中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (25): 3943-3948.doi: 10.12307/2021.002
• 干细胞基础实验 basic experiments of stem cells • 上一篇 下一篇
二乙酰吗啡致大鼠小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡过程中C-Jun、Cytc和Caspase-9的作用
苏丽萍1,路子扬2,刘 丽2,张 巍1,苏天园3,胡夏韵4,蒲红伟5,6,韩登峰7
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院,1病理科,3远程医学中心,5学科建设科,7神经内科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830011;2新疆医科大学基础医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;4西安交通大学第一附属医院胸外二科,陕西省西安市 710061;6河北医科大学法医学重点实验室,河北省石家庄市 050000
C-jun, Cytc and Caspase-9 in the apoptosis of cerebellar granule neurons induced by diacetylmorphine in rats
Su Liping1, Lu Ziyang2, Liu Li2, Zhang Wei1, Su Tianyuan3, Hu Xiayun4, Pu Hongwei5, 6, Han Dengfeng7
- 1Department of Pathology, 3Telemedicine center, 5Discipline Construction Section, 7Department of Neurology, First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2School of Basic Medicine, Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 4Second Department of Thoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, Shaanxi Province, China; 6Key Laboratory of Forensic Medicine of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
二乙酰吗啡:为半合成的阿片受体纯激动剂,由吗啡和醋酸酐为原料经化学反应制成,其镇痛作用强于吗啡,镇痛效果为吗啡的4-8倍,其成瘾速度快,戒断难度大。长期使用后不仅会对人体的免疫功能造成严重破坏,还可导致心、肝、肾等重要脏器的功能损害。
