中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (25): 3971-3976.doi: 10.12307/2023.416
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
丝素胶原蛋白复合支架联合富血小板血浆修复皮肤损伤
刘继超,赵金龙,于 洋
- 西安交通大学医学院附属三二〇一医院,陕西省汉中市 723000
Silk fibroin collagen composite scaffold combined with platelet-rich plasma for repairing skin injury
Liu Jichao, Zhao Jinlong, Yu Yang
- The 3201 Hospital Affiliated to Xi’an Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Hanzhong 723000, Shaanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
富血小板血浆:是自体全血经过2次离心后获得的富含生长因子的浓缩血小板的血浆,其所含血小板浓度为全血的4倍以上,并且含有多种组织修复需要的生长因子,可促进组织再生与创面愈合。胶原:是动物细胞外基质中最重要的纤维蛋白,是一种适合细胞生长、黏附与分化的天然基质,其是机体皮肤创面愈合的基础,为促进创面愈合的关键因素。
背景:胶原与丝素蛋白复合构建的组织工程支架,在皮肤、神经、血管、骨、软骨等组织工程领域应用广泛。富血小板血浆是血液经过2 次离心获得的血小板浓缩物,含有多种组织修复需要的生长因子,可促进组织再生与创面愈合。
目的:观察丝素胶原蛋白支架复合富血小板血浆在皮肤创面愈合中的作用。
方法:分别制备丝素胶原蛋白支架、SD大鼠富血小板血浆。取8周龄SD大鼠48只,每只背部制作2个直径2 cm的全层皮肤缺损创面,分4组处理:空白组缺损处注射生理盐水,单纯支架组缺损处植入丝素胶原蛋白复合支架,富血小板血浆组创缘注射同种异体富血小板血浆,联合组缺损处植入丝素胶原蛋白复合支架+创缘注射同种异体富血小板血浆,每组12只。造模后检测创面愈合率、创面炎症因子水平、创面组织学观察及相关蛋白表达。
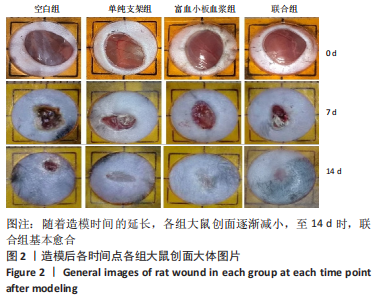
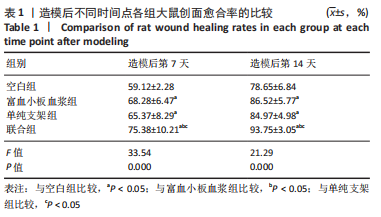
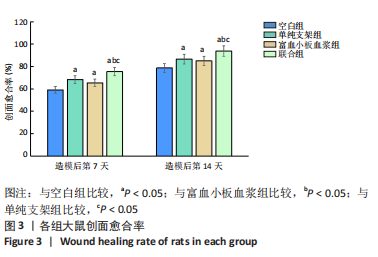
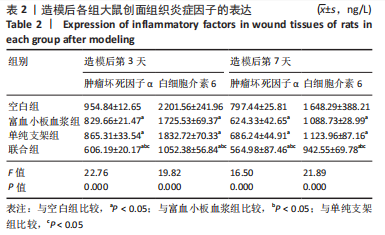
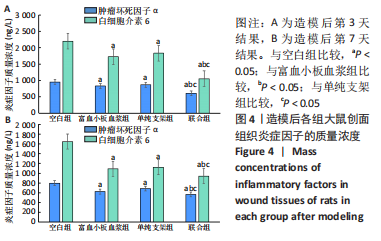
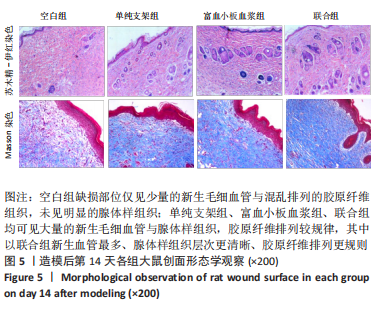
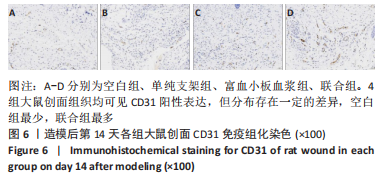
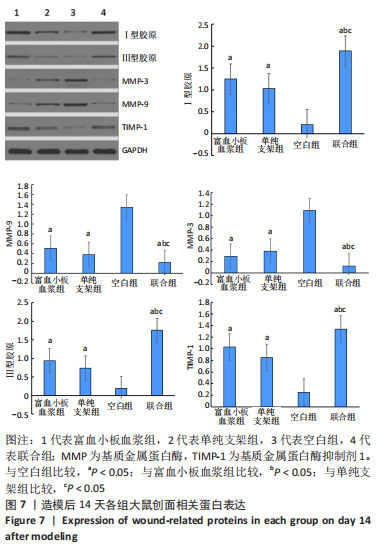
结果与结论:①联合组造模后第7,14天的创面愈合率大于空白组、单纯支架组、富血小板血浆组(P < 0.05)。②联合组造模后第7,14天的肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6水平均低于空白组、单纯支架组、富血小板血浆组(P < 0.05)。③造模后第14天的苏木精-伊红及Masson染色显示,空白组缺损处仅见少量的新生毛细血管与混乱排列的胶原纤维组织;其他3组可见大量的新生毛细血管与腺体样组织,胶原纤维排列较规律,其中以联合组新生血管最多、腺体样组织层次更清晰、胶原纤维排列更规则。免疫组化染色显示,空白组、单纯支架组、富血小板血浆组CD31+细胞密度少于联合组(P < 0.05)。④Western blot检测显示,相较于空白组、单纯支架组、富血小板血浆组,联合组创面Ⅰ型胶原、Ⅲ型胶原、基质金属蛋白酶抑制剂1的蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05),基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05)。⑤结果表明,丝素胶原蛋白支架复合富血小板血浆可通过抑制炎症反应、增加微血管密度、调节细胞外基质的代谢平衡来促进皮肤创面愈合。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2921-6046(刘继超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: