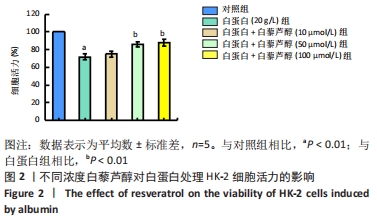
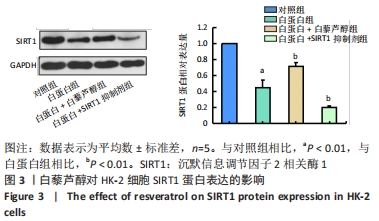
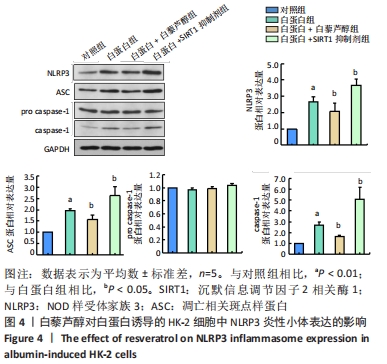
[1] XIONG W, MENG XF, ZHANG C. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Metabolic-Associated Kidney Diseases: An Update. Front Immunol. 2021;12:714340.
[2] LIU P, ZHANG Z, LI Y. Relevance of the Pyroptosis-Related Inflammasome Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12:603416.
[3] LU F, LAN Z, XIN Z, et al. Emerging insights into molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis and functions of inflammasomes in diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3207-3221.
[4] DING B, MA G, WANG Z, et al. Mechanisms of Kidney Cell Pyroptosis in Chronic Kidney Disease and the Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:1173324.
[5] PAIK S, KIM JK, SILWAL P, et al. An update on the regulatory mechanisms of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18(5):1141-1160.
[6] KIM YG, KIM SM, KIM KP, et al. The Role of Inflammasome-Dependent and Inflammasome-Independent NLRP3 in the Kidney. Cells. 2019; 8(11):1389.
[7] HOU Y, WANG Q, HAN B, et al. CD36 promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation via the mtROS pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells of diabetic kidneys. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(6):523.
[8] SONG SJ, KIM SM, LEE SH, et al. Rhabdomyolysis-Induced AKI Was Ameliorated in NLRP3 KO Mice via Alleviation of Mitochondrial Lipid Peroxidation in Renal Tubular Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(22):8564.
[9] SU Y, WANG Y, LIU M, et al. Hydrogen sulfide attenuates renal I/R‑induced activation of the inflammatory response and apoptosis via regulating Nrf2‑mediated NLRP3 signaling pathway inhibition. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(1):518.
[10] ZHENG T, TAN Y, QIU J, et al. Alternative polyadenylation trans-factor FIP1 exacerbates UUO/IRI-induced kidney injury and contributes to AKI-CKD transition via ROS-NLRP3 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(6):512.
[11] HOWITZ KT, BITTERMAN KJ, COHEN HY, et al. Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 2003; 425(6954):191-196.
[12] ZHUANG Y, HU C, DING G, et al. Albumin impairs renal tubular tight junctions via targeting the NLRP3 inflammasome. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2015;308(9):F1012-1019.
[13] 韩文超. EPA对白蛋白诱导肾小管上皮细胞损伤的保护作用的机制研究[D].济南:山东大学,2014.
[14] 丁丽红.蛋白尿引起肾小管间质损伤新机制[D].南京:东南大学, 2015.
[15] WANG Y, LI Y, XU Y. Pyroptosis in kidney disease. J Mol Biol. 2022;434(4): 167290.
[16] ZHANG Z, SHAO X, JIANG N, et al. Caspase-11-mediated tubular epithelial pyroptosis underlies contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(10):983.
[17] HAN Y, XU X, TANG C, et al. Reactive oxygen species promote tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy: The role of the mitochondrial ros-txnip-nlrp3 biological axis. Redox Biol. 2018;16:32-46.
[18] FAUSTINO VD, ARIAS SCA, FERREIRA ÁVILA V, et al. Simultaneous activation of innate and adaptive immunity participates in the development of renal injury in a model of heavy proteinuria. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20180762.
[19] HE WT, WAN H, HU L, et al. Gasdermin D is an executor of pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1β secretion. Cell Res. 2015;25(12):1285-1298.
[20] AACHOUI Y, SAGULENKO V, MIAO EA, et al. Inflammasome-mediated pyroptotic and apoptotic cell death, and defense against infection. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2013;16(3):319-326.
[21] GAO Q, ZHU H. The overexpression of sirtuin1 (SIRT1) alleviated lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute kidney injury (AKI) via inhibiting the activation of nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLR) family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:2718-2726.
[22] LAMKANFI M, DIXIT VM. Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell. 2014;157(5):1013-1022.
[23] SHEN J, WANG L, JIANG N, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome mediates contrast media-induced acute kidney injury by regulating cell apoptosis. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34682.
[24] DAS B, SARKAR C, RAWAT VS, et al. Promise of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibitors in In Vivo Disease Models. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):4996.
[25] KIM DH, JUNG YJ, LEE JE, et al. SIRT1 activation by resveratrol ameliorates cisplatin-induced renal injury through deacetylation of p53. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;301(2):F427-435.
[26] XIAO Z, CHEN C, MENG T, et al. Resveratrol attenuates renal injury and fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-β pathway on matrix metalloproteinase 7. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2016;241(2):140-146.
[27] 李方,曹建民,王传军,等.白藜芦醇通过调节SIRT1/NF-κB通路减轻力竭训练致大鼠肾的炎症反应[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2019,35(7):773-779.
[28] LI Y, WANG P, YANG X, et al. SIRT1 inhibits inflammatory response partly through regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome in vascular endothelial cells. Mol Immunol. 2016;77:148-156.
[29] ZHANG S, JIANG L, CHE F, et al. Arctigenin attenuates ischemic stroke via SIRT1-dependent inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;493(1):821-826.
[30] TUFEKCI KU, ELTUTAN BI, ISCI KB, et al. Resveratrol Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome-Induced Pyroptosis and miR-155 Expression in Microglia Through Sirt1/AMPK Pathway. Neurotox Res. 2021;39(6):1812-1829.
|