中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (5): 720-725.doi: 10.12307/2023.060
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
结扎不同部位输精管大鼠睾丸的生理功能
杨 恒1,2,郑丽英2,刘志立1,王勤章2,郝志强1,2,王敬珅1,2,汪 渊1,2,李永乐1,2,谭明辉1,2,邹晓峰2,张国玺2,黄若辉2,江 波2,钱 彪1,2
- 1石河子大学医学院第一附属医院泌尿外科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008;2赣南医学院第一附属医院泌尿外科,江西省赣州市 341000
Physiological function of the testis in rats undergoing different parts of vasectomy
Yang Heng1, 2, Zheng Liying2, Liu Zhili1, Wang Qinzhang2, Hao Zhiqiang1, 2, Wang Jingshen1, 2, Wang Yuan1, 2, Li Yongle1, 2, Tan Minghui1, 2, Zou Xiaofeng2, Zhang Guoxi2, Huang Ruohui2, Jiang Bo2, Qian Biao1, 2
- 1Department of Urology Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Medical College in Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Urology Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
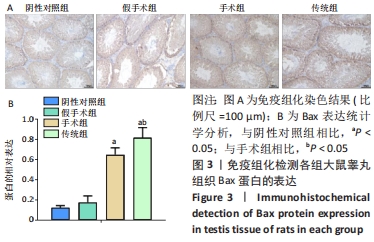
凋亡蛋白Bax:Bax蛋白于1993年被发现,它分布于细胞的膜结构上。目前认为,Bax的生理功能与Bcl-2相反,即促进细胞凋亡发生;Bax可通过增强线粒体膜通透性,改变跨膜电位,从而促使线粒体内细胞色素 C 释放到细胞质中引起半胱氨酸天冬氨酸酶的级联反应,最终导致 caspase-3 被激活,引发细胞的凋亡。
人附睾蛋白4(human epididymis protein 4,HE4):是一种糖蛋白,最初于人附睾上皮远端细胞中被发现,可表达于生殖系统如附睾、曲细精管、输精管上皮、前列腺及呼吸系统等多种正常组织的上皮细胞内,其在附睾中高度表达,它的表达量与精子密度、 精子总数、精子活力、前向运动精子数成负相关。
背景:输精管结扎是目前有效的男性节育方法,而人们主要关注的是输精管结扎后的临床并发症。
目的:研究不同手术方式的输精管结扎对大鼠睾丸生理功能的影响。
方法:12只雄性SD大鼠适应性喂养1周后随机分为4组,每组3只,分别为阴性对照组、假手术组、手术组和传统组。手术组大鼠行双侧输精管斜行切断,近端结扎,远端旷置;传统组行双侧输精管斜行切断,两端均结扎;假手术组游离双侧输精管,不结扎;阴性对照组不做特殊处理。术后3个月注射美蓝观察造模情况。收集睾丸行苏木精-伊红染色常规病理检测;免疫组化检测睾丸组织Bax、Bcl-2、3βHSD和附睾蛋白4的表达;TUNEL法检测睾丸组织细胞凋亡情况;ELISA/生化检测血清白细胞介素1、睾酮水平。
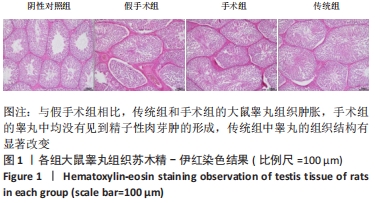
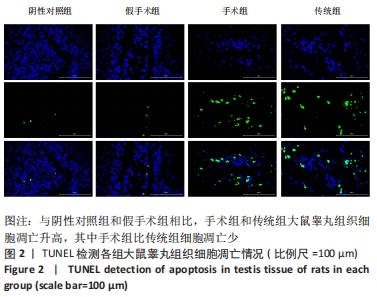
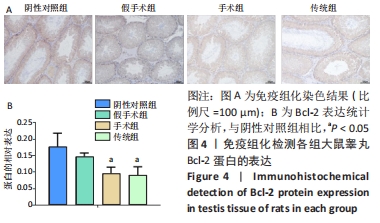
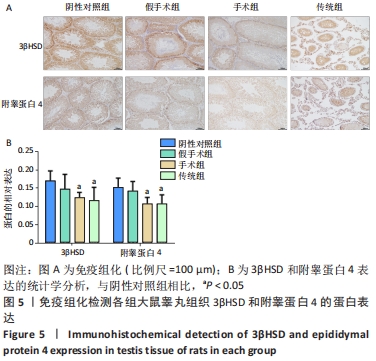
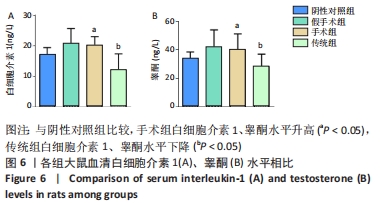
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色结果:与假手术组相比,传统组和手术组大鼠睾丸肿胀,质地较硬,传统组睾丸无菌性炎症的发生率高于阴性对照组,手术组的睾丸均未见到精子性肉芽肿的形成,传统组中的睾丸的组织结构则有显著改变;②TUNEL检测结果:与阴性对照组和假手术相比,手术组和传统组大鼠的细胞凋亡升高,其中手术组比传统组细胞凋亡更少;③免疫组化检测结果:与阴性对照组相比,假手术组Bax表达差异无显著性意义,手术组和传统组Bax表达升高,其中传统组更高;手术组和传统组的Bcl-2表达下降,其中传统组更低;与阴性对照组和假手术组相比,手术组和传统组大鼠睾丸组织3βHSD和附睾蛋白4蛋白的表达更低,其中手术组和传统组比较差异无显著性意义;④ELISA/生化检测结果:与阴性对照组相比,手术组大鼠血清白细胞介素1、睾酮水平升高(P < 0.05),传统组白细胞介素1、睾酮水平下降(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,盆部输精管结扎对大鼠睾丸生理功能影响较小。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8919-5905(杨恒)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: