中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (2): 200-207.doi: 10.12307/2023.830
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
复方生脉成骨胶囊修复激素性股骨头坏死的作用机制
林天烨1,2,吴智明3,张文胜1,2,何晓铭1,2,何敏聪1,2,张庆文1,2,何 伟1,2,魏秋实1,2,李子祺1,2
- 1广东省中医骨伤研究院,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第三附属医院,广东省广州市 510405;3广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510080
Mechanism of compound Shengmai Chenggu capsule in the repair of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head
Lin Tianye1, 2, Wu Zhiming3, Zhang Wensheng1, 2, He Xiaoming1, 2, He Mincong1, 2, Zhang Qingwen1, 2, He Wei1, 2, Wei Qiushi1, 2, Li Ziqi1, 2
- 1Guangdong Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Bone Trauma, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2The Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3The First Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
激素性股骨头坏死:是指长期大剂量应用糖皮质激素,总剂量过大或短期过大剂量使用肾上腺皮质类固醇激素,引起的股骨头坏死。是一项发病机制复杂、治疗困难、致残率高的疑难疾病,严重危及患者的生活和工作。核心岩藻糖基化:是一种通过岩藻糖基转移酶8催化岩藻糖基化的反应,核心岩藻糖基化修饰能够调控包括间充质干细胞在内的多种细胞的增殖、迁移与分化功能。
背景:复方生脉成骨胶囊治疗早期激素性股骨头坏死的疗效佳,但具体治疗机制尚不完全明确。
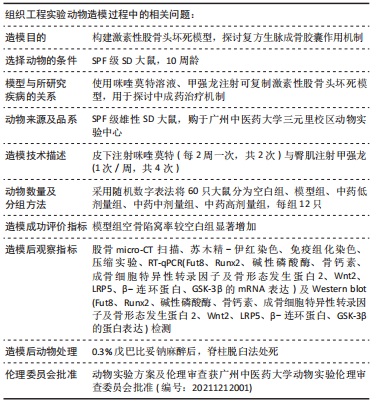
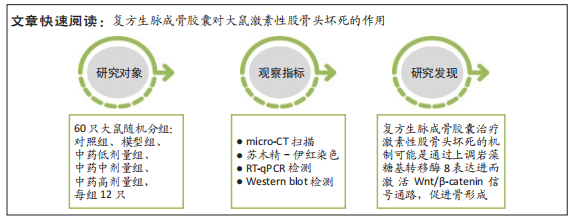
目的:观察复方生脉成骨胶囊干预对激素性股骨头坏死大鼠骨组织中岩藻糖基转移酶8、成骨基因及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路蛋白表达的影响。方法:取60只雄性SD大鼠,采用随机数字表法分为空白组、模型组、中药低剂量组、中药中剂量组及中药高剂量组,每组12只。模型组和中药低、中、高剂量组通过皮下注射咪喹莫特(每2周一次,共2次)与臀肌注射甲强龙(1次/周,共4次)的方法建立激素性股骨头坏死模型,末次造模给药后第2天,中药低、中、高剂量组分别灌胃给予1.89,3.78,7.56 g/(kg·d)的复方生脉成骨胶囊溶液,模型组灌胃给予等量生理盐水,连续给药8周。给药结束后,分别进行股骨头micro-CT扫描、组织学染色、压缩实验、RT-qPCR及Western blot检测。
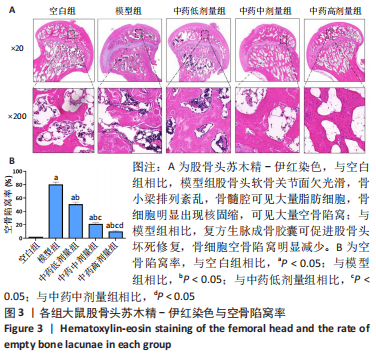
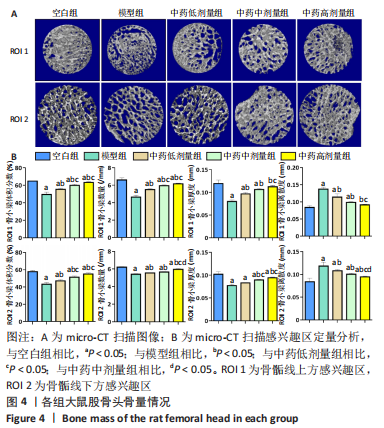
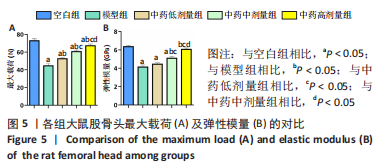
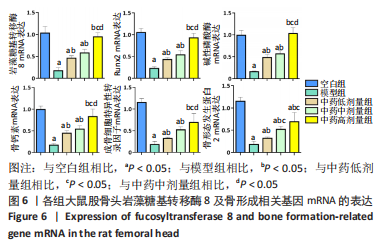
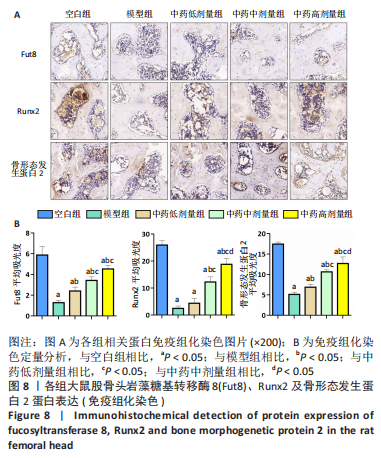
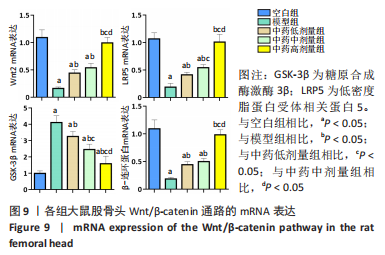
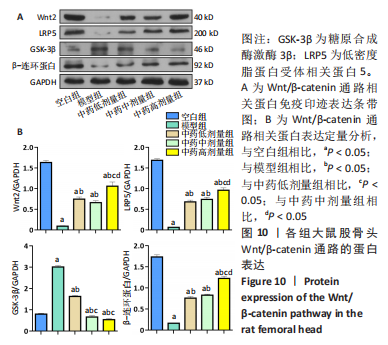
结果与结论:①micro-CT扫描显示,与空白组比较,模型组大鼠骨小梁体积分数、骨小梁数量及骨小梁厚度减少(P < 0.05),骨小梁离散度增加(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,中药低、中、高剂量组骨小梁体积分数、骨小梁数量及骨小梁厚度增加(P < 0.05),骨小梁离散度减少(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。②苏木精-伊红染色显示,与模型组比较,中药低、中、高剂量组空骨陷窝率减少(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性;免疫组化染色显示,与空白组比较,模型组岩藻糖基转移酶8、Runx2、骨形态发生蛋白2的蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,中药低、中、高剂量组岩藻糖基转移酶8、Runx2、骨形态发生蛋白2的蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。③压缩实验显示,与模型组相比,中药低、中、高剂量组股骨头最大载荷及弹性模量升高(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性;④RT-qPCR及Western blot检测显示,与空白组相比,模型组岩藻糖基转移酶8、Runx2、碱性磷酸酶、骨钙素、成骨细胞特异性转录因子及骨形态发生蛋白2的mRNA与蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与模型组相比,中药低、中、高剂量组上述指标的mRNA与蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。与空白组比较,模型组Wnt2、低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5及β-连环蛋白的mRNA与蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),糖原合成酶激酶3β的mRNA与蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,中药低、中、高剂量组Wnt2、低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5及β-连环蛋白的mRNA与蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),糖原合成酶激酶3β的mRNA与蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05),且呈剂量依赖性。⑤结果表明,复方生脉成骨胶囊治疗激素性股骨头坏死的机制可能是通过上调岩藻糖基转移酶8表达来激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进骨形成。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0286-5425(林天烨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: