中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (3): 355-359.doi: 10.12307/2023.837
• 水凝胶材料Hydrogel materials • 上一篇 下一篇
透明质酸水凝胶包裹骨髓间充质干细胞改善心肌梗死大鼠的心功能(Ⅲ)
林 峰1,程 玲2,高 勇2,周建业3,商青青2,3
- 滨州医学院附属医院,1麻醉科,2疼痛科,山东省滨州市 256603;3中国医学科学院,北京协和医学院,国家心血管病中心,阜外心血管病医院,心血管疾病国家重点实验室,北京市 100037
Hyaluronic acid hydrogel-encapsulated bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote cardiac function in myocardial infarction rats (III)
Lin Feng1, Cheng Ling2, Gao Yong2, Zhou Jianye3, Shang Qingqing2, 3
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, 2Department of Pain, Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Binzhou 256603, Shandong Province, China; 3State Key Laboratory of Cardiovascular Disease, Fuwai Hospital, National Center for Cardiovascular Diseases, Peking Union Medical College and Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100037, China
摘要:
文题释义:
透明质酸:是一种线性的糖胺聚糖,在多种天然组织细胞外基质中含量丰富,参与细胞黏附、迁移、增殖及分化,在机体组织水分保持、关节润滑和损伤修复过程中发挥重要作用。透明质酸通过化学交联方法能形成具备一定特性和机械性能的水凝胶。可注射水凝胶修复梗死心肌的作用机制:①作为细胞移植的载体,通过其本身的黏滞性阻止因心脏跳动和静脉回流导致的细胞逃逸,提高移植细胞的滞留,并能为移植细胞提供合适的三维立体生长环境,防止细胞的失巢凋亡,提高细胞存活率;②作为蛋白或者生长因子的控制释放载体,防止这些生物活性分子被体内酶降解,阻止其一过性释放,延长生物活性分子在体内的作用时间,并实现局部用药;③水凝胶通过材料堆积增加梗死区室壁厚度,提供力学支撑;④性能优良的水凝胶能为内源性修复创造条件,为干细胞植入提供附着支架;⑤水凝胶降解的活性生物片段招募内源性干细胞,促进心肌再生。
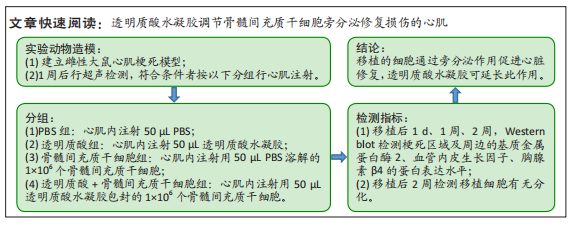
背景:作者前期的研究结果显示透明质酸水凝胶包裹骨髓间充质干细胞显著改善大鼠心肌梗死后心功能。
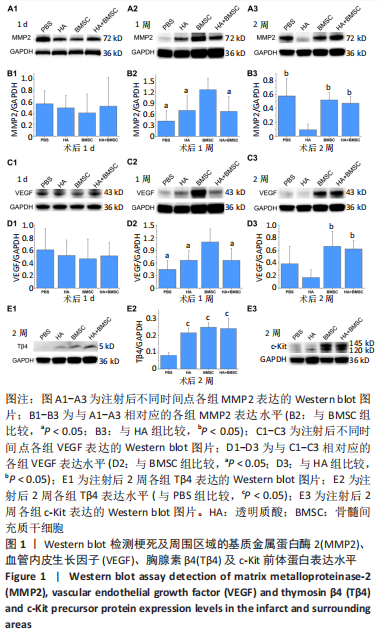
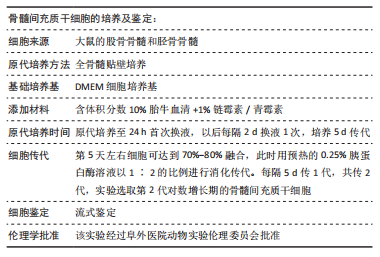
目的:探索透明质酸水凝胶及骨髓间充质干细胞促进心肌修复的分子机制。方法:分离培养雄性SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞,然后用透明质酸水凝胶包裹骨髓间充质干细胞在培养皿中进行体外三维培养。结扎雌性SD大鼠左冠状动脉前降支制作心肌梗死模型,1周后行超声检测,将符合条件的大鼠随机分为4组:①PBS组(n=12);②透明质酸组(n=12);③骨髓间充质干细胞组(n=15);④骨髓间充质干细胞+透明质酸组(n=15)。造模1周后将模型鼠行二次开胸,按照分组将PBS、透明质酸水凝胶、骨髓间充质干细胞、透明质酸水凝胶包裹骨髓间充质干细胞注射到梗死边缘区及梗死区。移植后1 d、1周、2周,Western blot检测梗死区域及周边的基质金属蛋白酶2、血管内皮生长因子、胸腺素β4以及c-Kit的蛋白表达水平,移植后2周免疫荧光检测移植细胞的分化情况。
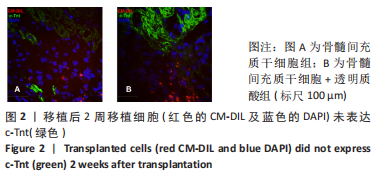
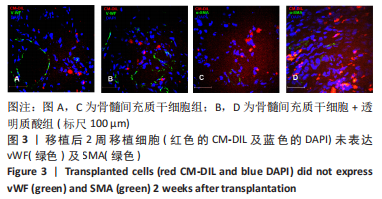
结果与结论:①在移植后1周时,骨髓间充质干细胞组的基质金属蛋白酶2及血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达水平明显高于其他3组(P < 0.05);在移植后2周时,透明质酸组的基质金属蛋白酶2及血管内皮生长因子的表达水平明显低于其他3组(P < 0.05),但骨髓间充质干细胞+透明质酸组的基质金属蛋白酶2及血管内皮生长因子表达水平与骨髓间充质干细胞组相比无差异,这可能反映了透明质酸水凝胶对骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的因子起到缓释作用以至于移植细胞的旁分泌效应得到延长,这种延长的旁分泌效应抵消了2周时透明质酸水凝胶引发的抑制效应;②与PBS组相比,透明质酸组、骨髓间充质干细胞组及骨髓间充质干细胞+透明质酸组的胸腺素β4及c-Kit表达水平明显升高(P < 0.05);③移植后2周未检测到移植细胞向心肌细胞或血管分化;④提示:移植的骨髓间充质干细胞是通过旁分泌作用促进心肌修复,透明质酸水凝胶延长了移植骨髓间充质干细胞的旁分泌作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3332-2642(商青青)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: