中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 505-509.doi: 10.12307/2023.989
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
关节腔注射医用臭氧对早期颞下颌骨关节炎模型大鼠髁突组织学的影响
买斯吐热木·黑力力1,2,张婉霞1,2,尼加提·努尔穆罕默德1,2,买买提吐逊·吐尔地1,2
- 1新疆医科大学第一附属医院(附属口腔医院)口腔颌面创伤正颌外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054;2新疆维吾尔自治区口腔医学研究所,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Effect of intraarticular injection of different concentrations of ozone on condylar histology of rats with early temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis
Maisituremu·Heilili1, 2, Zhang Wanxia1, 2, Nijiati·Nuermuhanmode1, 2, Maimaitituxun·Tuerdi1, 2
- 1Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Trauma and Orthognathic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital (Affiliated Stomatological Hospital) of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Institute of Stomatology, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
医用臭氧:臭氧是一种由3个氧原子组成的强氧化剂,它具有刺激氧化酶过度表达、中和炎症反应中产生的过量反应性氧化物、抑制炎症反应时细胞因子释放及通过改变关节腔内环境促进关节软骨修复和再生的作用,临床上一般采用关节腔内注射医用臭氧的方法以减缓骨关节炎症状和改善关节功能。碘乙酸钠:是目前动物实验中骨关节炎建模时最常用来注射的化合物,是甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶活性的抑制剂,可诱导软骨细胞凋亡,引起软骨基质改变、软骨降解丢失、滑膜炎症等病理改变。
背景:在临床以及动物实验中均已证实关节腔内注射医用臭氧可有效改善颞下颌关节炎的症状,减缓疾病的发展,但注射医用臭氧的最理想浓度及其范围仍有争议。
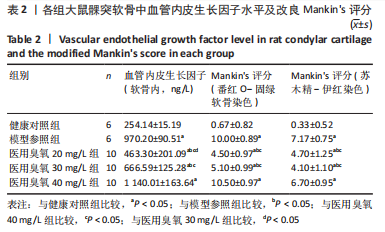
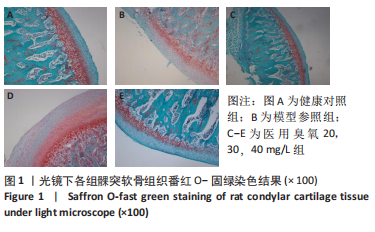
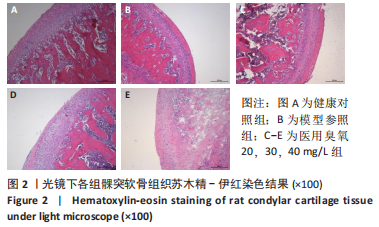
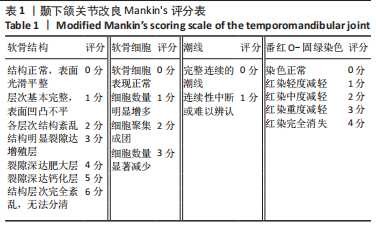
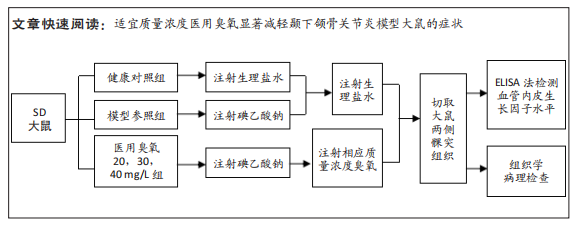
目的:观察颞下颌关节腔内注射不同质量浓度医用臭氧对颞下颌骨关节炎大鼠髁突软骨的影响。方法:从42只SD大鼠中随机抽取6只作为健康对照组,剩余大鼠采用关节腔内一次性注射碘乙酸钠法建立颞下颌骨关节炎模型,在建模成功的36只大鼠中选择6只作为模型参照组,其余的30只为20,30,40 mg/L医用臭氧组,每组10只。建模成功后医用臭氧组大鼠关节腔内分别注射质量浓度为20,30,40 mg/L医用臭氧,每周1次,连续注射3周,模型参照组和健康对照组分别注射等体积生理盐水,末次注射后1周,取单侧颞下颌关节组织,ELISA法检测髁突软骨中血管内皮生长因子水平,并取另一侧颞下颌关节组织进行苏木精-伊红染色和番红O-固绿染色,应用改良Mankin’s评分法评价颞下颌关节组织病理变化程度。
结果与结论:①与健康对照组相比,模型参照组、医用臭氧20,30,40 mg/L组大鼠髁突软骨中血管内皮生长因水平显著升高(P < 0.05);与模型参照组、医用臭氧40 mg/L组相比,医用臭氧20,30 mg/L组髁突软骨中血管内皮生长因子水平明显下降(P < 0.05);与医用臭氧30 mg/L组相比,医用臭氧20 mg/L组髁突软骨中血管内皮生长因子水平较低(P < 0.05);②组织学观察结果显示医用臭氧20,30,40 mg/L组及模型参照组改良Mankin’s评分均高于健康对照组(P < 0.05),医用臭氧20,30 mg/L组改良Mankin’s评分低于模型参照组、医用臭氧40 mg/L组(P < 0.05);③结果表明,关节腔内注射质量浓度分别为20,30 mg/L医用臭氧时,能明显缓解大鼠颞下颌骨关节炎的进展,尤其是注射20 mg/L医用臭氧时效果更佳,但是当臭氧质量浓度上升到40 mg/L时,反而会加重大鼠颞下颌骨关节炎的病变程度。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0505-0993(买买提吐逊·吐尔地)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: