[1] ATROSHI I, GUMMESSON C, JOHNSSON R, et al. Prevalence of carpaltunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA. 1999;282(2):153-158.
[2] Practice parameter for electrodiagnostic studies in carpal tunnel syndrome: summary statement. Muscle Nerve. 2002;25:918.
[3] LEE TH, LI Y. Consideration of repetitive nerve stimulation of the median nerve in patients being evaluated for myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 2019;60(6):658-661.
[4] SUCHER BM, SCHREIBER AL. Carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosis. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 2014;25(2):229-247.
[5] CHEN YT, WILLIAMS L, ZAK MJ, et al. Review of Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome and a Proposed Scanning Protocol. J Ultrasound Med. 2016;35:2311.
[6] BANG M, KIM JM, KIM HS. The usefulness of ultrasonography to diagnose the early stage of carpal tunnel syndrome in proximal to the carpal tunnel inlet: A prospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(26):e16039.
[7] 王晓春.腕管综合征误诊为颈椎病分析[J].中国现代医生,2010,48(26):82-87.
[8] 李阳,朱向阳,黄淮宇.腕管综合征的诊断进展[J].中国康复理论与实践, 2013,19(3):246-249.
[9] 吴香花,吴珊.神经超声在周围神经疾病中的诊断应用[J]. 中华脑科疾病与康复杂志(电子版),2018,8(1):45-48.
[10] GASPAROTTI R, PADUA L, BRIANI C, et al. New technologies for the assessment of neuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(4):203-216.
[11] LAMPI MC, REINHART-KING CA. Targeting extracellular matrix stiffness to attenuate disease: From molecular mechanisms to clinical trials. Sci Trans Med. 2018;10(422):eaao0475.
[12] BOBER BG, SHAH SB. Paclitaxel Alters Sensory Nerve Biomechanical Properties. J Biomech. 2015;48(13):S0021929015003978.
[13] 孟加新,向橙,马润瑶,等.剪切波弹性成像的临床应用前景[J].牡丹江医学院学报,2021,42(1):161-163.
[14] INAL M, TAN S, DEMIRKAN S, et al. Evaluation of optic nerve with strain and shear wave elastography in patients with behçet’s disease and healthy subjects. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2017;43(7):1348-1354.
[15] NOGUEIRA-BARBOSA MH, LUGÃO HB, GREGIO-JÚNIOR E, et al. Ultrasound elastography assessment of the median nerve in leprosy patients. Muscle Nerve. 2017;56(3):393-398.
[16] DISSELHORST-KLUG C, SCHMITZ-RODE T, RAU G. Surface electromyography and muscle force: Limits in sEMG-force relationship and new approaches for applications. Clin Biomech. 2009;24(3):225-235.
[17] SALMAN ROGHANI R, HASHEMI SE, HOLISAZ MT, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of median nerve ultrasonography in elderly patients with carpal tunnel syndrome: sensitivity and specificity assessment. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:1953-1962.
[18] 李辉萍,宋涛,左若群,等.体外冲击波与超声波治疗轻中度腕管综合征的对比研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2020,42(5):443-445.
[19] AZADEH A, VASAGHI A, JALLI R, et al. Comparison of inching electrodiagnosis method and ultrasonographic findings in the determination of median nerve entrapment site in carpal tunnel syndrome. AmJ Phys Med Rehab. 2017;96: 869-873.
[20] PARK JS, WON HC, OH JY, et al. Value of cross-sectional area of median nerve by MRI in carpal tunnel syndrome. Asian J Surg. 2020;43(6):654-659.
[21] PETROVER D, RICHETTE P. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome : from ultrasonography to ultrasound guided carpal tunnel release. Joint Bone Spine. 2018;85(5):545-552.
[22] SIGRIST RMS, LIAU J, KAFFAS AE, et al. Ultrasound elastography:review of techniques and clinical applications. Theranostics. 2017;7(5):1303-1329.
[23] VALENTE G, RINALDI L, MOGGIO G, et al. Point shear wave elastography and vibration controlled transient elastography for estimating liver fibrosis in a cohort of liver transplant patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(13):7357-7365.
[24] COSGROVE DO, BERG WA, DORÉ CJ, et al. Shear wave elastography for breast masses is highly reproducible. Eur Radiol. 2012;22(5):1023-1032.
[25] KOZINC Ž, ŠARABON N. Shear-wave elastography for assessment of trapezius muscle stiffness: Reliability and association with low-level muscle activity. PLoS One. 2020;15(6):e0234359.
[26] ZHU B, YAN F, HE Y, et al. Evaluation of the healthy median nerve elasticity: Feasibility and reliability of shear wave elastography. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(43):e12956.
[27] KANTARCI F, USTABASIOGLU FE, DELIL S, et al. Median nerve stiffness measurement by shear wave elastography: a potential sonographic method in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(2):434-440.
[28] 黄点点,陈路增,邢海英,等.正中神经剪切波弹性成像的可重复性评价[J].中国医学影像学杂志,2018,26(5):383-387.
[29] BLAND JM, ALTMAN DG. A note on the use of the intraclass correlation coefficient in the evaluation of agreement between two methods of measurement. Comp Biol Med. 1990;20(5):337-340.
[30] JAESCHKE R, THOIRS K, BAIN G, et al. Systematic review: hand activity and ultrasound of the median nerve. Occup Med (Lond). 2017;67(5):389-393.
[31] PANAGOPOULOS GN, WU T, FOWLER JR. Correlation of ultrasound cross-sectional area of the median nerve, nerve conduction studies and 2-point discrimination. Muscle Nerve. 2019;59(2):236-239.
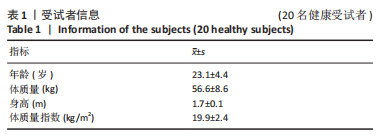
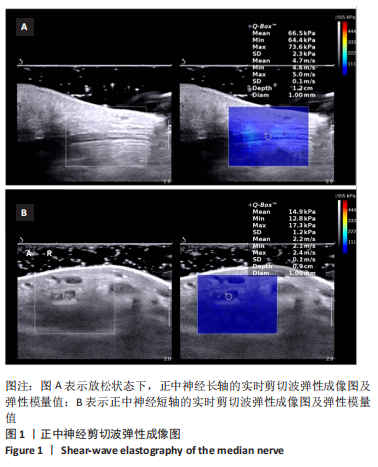
|