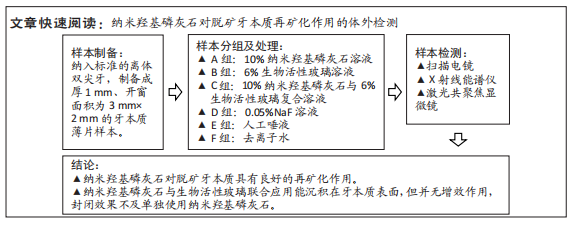
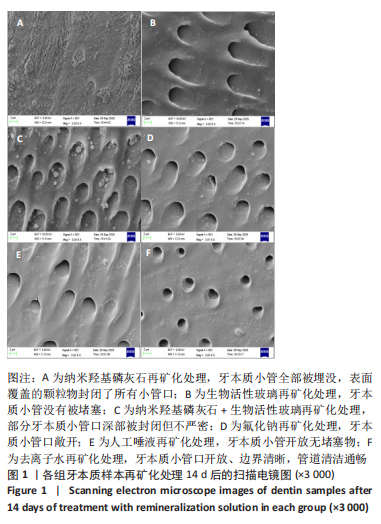
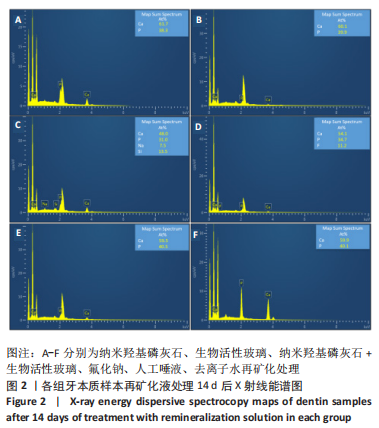
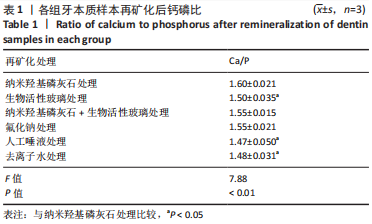
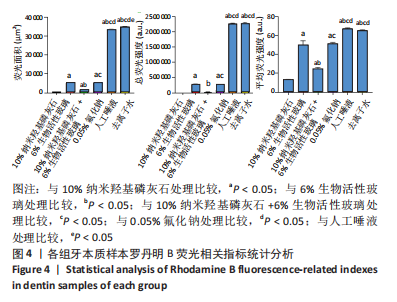
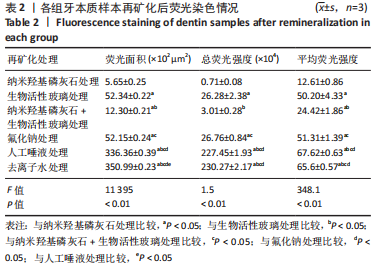
[1] 沈烨青, 朱亚琴. Nd:YAG 激光治疗牙本质敏感的研究进展[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2020,29(2):43-46.
[2] LIU XX, TENENBAUM HC, WILDER RS, et al. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of dentin hypersensitivity: an evidence-based overview for dental practitioners. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20(1):220-230.
[3] TRIEU A, MOHAMED A, LYNCH E. Silver diamine fluoride versus sodium fluoride for arresting dentine caries in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):2115-2124.
[4] POLLICK H. The Role of Fluoride in the Prevention of Tooth Decay. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2018;65(5):923-940.
[5] 殷凌云,于鸿滨,杨向红,等.两种参数设置的激光联合氟化物治疗牙本质敏感症的临床评价[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2022,3(11):34-39.
[6] TANWAR YS, FERREIRA N. The role of bioactive glass in the management of chronic osteomyelitis: a systematic review of literature and current evidence. Infect Dis (Lond). 2020;52(4):219-226.
[7] 孟宪敏,张志华,宫琳,等.牙本质敏感症患者患病状况与行为的相关性分析[J].山西医科大学学报,2014,45(8):722-725.
[8] 王薇,窦丽鑫,王宏远.生物活性玻璃骨修复支架材料的研究进展[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2018,19(6):362-366.
[9] FREITAS SAA, OLIVEIRA NMA, DE GEUS JL, et al. Bioactive toothpastes in dentin hypersensitivity treatment: A systematic review. Saudi Dent J. 2021;33(7):395-403.
[10] 岳阳丽,马贵霞,刘翠丽,等.生物活性玻璃促进牙本质再矿化的时间相关性体外研究[J].口腔医学研究,2020,36(12):1137-1141.
[11] GALLOB J, LING MR, AMINI P, et al. Efficacy of a dissolvable strip with calcium sodium phosphosilicate (NovaMin®) in providing rapid dentine hypersensitivity relief. J Dent. 2019;91:100003-100009.
[12] YU J, YANG H, LI K, et al. A novel application of nanohydroxyapatite/mesoporous silica biocomposite on treating dentin hypersensitivity: An in vitro study. J Dent. 2016;50:21-29.
[13] HIGUCHI J, FORTUNATO G, WOZNIAK B, et al. Polymer Membranes Sonocoated and Electrosprayed with Nano-Hydroxyapatite for Periodontal Tissues Regeneration. Nanomaterials. 2019;9(11):1625-1649.
[14] JEONG WJ. A Study on the Deposition of Hydroxyapatite Nano Thin Films Fabricated by Radio-Frequency Magnetron Sputtering for Biomedical Applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2020;20(7):4114-4119.
[15] ZIA I, MIRZA S, JOLLY R, et al. Trigonella foenum graecum seed polysaccharide coupled nano hydroxyapatite-chitosan: A ternary nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019; 124:88-101.
[16] SHUAI C, XU Y, FENG P, et al. Co-enhance bioactive of polymer scaffold with mesoporous silica and nano-hydroxyapatite. J Biomater Sci. 2019; 30(12):1097-1113.
[17] Hu ML, Zheng G, Lin H, et al. Network meta-analysis on the effect of desensitizing toothpastes on dentine hypersensitivity. J Dent. 2019; 88:103170-103181.
[18] WEST NX, ADDY M, JACKSON RJ, et al. Dentine hypersensitivity and the placebo response. A comparison of the effect of strontium acetate, potassium nitrate and fluoride toothpastes. J Clin Periodontol. 1997;24(4):209-215.
[19] PASHLEY DH. How can sensitive dentine become hypersensitive and can it be reversed. J Dent. 2013;41(Suppl 4):S49-S55.
[20] FAVARO ZEOLA L, SOARES PV, CUNHA-CRUZ J. Prevalence of dentin hypersensitivity: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2019; 81:1-6.
[21] 马贵霞.生物活性玻璃促进牙本质再矿化的时间相关性体外研究[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020.
[22] NIU LN, JEE SE, JIAO K, et al. Collagen intrafibrillar mineralization as a result of the balance between osmotic equilibrium and electroneutrality. Nat Mater. 2017;16(3):370-378.
[23] 吴媛媛,潘海华,唐睿康.胶原矿化与仿生修复[J].化学进展,2018, 30(10):1503-1510.
[24] BERTASSONI LE, HABELITZ S, KINNEY JH, et al. Biomechanical perspective on the remineralization of dentin. Caries Res. 2009;43(1): 70-77.
[25] GANDOLFI MG, TADDEI P, SIBONI F, et al. Biomimetic remineralization of human dentin using promising innovative calcium-silicate hybrid “smart” materials. Dent Mater. 2011;27(11):1055-1069.
[26] 周学东,梁景平.龋病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011:113-120.
[27] 田子璐,朱松.诱导牙本质再矿化以堵塞牙本质小管的研究进展[J].口腔医学研究,2021,37(1):11-14.
[28] YUAN PY, LIU SY, LV Y, et al. Effect of a dentifrice containing different particle sizes of hydroxyapatite on dentin tubule occlusion and aqueous Cr (VI) sorption. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:5243-5256.
[29] 毕良佳,李虹,刘来发,等.羟磷灰石同质间吸附效果及对牙本质小管封闭效果的研究[J].口腔医学研究,2006,22(5):501-503.
[30] DAAS I, BADR S, OSMAN E. Comparison between Fluoride and Nano-hydroxyapatite in Remineralizing Initial Enamel Lesion: An in vitro Study. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(3):306-312.
[31] BAGLAR S, ERDEM U, DOGAN M, et al. Dentinal tubule occluding capability of nano-hydroxyapatite; The in-vitro evaluation Microsc Res Tech. 2018;81(8):843-854.
[32] MEDVECKY L, STULAJTEROVA R, GIRETOVA M, et al. Effect of tetracalcium phosphate/monetite toothpaste on dentin remineralization and tubule occlusion in vitro. Dent Mater. 2018;34(3): 442-451.
[33] FIUME E, BARBERI J, VERNÉ E, et al. Bioactive Glasses: From Parent 45S5 Composition to Scaffold-Assisted Tissue-Healing Therapies. J Funct Biomater. 2018;9(1):1-33.
[34] 朱庆霞,徐琼琼,罗民华.碳酸羟基磷灰石的生物矿化研究[J].陶瓷学报,2010,31(2):234-239.
[35] 吴民行,谢玉芬,翟智皓,等.生物活性玻璃的制备与应用研究进展[J].人工晶体学报,2019,48(1):137-143,148.
[36] 张峻峰,蒋明慧,张顺锋,等.多孔羟基磷灰石生物陶瓷的制备及研究进展[J].中国陶瓷,2017,53(3):6-12.
[37] OSORIO R, TOLEDANO-OSORIO M, OSORIO E, et al. Zinc and silica are active components to efficiently treat in vitro simulated eroded dentin. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22(8):2859-2870.
[38] 申思敏,陈新梅,王盼盼,等.六氟硅酸铵溶液封闭牙本质小管的扫描电镜观察[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013;23(7):424-427.
[39] 万方.HAP/SiO2复合材料的制备与性能研究[D].郑州:郑州大学, 2011. |