[1] MA H, XIE C, CHEN Z, et al. MFG-E8 alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by suppressing pyroptosis and extracellular matrix degradation in nucleus pulposus cells via Nrf2/TXNIP/NLRP3 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):209-223.
[2] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, GONZÁLEZ-GAY MÁ, et al. A new immunometabolic perspective of intervertebral disc degeneration. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(1):47-60.
[3] VOS T, ABAJOBIR AA, ABATE KH, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211-1259.
[4] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47.
[5] ASHINSKY B, SMITH HE, MAUCK RL, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration and regeneration: a motion segment perspective. Eur Cell Mater. 2021;41:370-387.
[6] ZHANG X, HU Y, CHENG P, et al. Targeted therapy for intervertebral disc degeneration: inhibiting apoptosis is a promising treatment strategy, Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(13):2799-2813.
[7] KOS N, GRADISNIK L, VELNAR T. A Brief Review of the Degenerative Intervertebral Disc Disease. Med Arch. 2019;73(6):421-424.
[8] HUGHES SPF, FREEMONT AJ, HUKINS DWL, et al. The pathogenesis of degeneration of the intervertebral disc and emerging therapies in the management of back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2012;94(10):1298-304.
[9] KRUT Z, PELLED G, GAZIT D, et al. Stem Cells and Exosomes: New Therapies for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Cells. 2021;10(9):2241-2259.
[10] ATTWATERS M. Kindlin-2 reduces IVD inflammation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022;18(3):125.
[11] COSAMALON-GAN I, COSAMALON-GAN T, MATTOS-PIAGGIO G, et al. Inflammation in the intervertebral disc herniation. Neurocirugia
(Astur : Engl Ed). 2021;32(1):21-35.
[12] WUERTZ K, VO N, KLETSAS D, et al. Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: the roles of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;23:103-120.
[13] PHILLIPS KL, CULLEN K, CHIVERTON N, et al. Potential roles of cytokines and chemokines in human intervertebral disc degeneration: interleukin-1 is a master regulator of catabolic processes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1165-1177.
[14] MILLWARD-SADLER SJ, COSTELLO PW, FREEMONT AJ, et al. Regulation of catabolic gene expression in normal and degenerate human intervertebral disc cells: implications for the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11(3):R65.
[15] YANG X, WANG L, YUAN ZQ, et al. Interleukin-1beta induces apoptosis in annulus fibrosus cells through the extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(6):593-600.
[16] KOBAYASHI S, MEIR A, KOKUBO Y, et al. Ultrastructural analysis on lumbar disc herniation using surgical specimens: role of neovascularization and macrophages in hernias. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(7):655-662.
[17] CRAWLEY O, GILES AC, DESBOIS M, et al. A MIG-15/JNK-1 MAP kinase cascade opposes RPM-1 signaling in synapse formation and learning. PLoS Genet. 2017;13(12):e1007095.
[18] KUMAR S, SINGH SK, RANA B, et al. The regulatory function of mixed lineage kinase 3 in tumor and host immunity. Pharmacol Ther. 2021; 219:107704.
[19] LIN XL, ZHENG ZY, ZHANG QS, et al. Expression of miR-195 and its target gene Bcl-2 in human intervertebral disc degeneration and their effects on nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):412.
[20] ZHANG HJ, LIAO HY, BAI DY, et al. MAPK /ERK signaling pathway: A potential target for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;143:112170.
[21] SEGUIN CA, BOJARSKI M, PILLIAR RM, et al. Differential regulation of matrix degrading enzymes in a TNFalpha-induced model of nucleus pulposus tissue degeneration. Matrix Biol. 2006;25(7):409-418.
[22] STUDER RK, GILBERTSON LG, GEORGESCU H, et al. p38 MAPK inhibition modulates rabbit nucleus pulposus cell response to IL-1. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(7):991-998.
[23] WANG J, DENG B, LIU Q, et al. Pyroptosis and ferroptosis induced by mixed lineage kinase 3 (MLK3) signaling in cardiomyocytes are essential for myocardial fibrosis in response to pressure overload. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(7):574.
[24] RATTANASINCHAI C, GALLO KA. MLK3 Signaling in Cancer Invasion. Cancers (Basel). 2016;8(5):51-67.
[25] ZHU Y, SUN JM, SUN ZC, et al. MLK3 Is Associated With Poor Prognosis in Patients With Glioblastomas and Actin Cytoskeleton Remodeling in Glioblastoma Cells. Front Oncol. 2020;10:600762.
[26] DISTEFANO TJ, VASO K, DANIAS G, et al. Extracellular Vesicles as an Emerging Treatment Option for Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Therapeutic Potential, Translational Pathways, and Regulatory Considerations. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(5):e2100596.
[27] SAKAUE S, HIRATA J, MAEDA Y, et al. Integration of genetics and miRNA-target gene network identified disease biology implicated in tissue specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(22):11898-11909.
[28] CAI Y, XU L, XU C, et al. Hsa_circ_0001445 inhibits ox-LDL-induced HUVECs inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis by regulating miRNA-640. Perfusion. 2022;37(1):86-94.
[29] ZHU L, SHI Y, LIU L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes ameliorate nucleus pulposus cells apoptosis via delivering miR-142-3p: therapeutic potential for intervertebral disc degenerative diseases. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(14):1727-1739.
[30] TILOTTA V, VADALà G, AMBROSIO L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: The New Frontier for the Treatment of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Appl Sci. 2021;11(23):11222-11240.
[31] COSTACHESCU B, NICULESCU AG, TELEANU RI, et al. Recent Advances in Managing Spinal Intervertebral Discs Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(12):6460-6483.
[32] VERGROESEN PP, KINGMA I, EMANUEL KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(7):1057-1070.
[33] SANDY JD. Proteoglycan core proteins and catabolic fragments present in tissues and fluids. Methods Mol Biol. 2001;171:335-345.
[34] TEIXEIRA GQ, PEREIRA CL, FERREIRA JR, et al. Immunomodulation of Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Insights From a Proinflammatory/Degenerative Ex Vivo Model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(12):E673-E682.
[35] YANG W, YU XH, WANG C, et al. Interleukin-1beta in intervertebral disk degeneration. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;450:262-272.
[36] WANG Y, CHE M, XIN J, et al. The role of IL-1beta and TNF-alpha in intervertebral disc degeneration. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131: 110660.
[37] RISBUD MV, SHAPIRO IM. Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(1): 44-56.
[38] LI S, HUANG C, XIAO J, et al. The Potential Role of Cytokines in Diabetic Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Aging Dis. 2022;13(5):1323-1335.
[39] CHEN ZH, JIN SH, WANG MY, et al. Enhanced NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL- 1beta levels in degenerate human intervertebral disc and their association with the grades of disc degeneration. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2015;298(4):720-726.
[40] KANG H, DONG Y, PENG R, et al. Inhibition of IRE1 suppresses the catabolic effect of IL-1beta on nucleus pulposus cell and prevents intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 2022; 197:114932.
[41] CANNATA F, VADALA G, AMBROSIO L, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration: A focus on obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2020;36(1):e3224.
[42] GRUBER HE, HOELSCHER GL, INGRAM JA, et al. Senescent vs. non-senescent cells in the human annulus in vivo: cell harvest with laser capture microdissection and gene expression studies with microarray analysis. BMC Biotechnol. 2010;10(1):1-10.
[43] HUMPHREY RK, YU SM, BELLARY A, et al. Lysine 63-linked ubiquitination modulates mixed lineage kinase-3 interaction with JIP1 scaffold protein in cytokine-induced pancreatic beta cell death. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(4):2428-2440.
[44] CAZZANELLI P, WUERTZ-KOZAK K. MicroRNAs in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration, Apoptosis, Inflammation, and Mechanobiology. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3601.
[45] ZHU J, ZHANG X, GAO W, et al. lncRNA/circRNA‑miRNA‑mRNA ceRNA network in lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3160-3174.
[46] LUAN X, ZHOU X, FALLAH P, et al. MicroRNAs: Harbingers and shapers of periodontal inflammation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;124:85-98.
[47] ZINGALE VD, GUGLIANDOLO A, MAZZON E. MiR-155: An Important Regulator of Neuroinflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):90-113.
[48] KEOROCHANA G, JOHNSON JS, TAGHAVI CE, et al. The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010;10(11):1014-1023.
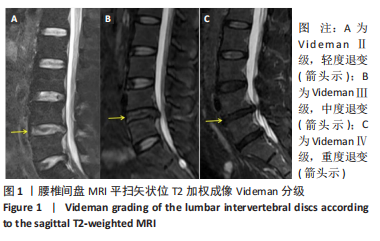
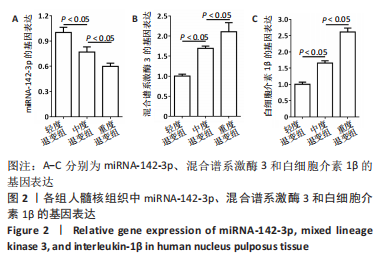
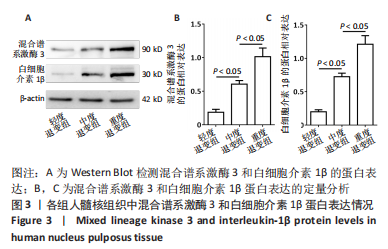
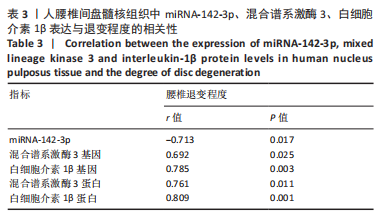
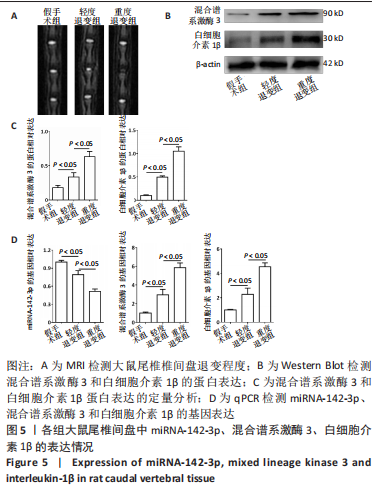
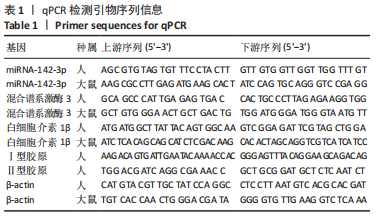
|