C-jun:作为最早被发现的JNK核内底物,属于碱性-亮氨酸拉链蛋白的主要成员,可与胞质中激活的c-jun氨基末端激酶特异性结合,与碱性-亮氨酸拉链蛋白转录因子(如c-fos家族和ATF家族成员)形成异二聚体,然后与DNA染色体结合,促进凋亡相关靶基因表达。
背景:二乙酰吗啡药物可导致神经元损伤,但是目前二乙酰吗啡是否诱导神经元细胞凋亡,c-jun、cytc 和caspase-9因子是否参与此过程尚未见报道。
目的:探讨C-jun、Cytc、Caspase-9是否参与二乙酰吗啡诱导神经元细胞凋亡过程。
方法:将SD乳鼠小脑颗粒神经元细胞体外培养7 d,采用不同质量浓度二乙酰吗啡(0,10,40,80,100,120 mg/L)干预神经元细胞24 h,在倒置荧光显微镜下观察神经元细胞形态改变,流式细胞仪检测细胞凋亡率。采用100 mg/L二乙酰吗啡和20 μmol/L JNK抑制剂SP600125作用于细胞24 h,通过免疫荧光和蛋白印迹方法检测c-jun、cytc 和caspase-9蛋白的表达。
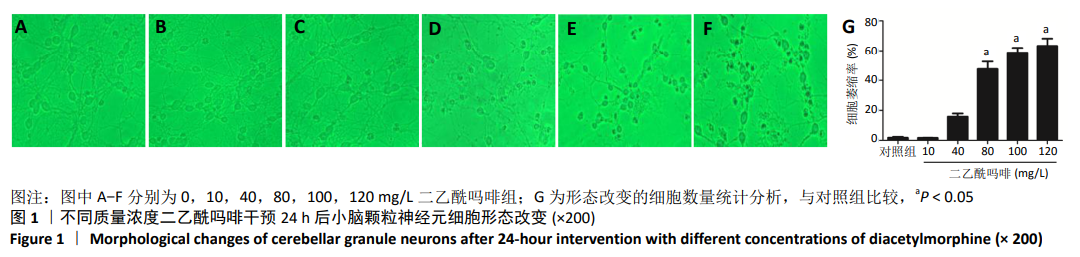
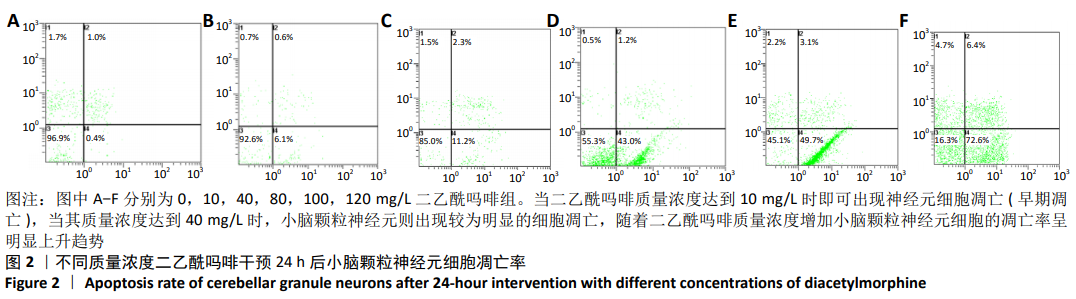
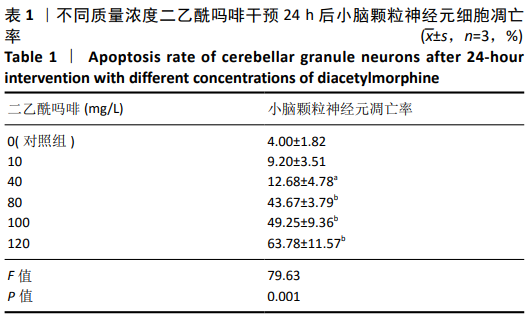
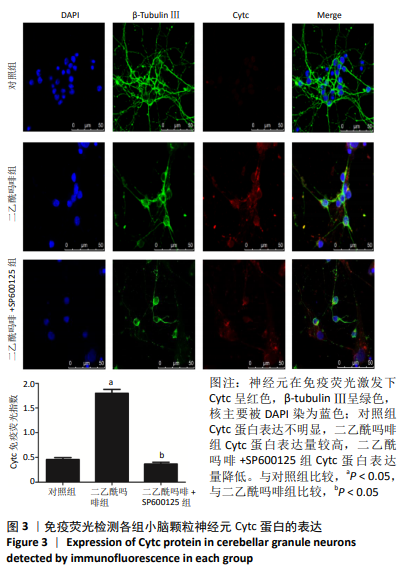
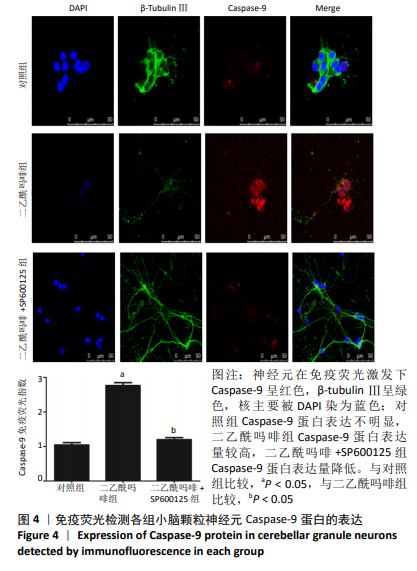
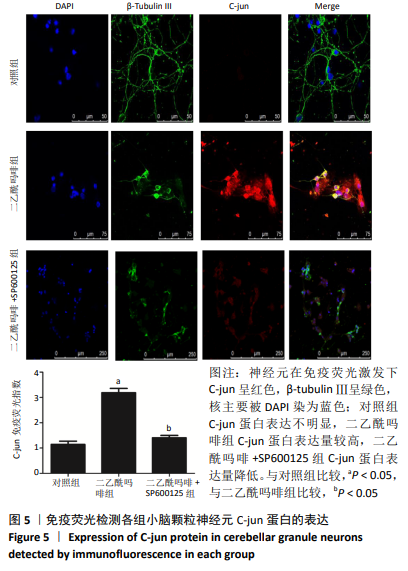
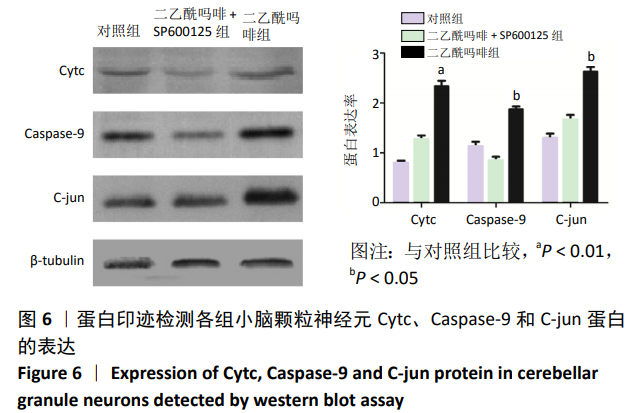
结果与结论:①在不同质量浓度二乙酰吗啡干预下,随着给药质量浓度的增加,神经元细胞胞体萎缩、亮度降低,部分呈灰黑色,细胞碎裂,神经元网状结构不同程度的消失,细胞改变数量逐渐增加;②随着给药质量浓度的增加,形态改变的细胞数量明显增多(P < 0.01),细胞凋亡率也显著增高(P < 0.01);③与对照组相比,100 mg/L二乙酰吗啡作用神经元细胞时,二乙酰吗啡组c-jun、cytc和caspase-9 蛋白呈高表达,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);与二乙酰吗啡组相比,二乙酰吗啡+SP600125组c-jun、cytc和caspase-9 蛋白表达明显下调,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④结果表明,二乙酰吗啡可诱导小脑颗粒神经元细胞凋亡,c-jun、cytc 和caspase-9参与了二乙酰吗啡致神经元细胞凋亡的过程。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5113-6050(苏丽萍)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: