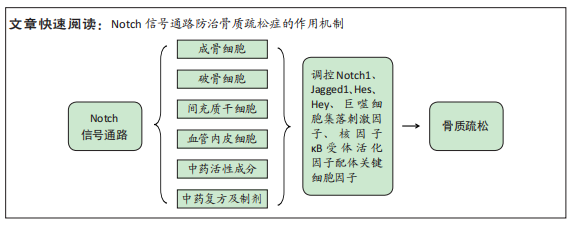
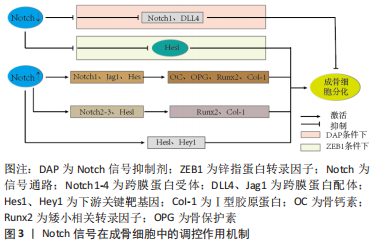
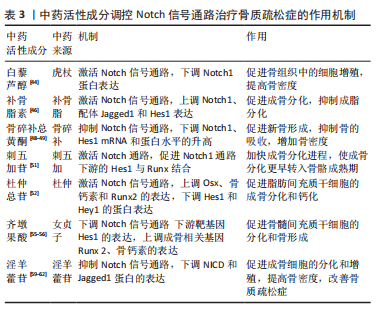
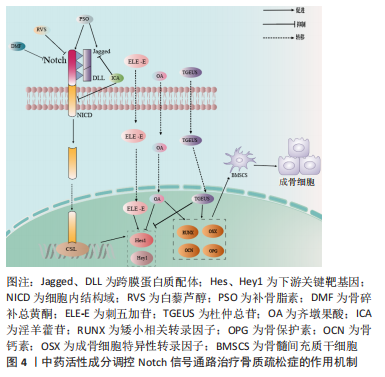
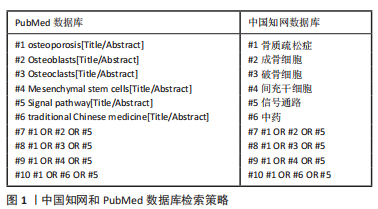
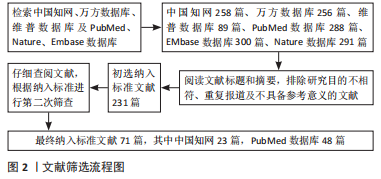
[1] LI H, XIAO Z, QUARLES LD, et al. Osteoporosis: Mechanism, Molecular Target and Current Status on Drug Development. Curr Med Chem. 2021; 28(8):1489-1507.
[2] ROSEN CJ. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis//FEINGOLD KR, ANAWALT B, BOYCE A, et al. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc., 2020.
[3] NOH JY, YANG Y, JUNG H. Molecular Mechanisms and Emerging Therapeutics for Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7623.
[4] SALARI N, DARVISHI N, BARTINA Y, et al. Global prevalence of osteoporosis among the world older adults: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):669.
[5] LEBOFF MS, GREENSPAN SL, INSOGNA KL, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10): 2049-2102.
[6] LU J, HU D, MA C, et al. Advances in Our Understanding of the Mechanism of Action of Drugs (including Traditional Chinese Medicines) for the Intervention and Treatment of Osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:938447.
[7] AIBAR-ALMAZÁN A, VOLTES-MARTÍNEZ A, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Current Status of the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9465.
[8] JOHNSTON CB, DAGAR M. Osteoporosis in Older Adults. Med Clin North Am. 2020;104(5):873-884.
[9] MCINTYRE B, ASAHARA T, ALEV C. Overview of Basic Mechanisms of Notch Signaling in Development and Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1227:9-27.
[10] MATSUNO K. Notch signaling. Dev Growth Differ. 2020;62(1):3.
[11] REICHRATH J, REICHRATH S. A Snapshot of the Molecular Biology of Notch Signaling: Challenges and Promises. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1227:1-7.
[12] ZHOU B, LIN W, LONG Y, et al. Notch signaling pathway: architecture, disease, and therapeutics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):95.
[13] SPRINZAK D, BLACKLOW SC. Biophysics of Notch Signaling. Annu Rev Biophys. 2021;50:157-189.
[14] YU J, CANALIS E. Notch and the regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function. Bone. 2020;138:115474.
[15] SONG S, GUO Y, YANG Y, et al. Advances in pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies for osteoporosis. Pharmacol Ther. 2022;237:108168.
[16] CANALIS E, ZANOTTI S, SCHILLING L, et al. Activation of Notch3 in osteoblasts/osteocytes causes compartment-specific changes in bone remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2021;296:100583.
[17] WATSON EC, ADAMS RH. Biology of Bone: The Vasculature of the Skeletal System. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(7):a031559.
[18] HOU X, TIAN F. STAT3-mediated osteogenesis and osteoclastogenesis in osteoporosis. Cell Commun Signal. 2022;20(1):112.
[19] LIAO J, HUANG Y, WANG Q, et al. Gene regulatory network from cranial neural crest cells to osteoblast differentiation and calvarial bone development. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79(3):1-15.
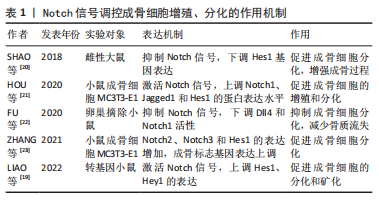
[20] SHAO J, ZHOU Y, LIN J, et al. Notch expressed by osteocytes plays a critical role in mineralisation. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018;96(3-4):333-347.
[21] HOU HW, XUE P, WANG Y, et al. Liraglutide regulates proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of preosteoblasts through a signaling network of Notch/Wnt/Hedgehog signaling pathways. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(23):12408-12422.
[22] FU R, LV WC, XU Y, et al. Endothelial ZEB1 promotes angiogenesis-dependent bone formation and reverses osteoporosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):460.
[23] ZHANG Z, QI H, XIA H, et al. Preosteoblast-enriched lnc-Evf2 facilitates osteogenic differentiation by targeting Notch. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2021;53(2):179-188.
[24] GAO J, WU P, CHI Y, et al. LY450139 Inhibited Ti-Particle-Induced Bone Dissolution via Suppressing Notch and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022;111(2):211-223.
[25] Ashley JW, Ahn J, Hankenson KD. Notch signaling promotes osteoclast maturation and resorptive activity. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(11):2598-2609.
[26] HUANG T, ZHAO C, ZHAO Y, et al. RO4929097 regulates RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and LPS-mediated bone resorption. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(9): 12526-12536.
[27] YU J, SCHILLING L, ELLER T, et al. Hairy and enhancer of split 1 is a primary effector of NOTCH2 signaling and induces osteoclast differentiation and function. J Biol Chem. 2021;297(6):101376.
[28] YANG B, FU C, WU Y, et al. γ-Secretase inhibitors suppress IL-20-mediated osteoclastogenesis via Notch signalling and are affected by Notch2 in vitro. Scand J Immunol. 2022;96(2):e13169.
[29] JIANG Y, ZHANG P, ZHANG X, et al. Advances in mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for the treatment of osteoporosis. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(1): e12956.
[30] Chen T, Yang T, Zhang W, et al. The therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in treating osteoporosis. Biol Res. 2021;54(1):42.
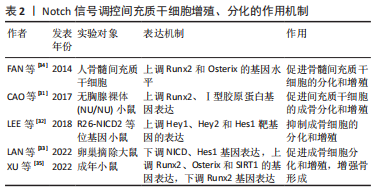
[31] CAO J, WEI Y, LIAN J, et al. Notch signaling pathway promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by enhancing BMP9/Smad signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(2):378-388.
[32] LEE SY, LONG F. Notch signaling suppresses glucose metabolism in mesenchymal progenitors to restrict osteoblast differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(12):5573-5586.
[33] LAN X, MA H, CHENG Q, et al. SIRT1/Notch1 signal axis involves in the promoting effect of Segetalin B on bone formation. Drug Dev Res. 2022; 83(8):1845-1857.
[34] FAN JZ, YANG L, MENG GL, et al. Estrogen improves the proliferation and differentiation of hBMSCs derived from postmenopausal osteoporosis through notch signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;392(1-2):85-93.
[35] XU C, DINH VV, KRUSE K, et al. Induction of osteogenesis by bone-targeted Notch activation. Elife. 2022;11:e60183.
[36] RAMASAMY SK, KUSUMBE AP, SCHILLER M, et al. Blood flow controls bone vascular function and osteogenesis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13601.
[37] LIU Y, BERENDSEN AD, JIA S, et al. Intracellular VEGF regulates the balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9): 3101-3113.
[38] CHEN W, JIN X, WANG T, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 interferes with the progression of diabetic osteoporosis by promoting type H angiogenesis modulating vasculogenic and osteogenic coupling. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13:1010937.
[39] 石敏,赵继荣,薛旭,等.从“肾”论治激素性骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(1):174-176.
[40] 赵继荣,蒋鹏,陈文,等.Nrf2/HO-1信号通路在骨质疏松症中的作用及中药干预研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(20):241-249.
[41] 胡芳科,张银光.LncRNA在骨质疏松中对破骨细胞作用的研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志,2022,42(19):4899-4903.
[42] LIN J, ZHU J, WANG Y, et al. Chinese single herbs and active ingredients for postmenopausal osteoporosis: From preclinical evidence to action mechanism. Biosci Trends. 2017;11(5):496-506.
[43] AMEEN O, YASSIEN RI, NAGUIB YM. Activation of FoxO1/SIRT1/RANKL/OPG pathway may underlie the therapeutic effects of resveratrol on aging-dependent male osteoporosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):375.
[44] 邹庆峰,李守民,舒隆钧,等.白藜芦醇对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠的促细胞增殖作用[J].实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(19):86-89.
[45] XIN Z, WU X, YU Z, et al. Mechanisms explaining the efficacy of psoralidin in cancer and osteoporosis, a review. Pharmacol Res. 2019;147:104334.
[46] 邢贞武.补骨脂素对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].中医学报,2017,32(11):2181-2184.
[47] JIN H, JIANG N, XU W, et al. Effect of flavonoids from Rhizoma Drynariae on osteoporosis rats and osteocytes. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113379.
[48] 韩亚力,罗奕,曾佳学.骨碎补总黄酮基于Notch信号通路改善骨质疏松的作用及机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2018,34(2):261-266.
[49] 黄翔宇,林立垚,郝敏,等.骨碎补总黄酮基于Notch信号通路改善骨质疏松的作用及机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(19):4361-4363.
[50] YANG X, LIU T, QI S, et al. Tea saponin additive to extract eleutheroside B and E from Eleutherococcus senticosus by ultrasonic mediation and its application in a semi-pilot scale. Ultrason Sonochem. 2022;86:106039.
[51] 黄月,颜亮,崔向荣,等.刺五加苷诱导大鼠间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2019,44(3):215-221.
[52] ZHOU YH, XIE Q. Total glycosides from Eucommia ulmoides seed promoted osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats through regulating Notch signaling pathway. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):660.
[53] 刘美红,邹峥嵘.女贞子化学成分、药理作用及药动学研究进展[J].热带亚热带植物学报,2022,30(3):446-460.
[54] Sen A. Prophylactic and therapeutic roles of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases. World J Clin Cases. 2020;8(10):1767-1792.
[55] 程韶,杨骏杰,王晶,等.齐墩果酸局部给药对去卵巢小鼠骨折愈合的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2021,27(12):1717-1725.
[56] BIAN Q, LIU SF, HUANG JH, et al. Oleanolic acid exerts an osteoprotective effect in ovariectomy-induced osteoporotic rats and stimulates the osteoblastic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Menopause. 2012;19(2): 225-233.
[57] LI LR, SETHI G, ZHANG X, et al. The neuroprotective effects of icariin on ageing, various neurological, neuropsychiatric disorders, and brain injury induced by radiation exposure. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(3):1562-1588.
[58] 李时斌,夏天,章晓云,等.淫羊藿活性单体成分调控骨质疏松症相关信号通路影响骨吸收与骨形成的稳态[J].中国组织工程研究,2022, 26(11):1772-1779.
[59] 李永贤,张顺聪,梁德,等.补肾中药通过调控Notch1蛋白的表达治疗大鼠骨质疏松性骨折的作用研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2017,23(11): 1425-1430.
[60] 孙杰,宋鑫,王健.淫羊藿提取物对骨质疏松骨折大鼠愈合过程Notch信号通路的影响[J].中国中医急症,2019,28(4):611-614.
[61] LIU H, XIONG Y, ZHU X, et al. Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(4):1360-1368.
[62] 汪小飞,李晶晶.淫羊藿总黄酮对老年骨质疏松大鼠Notch和Smads通路蛋白表达的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(2):1-5.
[63] 周灵通.固本增骨方含药血清调节Notch通路干预大鼠BMSCs成骨分化的机制研究[D].兰州:甘肃中医药大学,2018.
[64] 许日明,陈美雄,林业武,等.温肾固疏方对绝经后骨质疏松症肾阳虚型患者类固醇激素受体辅激活子3、转录元件辅激活蛋白、B细胞淋巴瘤基因-2的蛋白表达及骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J].河北中医,2019,41(10):1470-1474.
[65] 王洁芳.益骨胶囊对去卵巢大鼠骨组织Notch信号通路的影响[D].广州:暨南大学,2015.
[66] 刘蔚楠,周晓霞,朱玮,等.益肾健骨膏对去卵巢骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(6):857-862.
[67] 周强,孙鑫,邓洋洋,等.左归丸对去卵巢致绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠骨组织中Notch1、BMP9表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(7): 2782-2784.
[68] 刘家峰,舒庆,张颖.左归丸含药血清对大鼠海马神经元和胶质细胞氧糖剥夺损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2022,51(1):15-19.
[69] 麦聪英,谭峰,李星,等.左归丸对绝经后骨质疏松症合并骨关节炎模型大鼠下丘脑神经肽P物质及其受体的影响[J].中医杂志,2021,62(14): 1259-1265.
[70] 孙鑫.左、右归丸对绝经后骨质疏松症大鼠Notch信号通路调节机制的比较研究[D].沈阳:辽宁中医药大学,2015.
[71] 王军,高峰,范涛,等.骨松益骨方联合芦丁对绝经后骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞Notch信号通路的影响[J/OL].中华中医药学刊:1-8[2022-10-22] |