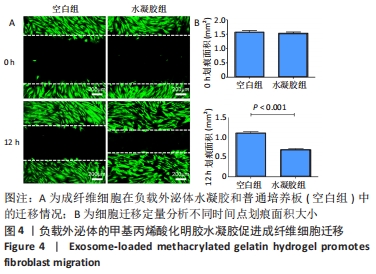
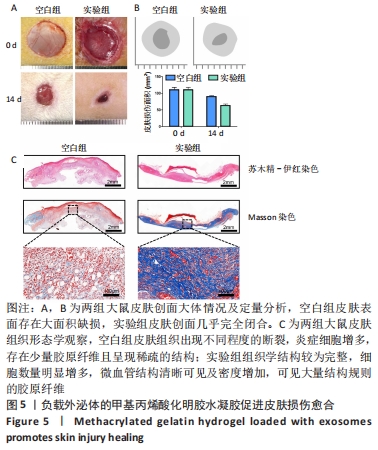
[1] 陶苏皖,朱链,许娜.水凝胶负载干细胞来源的外泌体用于皮肤伤口修复[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2021,37(8):1024-1031.
[2] 廖文强,詹剑华,罗锦花,等.慢性创面临床防治的现状与思考[J].实用临床医学,2021,22(2):83-89.
[3] 唐乾利,唐强,龚元勋.慢性难愈合创面的基础研究及临床应用进展[J].右江医学,2020,48(11):801-806.
[4] SHEN YF, HUANG JH, WANG KY, et al. PTH Derivative promotes wound healing via synergistic multicellular stimulating and exosomal activities. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):40.
[5] ZHAO R, JIN X, LI A, et al. Precise Diabetic Wound Therapy: PLS Nanospheres Eliminate Senescent Cells via DPP4 Targeting and PARP1 Activation. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(1):e2104128.
[6] LI M, HOU Q, ZHONG L, et al. Macrophage Related Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Wounds. Front Immunol. 2021;12(2):131-156.
[7] 蔡伟杰,韩培.水凝胶敷料治疗慢性创面研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2020,41(4):195-198.
[8] 刘瑞雪,周腾,樊晓敏,等.明胶基复合水凝胶研究进展[J].轻工学报,2018,33(6):42-54.
[9] 罗雅馨,毕浩然,陈晓旭,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体与再生医学:无细胞疗法临床应用的未来[J].中国组织工程研究,2020, 24(19):3055-3062.
[10] 孙璇,毛念渝,刘明珠,等.间充质干细胞来源外泌体在皮肤损伤修复中的研究进展[J].系统医学,2019,4(16):196-198.
[11] FAN L, XIAO C, GUAN P, et al. Extracellular Matrix-Based Conductive Interpenetrating Network Hydrogels with Enhanced Neurovascular Regeneration Properties for Diabetic Wounds Repair. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(1):e2101556.
[12] SHEN Y, XU G, HUANG H, et al. Sequential Release of Small Extracellular Vesicles from Bilayered Thiolated Alginate/Polyethylene Glycol Diacrylate Hydrogels for Scarless Wound Healing. Acs Nano. 2021;15(4): 6352-6368.
[13] ALVEN S, PETER S, MBESE Z, et al. Polymer-Based Wound Dressing Materials Loaded with Bioactive Agents: Potential Materials for the Treatment of Diabetic Wounds. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(4):724.
[14] 吴兴,刘肇兴,林欢欢,等.甲基丙烯酸酐明胶材料学特性及在皮肤组织工程应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(2):323-328.
[15] GUAN P, LIU C, XIE D, et al. Exosome-loaded extracellular matrix-mimic hydrogel with anti-inflammatory property Facilitates/promotes growth plate injury repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;22(7):600-610.
[16] ZHU D, LI Z, HUANG K, et al. Minimally invasive delivery of therapeutic agents by hydrogel injection into the pericardial cavity for cardiac repair. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1412.
[17] BRENNAN MÁ, LAYROLLE P, MOONEY DJ. Biomaterials Functionalized with MSC Secreted Extracellular Vesicles and Soluble Factors for Tissue Regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(37):1909125.
[18] FAN L, LIU C, CHEN X, et al. Directing Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Neural Stem Cell Fate with a Three-Dimensional Biomimetic Hydrogel for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2018; 10(21):17742-17755.
[19] OUYANG X, HAN X, CHEN Z, et al. MSC-derived exosomes ameliorate erectile dysfunction by alleviation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle apoptosis in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):246.
[20] 边晓玮,张翠萍,李炳旻,等.胎盘间充质干细胞外泌体对高糖培养的成纤维细胞衰老的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(12): 1163-1173.
[21] 田新立,江波,颜洪.脂肪间充质干细胞来源外泌体对角质形成细胞增殖和迁移的影响与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(1):68-73.
[22] 李超然,黄桂林,王帅.间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进损伤组织修复与再生的应用与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):133-139.
[23] 林宇建,韩兵,麦钰仪,等.深度创伤后瘢痕发生发展机制及干细胞来源的外泌体治疗研究进展[J].广东药科大学学报,2021,37(1): 142-147.
[24] WANG G, XIE L, LI B, et al. A nanounit strategy reverses immune suppression of exosomal PD-L1 and is associated with enhanced ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):5733.
[25] 陶苏皖,朱链,许娜.水凝胶负载干细胞来源的外泌体用于皮肤伤口修复[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2021,37(8):1024-1031.
[26] 程远航,陈津,吴卫真.间充质干细胞及其外泌体修复电离辐射损伤的研究进展[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志(电子版),2020,10(5): 310-313.
[27] ZHANG C, ZHU Z, GAO J, et al. Plasma exosomal miR-375-3p regulates mitochondria-dependent keratinocyte apoptosis by targeting XIAP in severe drug-induced skin reactions. Sci Transl Med. 2020;12(574): eaaw6142.
[28] WANG X, JIAO Y, PAN Y, et al. Fetal Dermal Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Accelerate Cutaneous Wound Healing by Activating Notch Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1-11.
[29] WANG T, JIAN Z, BASKYS A, et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials. 2020;257:120264.
[30] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cell Transl Med. 2016;5(10): 1425-1439.
[31] 唐建宏,张霓霓,黄桂林,等.间充质干细胞源性外泌体在组织纤维化修复中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25):4022-4027.
[32] ZHANG K, ZHAO X, CHEN X, et al. Enhanced Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes with an Injectable Hydrogel for Hindlimb Ischemia Treatment. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2018;10(36): 30081-30091.
[33] WATERS R, ALAM P, PACELLI S, et al. Stem cell-inspired secretome-rich injectable hydrogel to repair injured cardiac tissue. Acta Biomater. 2018;69: 95-106.
[34] SUN G, LI G, LI D, et al. hucMSC derived exosomes promote functional recovery in spinal cord injury mice via attenuating inflammation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:194-204.
[35] ROMANELLI P, BIELER L, SCHARLER C, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Can Deliver Anti-inflammatory and Anti-scarring Activities of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells After Spinal Cord Injury. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1225.
[36] 姜文彬,陈雳风,孙家明.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体在皮肤创面修复中的作用机制[J].组织工程与重建外科,2021,17(4):352-357.
[37] LI W, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Tissue-Engineered Bone Immobilized with Human Adipose Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Promotes Bone Regeneration. Acs Appl Mater Inter. 2018;10(6):5240-5254.
[38] 崔国宁,刘喜平,虎峻瑞,等.干细胞来源外泌体的生物学特性研究进展[J].今日药学,2020,30(2):106-109.
[39] CHEN P, ZHENG L, WANG Y, et al. Desktop-stereolithography 3D printing of a radially oriented extracellular matrix/mesenchymal stem cell exosome bioink for osteochondral defect regeneration. Theranostics. 2019;9(9):2439-2459.
[40] ZHU Y, LIU H, QIN S, et al. Antibacterial Sericin Cryogels Promote Hemostasis by Facilitating the Activation of Coagulation Pathway and Platelets. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022:e2102717.
[41] TSARYK R, GLORIA A, RUSSO T, et al. Collagen-low molecular weight hyaluronic acid semi-interpenetrating network loaded with gelatin microspheres for cell and growth factor delivery for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2015;20:10-21.
[42] CASADO-DÍAZ A, QUESADA-GÓMEZ JM, DORADO G. Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC) in Regenerative Medicine: Applications in Skin Wound Healing. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology. 2020;8:146.
[43] 周欣,王颖,张馨欣.间充质干细胞外泌体-温敏水凝胶的制备及其在表皮创伤修复中的应用[J].中国医药工业杂志,2021,52(9): 1199-1207.
|