线粒体可以适应机体代谢变化需求,通过线粒体生成和融合的过程形成新的线粒体并修复亚健康状态的线粒体。新形成的和修复后的线粒体与邻近的细胞器相连,以增加其ATP合成、代谢产物共享和Ca2+处理的能力[17]。相反,当线粒体过多或功能失调时,会发生分裂和自噬过程,以重建细胞内的代谢稳态并维持线粒体健康[18]。这些变化过程均处于流动状态,这取决于机体的代谢需求,以促进形成最佳的线粒体库。当细胞受到不良刺激时,如运动或衰老,线粒体调节中的这种平衡可以转向合成和融合的增加,或分裂和自噬的增加。
3.1 运动对骨骼肌线粒体动力学影响 剧烈的运动将极大改变骨骼肌的能量需求,对线粒体融合、分裂有很大影响。线粒体融合和分裂是调节线粒体形态的关键事件,需要平衡以支持正常线粒体功能[19]。线粒体融合的经典机制是通过线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1的活性实现的,这3种蛋白分别促进相邻的外膜和内膜融合,从而建立一个扩展的细胞器网络[20]。相反,线粒体分裂是由DRP1、FIS1和线粒体裂变因子共同作用完成的,其作用最终导致细胞器片段从网络中收缩和分裂,以便进行适当的清除[21-22]。
在哺乳动物细胞中,线粒体的融合是由2种属于动力相关的大型GTPases家族的有丝分裂蛋白调控的,线粒体融合蛋白1和线粒体融合蛋白2位于线粒体外膜,视神经萎缩蛋白1位于线粒体内膜。线粒体融合蛋白1和线粒体融合蛋白2表现出高度的同源性和相似的结构组织。然而,遗传和生化研究认为这2种有丝分裂蛋白具有不同的功能,线粒体融合蛋白1与视神经萎缩蛋白1是融合反应的核心成分,而线粒体融合蛋白2在融合中的确切作用仍不是很清楚。但它已被证明参与线粒体的相关反应以及线粒体与其他细胞器的反应,认为其具有调节能量生成、线粒体内质网偶联和自噬等生理功能[23-25]。研究表明,细胞内线粒体融合蛋白1或线粒体融合蛋白2的下调或缺失会导致线粒体碎裂成颗粒状,显著降低耗氧量和ATP生成,同时两者都失去融合功能;而融合受阻可能导致线粒体变小、线粒体DNA缺失或线粒体DNA突变[26],使线粒体功能受到严重损害。
视神经萎缩蛋白1在线粒体膜融合中的作用在线粒体动力学早期就已确立,其作用被认为是线粒体外膜与线粒体内膜融合的协调作用[27]。视神经萎缩蛋白1的缺失将会削弱线粒体融合能力,甚至导致线粒体的断裂[19],而视神经萎缩蛋白1过表达会诱导线粒体增长[28]。正常状态下,线粒体处于丝状或管状,即融合状态,但在高强度运动的刺激下将会导致线粒体出现碎片化,线粒体融合与分裂动态平衡出现紊乱,导致线粒体功能障碍。
线粒体分裂是一个多步骤的过程。FIS1和DRP1是哺乳动物线粒体分裂机制的核心组成部分,FIS1位于整个外膜表面并募集DRP1以刺穿裂变点,其中GTPase DRP1在其中起着至关重要的作用[29-30]。DRP1可以动态地作用于线粒体和过氧化物酶体膜,在那里它以GTP依赖性方式寡聚化并驱动膜收缩[28]。它从细胞质转位到线粒体,结合到它的线粒体外膜受体,结合之后,DRP1寡聚并驱动分裂[19]。线粒体分裂是骨骼肌线粒体维持和质量所必需的,过度分裂将产生促凋亡信号,导致线粒体从网络中分离并降低ATP生成效率,这通常被认为是线粒体功能障碍的标志。因此,平衡线粒体融合和分裂对于维持线粒体动力学和功能至关重要。
当疲劳发生后大鼠线粒体融合被抑制,线粒体功能受到损害,对骨骼肌产生不利影响。CHEN等[31]曾研究表明,敲除小鼠线粒体融合蛋白1和线粒体融合蛋白2的基因后导致肌肉出现萎缩和线粒体DNA减少现象;此外,VARANITA等[32]证明视神经萎缩蛋白1基因过表达可以消除由去神经引起的线粒体功能障碍。
在此次研究中,疲劳大鼠骨骼肌中线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1基因表达显著降低,FIS1和DRP1基因水平显著升高,提示疲劳后大鼠线粒体融合被抑制,线粒体过度分裂,线粒体功能受损。HUANG等[4]在研究中发现过度运动使小鼠线粒体融合相关基因线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1表达降低,分裂相关基因DRP1表达增加,FIS1基因表达没有显著变化,表明过度运动会导致线粒体融合受到抑制,分裂受到刺激。BENARD等[33]曾在研究中发现DRP1的RNAi诱导了线粒体网络组织的改变,增殖速度减慢,DRP1缺失的细胞中线粒体能量的产生受到影响。于滢[34]在一次大负荷运动后24 h发现,大鼠线粒体融合蛋白2蛋白表达显著降低。DING等[26]在研究中发现长时间的剧烈运动抑制了融合蛋白线粒体融合蛋白1/2的基因表达,同时增加了裂变蛋白FIS1的表达,改变了ATP合酶活性,并且这些改变的幅度取决于运动持续时间。这些发现表明,线粒体融合、分裂相关因子的表达可以迅速改变以响应骨骼肌中不断变化的能量需求,这与此次研究结果一致。
3.2 补充白藜芦醇对骨骼肌线粒体动力学影响 白藜芦醇作为一种天然存在的植物多酚抗氧化剂,可以在70多种植物及其产品中找到。白藜芦醇是植物为对抗微生物而产生的,这种特殊的化合物对线粒体的功能有一定的影响[7-8]。
此次研究中,证明了补充白藜芦醇可以促进线粒体融合,抑制线粒体的过度分裂,改善线粒体动力学状态。张琦[35]在研究中发现,补充白藜芦醇可改善镉暴露导致的鸡肾脏线粒体融合相关因子线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2、视神经萎缩蛋白1转录水平降低和线粒体分裂相关因子FIS1、线粒体裂变因子转录水平升高的状态,抑制过度的线粒体分裂,平衡线粒体动力学,缓解镉暴露导致的鸡肾脏线粒体损伤。杨济宁[36]在人脐静脉内皮细胞氧化应激模型中,发现线粒体出现碎裂,且线粒体融合相关蛋白线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1表达下降,而白藜芦醇处理可减少人脐静脉内皮细胞氧化应激模型中线粒体碎片化程度,上调融合相关蛋白线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1的表达,促进线粒体融合。孙秀玉[37]发现在白藜芦醇预处理后,缺氧/复氧造成损伤的心肌细胞内线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2、视神经萎缩蛋白1的mRNA表达水平显著提高,FIS1的mRNA表达水平有所上升,过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ共激活因子1α(peroxisome proliferators-activated reptory coactivator-1α,PGC-1α)的mRNA水平也明显提高。表明白藜芦醇能够通过促进缺氧/复氧损伤后心肌细胞线粒体融合与分裂,上调线粒体生物合成,调控线粒体动态变化。
研究发现,白藜芦醇可调节沉默信息调节因子1的去乙酰酶活性导致PGC-1α的乙酰化减少,PGC-1α通过与DRP1启动子结合直接调节DRP1表达,抑制线粒体断裂并保护神经细胞[38]。CANNAVINO等[39]研究报道,骨骼肌中PGC-1α的过表达可以阻止线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1蛋白的减少。同时SORIANO等[40]在研究中发现PGC-1α对肌肉细胞中线粒体融合蛋白2 mRNA和蛋白质表达有刺激作用,并且PGC-1α还刺激了线粒体融合蛋白2启动子的活性。作者所在课题组在前期研究中也发现补充白藜芦醇可促进PGC-1α过表达,这与以上研究结果呈一致现象。
上官若男[41]在研究中表明,一次大强度运动后线粒体形态片段化,线粒体融合蛋白1和视神经萎缩蛋白1蛋白减少,通过针刺治疗可上调线粒体融合蛋白1、线粒体融合蛋白2和视神经萎缩蛋白1表达,增强线粒体融合能力。白胜超等[42]在对大鼠进行一次离心运动后发现,运动组大鼠DRP1蛋白升高,而离心运动后进行针刺干预后发现DRP1蛋白降低,同时透射电镜结果显示离心运动后进行针刺干预能够降低线粒体的分裂程度,有利于线粒体的功能恢复。在此次研究中发现补充白藜芦醇与传统疗法针刺在改善线粒体动力学方面出现相同的趋势。因此,白藜芦醇可作为一种营养补充剂用于改善线粒体动力学、促进线粒体功能障碍恢复。
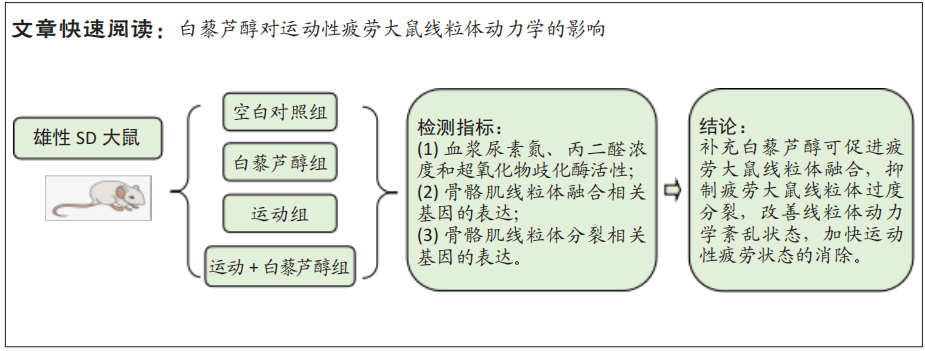
结论:补充白藜芦醇可改变疲劳大鼠线粒体动力学的相关基因,提示补充白藜芦醇可能促进疲劳大鼠线粒体融合,抑制线粒体过度分裂,改善线粒体动力学紊乱状态,加快运动性疲劳状态的消除。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程