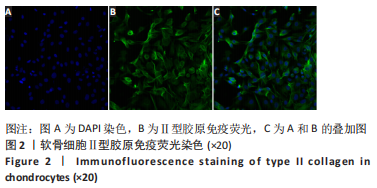
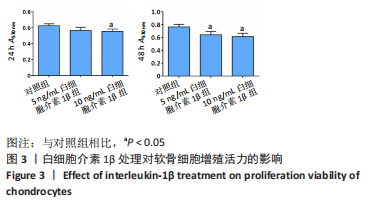
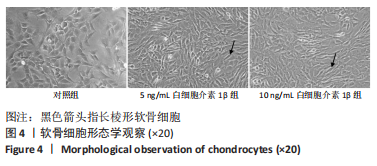
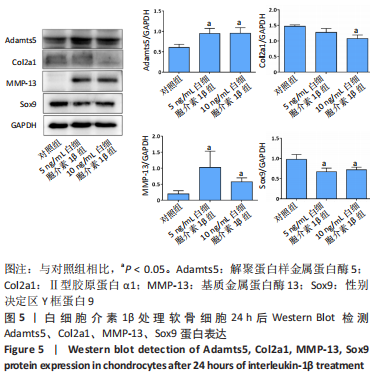
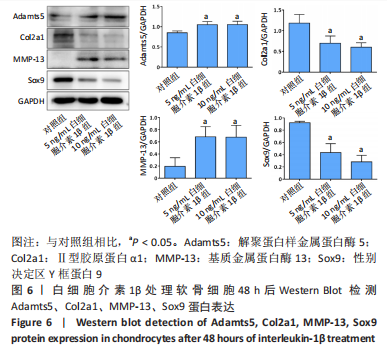
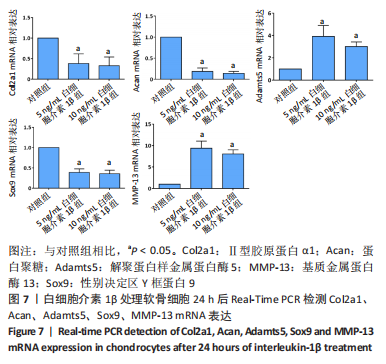
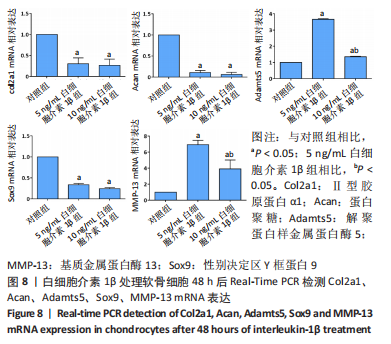
[1] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[2] ROBINSON WH, LEPUS CM, WANG Q, et al. Low-grade inflammation as a key mediator of the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016; 12(10):580-592.
[3] SHENTU CY, YAN G, XU DC, et al.Emerging pharmaceutical therapeutics and delivery technologies for osteoarthritis therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13: 1-16.
[4] ANSARI MY, AHMAD N, HAQQI TM.Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;129:1-9.
[5] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[6] WOJDASIEWICZ P, PONIATOWSKI LA, SZUKIEWICZ D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:1-19.
[7] CHEN J, GU YT, XIE JJ, et al. Gastrodin reduces IL-1beta-induced apoptosis, inflammation, and matrix catabolism in osteoarthritis chondrocytes and attenuates rat cartilage degeneration in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018; 97:642-651.
[8] SUN FF, HU PF, XIONG Y, et al. Tricetin Protects Rat Chondrocytes against IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019; 2019:1-10.
[9] GUO Z, LIN J, SUN K, et al. Deferoxamine Alleviates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting Chondrocyte Ferroptosis and Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1-15.
[10] JIANG Z, QI G, LU W, et al. Omaveloxolone inhibits IL-1beta-induced chondrocyte apoptosis through the Nrf2/ARE and NF-kappaB signalling pathways in vitro and attenuates osteoarthritis in vivo. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1-16.
[11] ZHOU Q, WANG W, WU J, et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 3 attenuates interleukin-1beta-mediated chondrocyte senescence by deacetylating forkhead box O-3 via sirtuin-3. Bioengineered. 2022;13(2):2017-2027.
[12] KONG J, WANG J, GONG X, et al. Punicalagin Inhibits Tert-Butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Apoptosis and Extracellular Matrix Degradation in Chondrocytes by Activating Autophagy and Ameliorates Murine Osteoarthritis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:5521-5533.
[13] VARELA-EIRIN M, LOUREIRO J, FONSECA E, et al. Cartilage regeneration and ageing: Targeting cellular plasticity in osteoarthritis. Ageing Res Rev. 2018; 42:56-71.
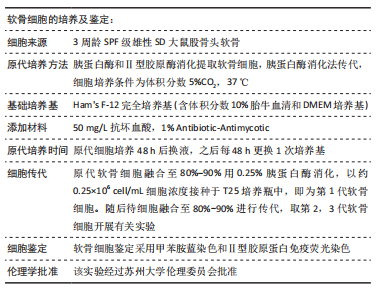
[14] 杨帆, 刘保一, 刘家河,等.体外培养SD大鼠关节软骨细胞原代至第3代的形态学特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2161-2165.
[15] LI Z, MENG D, LIU Y, et al. Circular RNA VMA21 ameliorates IL-1beta-engendered chondrocyte injury through the miR-495-3p/FBWX7 signaling axis. Clin Immunol. 2022;238:1-10.
[16] MU Y, WANG L, FU L, et al.K nockdown of LMX1B Suppressed Cell Apoptosis and Inflammatory Response in IL-1β-Induced Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes through NF-κB and NLRP3 Signal Pathway. Mediators Inflamm. 2022;2022:1-15.
[17] FU G, YIN F, ZHAO J. Depletion of circ_0128846 ameliorates interleukin-1beta-induced human chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation through the miR-940/PTPN12 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;110:1-10.
[18] LI X, FENG K, LI J, et al. Curcumin Inhibits Apoptosis of Chondrocytes through Activation ERK1/2 Signaling Pathways Induced Autophagy. Nutrients. 2017; 9(4):1-14.
[19] FU S, FAN Q, XU J, et al. Circ_0008956 contributes to IL-1beta-induced osteoarthritis progression via miR-149-5p/NAMPT axis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:1-9.
[20] MA Y, TU C, LIU W, et al. Isorhapontigenin Suppresses Interleukin-1beta-Induced Inflammation and Cartilage Matrix Damage in Rat Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 2019;42(6):2278-2285.
[21] HAO L, MA C, LI Z, et al. Effects of type II collagen hydrolysates on osteoarthritis through the NF-kappaB, Wnt/beta-catenin and MAPK pathways. Food Funct. 2022;13(3):1192-1205.
[22] JORGENSEN AEM, KJAER M, HEINEMEIER KM. The Effect of Aging and Mechanical Loading on the Metabolism of Articular Cartilage.J Rheumatol. 2017;44(4):410-417.
[23] LEFEBVRE V, DVIR-GINZBERG M. SOX9 and the many facets of its regulation in the chondrocyte lineage. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(1):1-22.
[24] LIU CF, LEFEBVRE V. The transcription factors SOX9 and SOX5/SOX6 cooperate genome-wide through super-enhancers to drive chondrogenesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(17):8183-8203.
[25] HATTORI T, M LLER C, GEBHARD S. SOX9 is a major negative regulator of cartilage vascularization, bone marrow formation and endochondral ossification. Development. 2010;137(6):901-911.
[26] HASEEB A, KC R, ANGELOZZI M, et al. SOX9 keeps growth plates and articular cartilage healthy by inhibiting chondrocyte dedifferentiation/osteoblastic redifferentiation. PNAS. 2021;118(8):1-11.
[27] BREW CJ, CLEGG PD, BOOT-HANDFORD RP, et al. Gene expression in human chondrocytes in late osteoarthritis is changed in both fibrillated and intact cartilage without evidence of generalised chondrocyte hypertrophy. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(1):234-240.
[28] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M, PLUMB DA, et al. Roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism signals and multiple effectors converge upon MMP-13 regulation in osteoarthritis. Eur Cell Mater. 2011; 21:1-29.
[29] RAHMATI M, MOBASHERI A, MOZAFARI M. Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: A critical review of the state-of-the-art, current prospects, and future challenges. Bone. 2016;85:81-90.
[30] ZREIQAT H, BELLUOCCIO D, SMITH MM. S100A8 and S100A9 in experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):1-13.
[31] POZGAN U, CAGLIC D, ROZMAN B, et al. Expression and activity profiling of selected cysteine cathepsins and matrix metalloproteinases in synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Biol Chem. 2010;391(5):571-579.
[32] GOLDRING MB, OTERO M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(5):471-478.
[33] APTE SS. Anti-ADAMTS5 monoclonal antibodies: implications for aggrecanase inhibition in osteoarthritis. Biochem J. 2016;473(1):e1-e4.
|