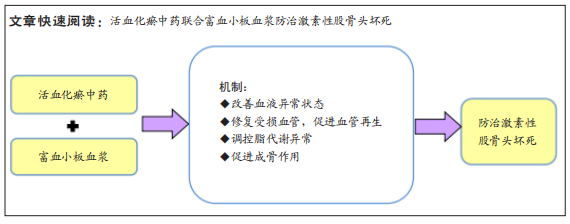
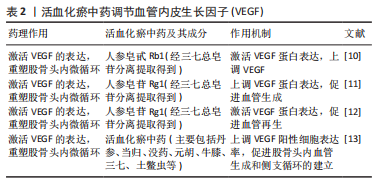
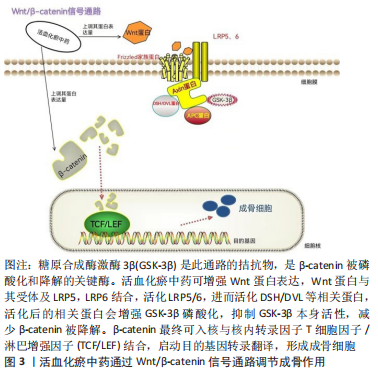
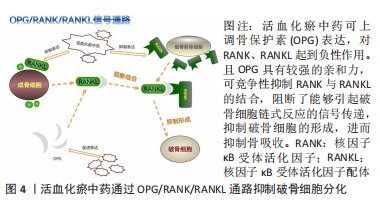
[1] 李泰贤,陈志伟,王荣田,等.基于文献计量学分析中医药治疗股骨头坏死的研究现状[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(4):41-46.
[2] LI SM, XU H, CHEN KJ. The diagnostic criteria of blood-stasis syndrome: considerations for standardization of pattern identification. Chin J Integr Med. 2014;20(7):483-489.
[3] 包杭生,李逸群,涂泽松.血液流变学在骨伤科疾病中的应用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2010,18(10):67-69.
[4] HUANG YX, XU DQ, YUE SJ, et al. Deciphering the Active Compounds and Mechanisms of Qixuehe Capsule on Qi Stagnation and Blood Stasis Syndrome: A Network Pharmacology Study. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:5053914.
[5] 田伟明,王文智,王鑫国.骨复活汤对激素性股骨头坏死血液流变学及脂代谢的影响[J].中国中药杂志,2002,27(10):769-771.
[6] 段卫峰,刘骏逸,杜志军,等.补肾祛瘀法对激素诱导股骨头坏死兔血脂及凝血指标的影响[J].西部中医药,2019,32(11):26-31.
[7] 齐振熙,曹阳.活血化瘀中药防治激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的实验研究[J]中国临床康复,2001,5(24):118-119.
[8] 方圣杰,章轶立,朱嘉,等.糖皮质激素抑制Leptin,VEGF蛋白表达诱导骨质疏松作用机制研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(3):320-324,367.
[9] SUZUKI O, BISHOP AT, SUNAGAWA T, et al. VEGF-promoted surgical angiogenesis in necrotic bone. Microsurgery. 2004;24(1):85-91.
[10] YE J, WEI D, PENG L, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents steroid‑induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head through the bone morphogenetic protein‑2 and vascular endothelial growth factor pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3175-3181.
[11] LEUNG KW, NG HM, TANG MK, et al. Ginsenoside-Rg1 mediates a hypoxia-independent upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α to promote angiogenesis. Angiogenesis. 2011;14(4):515-522.
[12] LEUNG KW, PON YL, WONG RN, et al. Ginsenoside-Rg1 induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression through the glucocorticoid receptor-related phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and beta-catenin/T-cell factor-dependent pathway in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(47):36280-36288.
[13] LI JH, WU YL, YE JH, et al. Effects of blood-activating and stasis-removing drugs combined with VEGF gene transfer on angiogenesis in ischemic necrosis of the femoral head. J Tradit Chin Med. 2009;29(3):216-219.
[14] 史风雷,任丽霞,孙升云,等.复方丹参注射液预防激素性股骨头坏死的初步研究[J].中医正骨,2002,14(4):3-5.
[15] 李峻辉,栾晓文,宁亚功,等. 补肾活骨方对激素性股骨头坏死模兔血液流变学及血脂影响的研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2002,8(7):20-22.
[16] JIANG Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Pravastatin prevents steroid-induced osteonecrosis in rats by suppressing PPARγ expression and activating Wnt signaling pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014;239(3):347-355.
[17] PUTNAM SE, SCUTT AM, BICKNELL K, et al. Natural products as alternative treatments for metabolic bone disorders and for maintenance of bone health. Phytother Res. 2007;21(2):99-112.
[18] YUN SI, YOON HY, JEONG SY, et al. Glucocorticoid induces apoptosis of osteoblast cells through the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(2):140-148.
[19] 高彦淳,冯勇,张长青.激素性股骨头坏死发生机制的研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(4):231-234
[20] JIA D, O’BRIEN CA, STEWART SA, et al. Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoclasts to increase their life span and reduce bone density. Endocrinology. 2006;147(12):5592-5599.
[21] GAO ZR, FENG YZ, ZHAO YQ, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine promotes bone regeneration in bone tissue engineering. Chin Med. 2022;17(1):86.
[22] CLEVERS H, NUSSE R. Wnt/β-catenin signaling and disease. Cell. 2012;149(6):1192-1205.
[23] 吴忠书,韦雨柔,陈哓俊,等.活血通络胶囊促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中的ERα-Wnt/β-catenin信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25):3937-3943.
[24] 陈杰,张堃,孔令俊,等.三七总皂苷通过调控Wnt/β-catenin通路减轻家兔股骨头坏死[J].中药药理与临床,2019,35(4):95-99.
[25] HUANG W, JIN S, YANG W, et al. Protective effect of Agrimonia pilosa polysaccharides on dexamethasone-treated MC3T3-E1 cells via Wnt/β-Catenin pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(3):2169-2177.
[26] LO WW, WUNDER JS, DICKSON BC, et al. Involvement and targeted intervention of dysregulated Hedgehog signaling in osteosarcoma. Cancer. 2014;120(4):537-547.
[27] 迟博婧,刘光源,邢磊,等. Hedgehog 信号通路调控骨形成及BMSCs成骨分化的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(12):1545-1550.
[28] 吴修团,李文良,谢柳蓉,等. Hedgehog 信号通路调节成骨细胞 RANKL表达的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(8):1294-1300.
[29] 梁学振,杨曦,李嘉程,等.补肾活血胶囊介导Hedgehog信号通路调控大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨成脂分化 [J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(7):1020-1026.
[30] 邓洋洋,刘明欣,孙鑫,等.Hedgehog信号通路与“肾虚血瘀”骨代谢失常的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(8):1112-1116.
[31] MA X, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Jolkinolide B inhibits RANKL induced osteoclastogenesis by suppressing the activation NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;445(2):282-288.
[32] 李永志,董博,欧国峰,等.骨复生对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠骨组织中OPG及RANK表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2018,26(11):1-6.
[33] 宋红梅,魏迎辰,吴斌,等.温阳补肾方对兔激素性股骨头坏死组织RANKL/RANK/OPG通路的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(1):302-305.
[34] SONG HM, WEI YC, LI N, et al. Effects of Wenyangbushen formula on the expression of VEGF, OPG, RANK and RANKL in rabbits with steroid-induced femoral head avascular necrosis. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(6):8155-8161.
[35] JIANG Y, ZHANG Y, CHEN W, et al. Achyranthes bidentata extract exerts osteoprotective effects on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats by regulating RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling. J Transl Med. 2014;12:334.
[36] KAR S, SAMII A, BERTALANFFY H. PTEN/PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling and the cross talk to KRIT1, CCM2, and PDCD10 proteins in cerebral cavernous malformations. Neurosurg Rev. 2015;38(2):229-236;discussion 236-237.
[37] CAO F, QIN KR, KANG K, et al. Ginkgo biloba L. extract prevents steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head by rescuing apoptosis and dysfunction in vascular endothelial cells via the PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;296:115476.
[38] LV W, YU M, YANG Q, et al. Total flavonoids of Rhizoma drynariae ameliorate steroid‑induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(5):345.
[39] XUE XH, FENG ZH, LI ZX, et al. Salidroside inhibits steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(3):3751-3757.
[40] YANG Q, YIN W, CHEN Y, et al. Betaine alleviates alcohol-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head via mTOR signaling pathway regulation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;120:109486.
[41] 朱道宇,杨前昊,高悠水,等.TLR4通路与激素性股骨头坏死关系的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2019,8(1):75-79.
[42] LI H, SUN B. Toll-like receptor 4 in atherosclerosis. J Cell Mol Med. 2007;11(1):88-95.
[43] 田雷,周东生,孙水,等.Toll样受体4信号通路过度激活在大鼠激素性股骨头坏死中的作用[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2014,35(5):622-629.
[44] TIAN L, WEN Q, DANG X, et al. Immune response associated with Toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway leads to steroid-induced femoral head osteonecrosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15;15:18.
[45] PEI J, FAN L, NAN K, et al. Excessive Activation of TLR4/NF-κB Interactively Suppresses the Canonical Wnt/β-catenin Pathway and Induces SANFH in SD Rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11928.
[46] 刘金富,曾平,农焦,等.通络生骨胶囊对激素性股骨头坏死模型大鼠Toll样受体4信号通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(26):4150-4155.
[47] RIDDELL JR, MAIER P, SASS SN, et al. Peroxiredoxin 1 stimulates endothelial cell expression of VEGF via TLR4 dependent activation of HIF-1α. PLoS One. 2012;7(11): e50394.
[48] 王楠锴,刘浩,张天久,等.转化生长因子β信号通路相关因子在幼兔激素性股骨头坏死模型中的表达及意义[J].中华实用儿科临床杂志,2021,36(23):1811-1814.
[49] QIAN C, ZHU C, YU W, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 promotes osteogenesis of bone marrow stromal cells in type 2 diabetic rats via the Wnt signaling pathway. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016;80:143-153.
[50] YANG Y, NIAN H, TANG X, et al. Effects of the combined Herba Epimedii and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi on bone turnover and TGF-β1/Smads pathway in GIOP rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017;201:91-99.
[51] CHEN WH, KONG XY, WAN R, et al. Effects of huogu I formula (I) on correlated factors of bone regeneration in chickens with steroid-induced necrosis of femoral head. Chin J Integr Med. 2012;18(5):378-384.
[52] YU GY, ZHENG GZ, CHANG B, et al. Naringin Stimulates Osteogenic Differentiation of Rat Bone Marrow Stromal Cells via Activation of the Notch Signaling Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:7130653.
[53] HUANG D, LI Z, CHEN B, et al. Naringin protects against steroid‑induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head through upregulation of PPARγ and activation of the Notch signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2):3328-3335.
[54] 刘禄林,黄为民,刘午阳.富血小板血浆治疗早期股骨头缺血性坏死的研究进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报,2022,42(4):399-403,410.
[55] HAN J, GAO F, LI Y, et al. The Use of Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Treatment of Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: A Systematic Review. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:2642439.
[56] EVERTS P, ONISHI K, JAYARAM P, et al. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7794.
[57] 吴晓斌,刘朝阳.股骨头坏死手术治疗及其自体PRP在保髋手术中的应用进展[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2017,9(3):186-191.
[58] 张波,韦冰丹,甘坤宁,等.富血小板血浆联合骨髓间充质干细胞对兔股骨头坏死BMP-2/Smads通路的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016,22(2):131-134,227.
[59] YOKOTA K, ISHIDA O, SUNAGAWA T, et al. Platelet-rich plasma accelerated surgical angio-genesis in vascular-implanted necrotic bone: an experimental study in rabbits. Acta Orthop. 2008;79(1):106-110.
[60] TONG S, YIN J, LIU J. Platelet-rich plasma has beneficial effects in mice with osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(2):1781-1788.
[61] WU PI, DIAZ R, BORG-STEIN J. Platelet-Rich Plasma. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2016;27(4):825-853.
[62] LIU HY, WU AT, TSAI CY, et al. The balance between adipogenesis and osteogenesis in bone regeneration by platelet-rich plasma for age-related osteoporosis. Biomaterials. 2011;3(28):6773-6780.
[63] ZHANG XL, SHI KQ, JIA PT, et al. Effects of platelet-rich plasma on angiogenesis and osteogenesis-associated factors in rabbits with avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(7):2143-2152.
[64] XU H, LI S, FANG L, et al. Platelet- rich plasma promotes bone formation, restrains adipogenesis and accelerates vascularization to relieve steroids-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Platelets (Edinburgh). 2021;32(7):950-959.
[65] YAMAGUCHI R, KAMIYA N, ADAPALA NS, et al. HIF-1-Dependent IL-6 Activation in Articular Chondrocytes Initiating Synovitis in Femoral Head Ischemic J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2016;98(13):1122-1131.
[66] ADAPALA NS, YAMAGUCHI R, PHIPPS M, et al. Necrotic Bone Stimulates Proinflammatory Responses in Macrophages through the Activation of Toll-Like Receptor 4. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(11):2987-2999.
[67] 沈烈军,李展振.股骨头坏死的减压植骨联合唑来膦酸和富血小板血浆[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2022,30(9):785-790.
[68] 洪坤豪,马振尉,刘军,等.基于数据挖掘的股骨头坏死用药规律研究 [J].世界中西医结合杂志,2015,10(8):1042-1044.
[69] XIA Q, MA Z, MEI X, et al. Assay for the developmental toxicity of safflower(Carthamus tinctorius L.) to zebrafish embryos/larvae. J Traditional Chin Med Sci. 2017;4(1):71-81.
[70] ZHANG LL, TIAN K, TANG ZH, et al. Phytochemistry and Pharmacology of Carthamus tinctorius L. Am J Chin Med. 2016;44(2):197-226.
[71] CUI D, ZHAO D, WANG B, et al. Safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) polysaccharide attenuates cellular apoptosis in steroid-induced avascular necrosis of femoral head by targeting caspase-3-dependent signaling pathway. Biol Macromol. 2018;116:106-112.
[72] CUI D, ZHAO D, HUANG S. Beneficial contribution of a safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) polysaccharide on steroid-induced avascular necrosis of the femoral head in rats. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;123:581-586.
[73] CUI D, ZHAO D, HUANG S. Structural characterization of a safflower polysaccharide and its promotion effect on steroid-induced osteonecrosis in vivo. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;233:115856.
[74] 徐辉辉,李索咪,范梦强,等.富血小板血浆联合桃红四物汤对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头组织VEGF、CD31、ALP、β-catenin蛋白表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2020,35(3):1501-1504.
[75] SUN Z, SU W, WANG L, et al. Clinical Effect of Bushen Huoxue Method Combined with Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis and Its Effect on IL-1, IL-6, VEGF, and PGE-2. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:9491439. |