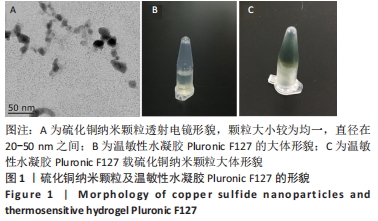
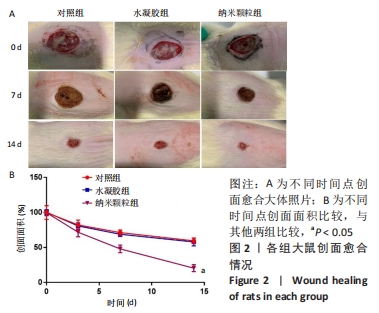
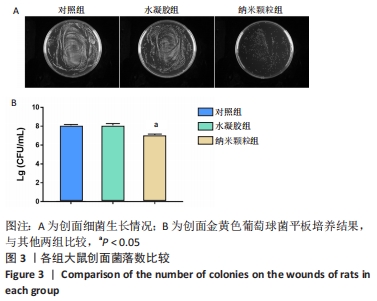
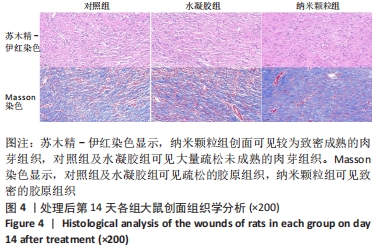
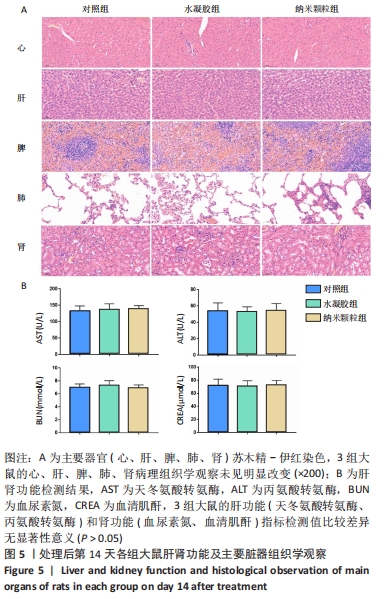
[1] 卢毅飞,邓君,王竞,等.乳酸乳球菌温敏水凝胶对糖尿病小鼠全层皮肤缺损创面愈合的影响及其机制[J].中华烧伤杂志,2020, 36(12):1117-1129.
[2] WILKINS RG, UNVERDORBEN M. Wound cleaning and wound healing: a concise review. Adv Skin Wound Care. 2013;26(4):160-163.
[3] KLEIN DG, FRITSCH DE, AMIN SG. Wound infection following trauma and burn injuries. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am. Critical care nursing clinics of North America. 1995;7(4):627-642.
[4] 刘方,单争明,汤雨蕾,等.臭氧缓释水凝胶止血及促伤口愈合作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(22):3445-3449.
[5] BAI Q, HAN K, DONG K, et al. Potential Applications of Nanomaterials and Technology for Diabetic Wound Healing. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020; 15:9717-9743.
[6] HUANG J, ZHOU J, ZHUANG J, et al. Strong Near-Infrared Absorbing and Biocompatible CuS Nanoparticles for Rapid and Efficient Photothermal Ablation of Gram-Positive and -Negative Bacteria. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(42):36606-36614.
[7] LIANG Y, ZHANG J, QUAN H, et al. Antibacterial Effect of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles on Infected Wound Healing. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021; 22(9):894-902.
[8] DUNG TH, HUONG LT, YOO H. Morphological Feature of Pluronic F127 and Its Application in Burn Treatment. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2018;18(2):829-832.
[9] YANG K, ZHU L, NIE L, et al. Visualization of protease activity in vivo using an activatable photo-acoustic imaging probe based on CuS nanoparticles. Theranostics. 2014;4(2):134-141.
[10] ZAREI F, SOLEIMANINEJAD M. Role of growth factors and biomaterials in wound healing. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup1):906-911.
[11] LINDLEY LE, STOJADINOVIC O, PASTAR I, et al. Biology and Biomarkers for Wound Healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2016;138(3 Suppl):18s-28s.
[12] VEITH AP, HENDERSON K, SPENCER A, et al. Therapeutic strategies for enhancing angiogenesis in wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019; 146:97-125.
[13] WILKINSON HN, HARDMAN MJ. Wound healing: cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes. Open Biol. 2020;10(9):200223.
[14] CALDWELL MD. Bacteria and Antibiotics in Wound Healing. Surg Clin North Am. 2020;100(4):757-776.
[15] ZHAO H, HUANG J, LI Y, et al. ROS-scavenging hydrogel to promote healing of bacteria infected diabetic wounds. Biomaterials. 2020;258: 120286.
[16] JIN P, WANG L, SHA R, et al. A blood circulation-prolonging peptide anchored biomimetic phage-platelet hybrid nanoparticle system for prolonged blood circulation and optimized anti-bacterial performance. Theranostics. 2021;11(5):2278-2296.
[17] BAND VI, HUFNAGEL DA, JAGGAVARAPU S, et al. Antibiotic combinations that exploit heteroresistance to multiple drugs effectively control infection. Nat Microbiol. 2019;4:1627-1635.
[18] MALASALA S, AHMAD MN, AKUNURI R, et al. Synthesis and evaluation of new quinazoline-benzimidazole hybrids as potent anti-microbial agents against multidrug resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Med Chem. 2021;212:112996.
[19] AHMED KBA, SUBRAMANIYAN SB, BANU SF, et al. Jacalin-copper sulfide nanoparticles complex enhance the antibacterial activity against drug resistant bacteria via cell surface glycan recognition. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2018;163:209-217.
[20] KONG Y, HOU Z, ZHOU L, et al. Injectable Self-Healing Hydrogels Containing CuS Nanoparticles with Abilities of Hemostasis, Antibacterial activity, and Promoting Wound Healing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021; 7(1):335-349.
[21] LAN QH, DU CC, YU RJ, et al. Disulfiram-loaded copper sulfide nanoparticles for potential anti-glioma therapy. Int J Pharm. 2021;607: 120978.
[22] LIU Y, JI M, WANG P. Recent Advances in Small Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles for Molecular Imaging and Tumor Therapy. Mol Pharm. 2019;16(8):3322-3332.
[23] SHARMA V, JEEVANANDAM P. Synthesis of Copper Sulfide Nanoparticles by Thermal Decomposition Approach and Morphology Dependent Peroxidase-Like Activity. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020;20(5):2763-2780.
[24] JIANG T, GUO H, XIA YN, et al. Hepatotoxicity of copper sulfide nanoparticles towards hepatocyte spheroids using a novel multi-concave agarose chip method. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2021;16(17): 1487-1504.
[25] ZAMORA-PEREZ P, PELAZ B, TSOUTSI D, et al. Hyperspectral-enhanced dark field analysis of individual and collective photo-responsive gold-copper sulfide nanoparticles. Nanoscale. 2021;13(31):13256-13272.
[26] YANG J, CHEN Z, PAN D, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:5911-5926.
|