(4):284-297.
[63] KWAK JH, ZHANG Y, PARK J, et al. Pharmacokinetics and osteogenic potential of PEGylated NELL-1 in vivo after systemic administration. Biomaterials. 2015;57:73-83.
[64] LEE S, WANG C, PAN HC, et al. Combining Smoothened Agonist and NEL-Like Protein-1 Enhances Bone Healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(6):1385-1396.
[65] WANG Z, KAMBHAMPATI S, CHENG Y, et al. Methylation Biomarker Panel Performance in EsophaCap Cytology Samples for Diagnosing Barrett’s Esophagus: A Prospective Validation Study. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25(7):2127-2135.
[66] SHEN J, LACHAUD G, KHADARIAN K, et al. NELL-1 expression in benign and malignant bone tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460(2):368-374.
[67] ZHAI Y, WEI R, SHA S, et al. Effect of NELL1 on lung cancer stem‑like cell differentiation. Oncol Rep. 2019;41(3):1817-1826.
[68] NAKAMURA R, OYAMA T, TAJIRI R, et al. Expression and regulatory effects on cancer cell behavior of NELL1 and NELL2 in human renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2015;106(5):656-664.
|