1.1 设计 分组设计细胞学实验。数据符合正态分布,则组间比较采用单因素方差分析,方差齐则用LSD分析,方差不齐则用Game’s-Howell分析;数据不符合正态分布则进行秩和检验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2022-09-01/10-31在济宁市第一人民医院肿瘤转化实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 实验动物 健康8周龄SD大鼠4只,雌雄不限,体质量200 g左右,由济南朋悦实验动物繁育有限公司提供,许可证号:SCXK(鲁)20190003。
动物实验符合济宁市第一人民医院动物实验伦理审查标准(伦理编号:JNRM-2022-DW-023)。
1.3.2 实验试剂 青藤碱购自美国MedChemExpress公司,锌原卟啉(Zinc Protoporphyrin,HO-1抑制剂,货号:HY-101193,规格:1 mg,品牌:MCE)购自MedChemExpress公司。胰蛋白酶购自汉强生物技术有限公司,Ⅱ型胶原蛋白酶购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司,南美胎牛血清购自澳大利亚AusGeneX公司,CCK-8试剂盒购自日本同仁化学研究所,Annexin V PE Apoptosis Detection Kit购自美国Biogems公司,Fast Pure Cell/Tissue Total RNA Isolation Kit V2试剂盒、HiScript III RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper)试剂盒、BCA Protein Quantification Kit购自南京诺唯赞公司,HO-1 Antibody、Beta Actin Antibody、Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG(H+L) HRP购自美国Affinity Biosciences 公司。
1.3.3 实验仪器 细胞计数仪(型号:AMQA2000,生产企业:赛默飞世尔,S/N:2187A20090034)。流式细胞仪(型号:CytoFLEX,生产企业:贝克曼(中国),S/N:BE39397)。细胞培养箱(型号:3111,生产企业:赛默飞世尔,批号:S/N:300209779)。Multiskan™ FC酶标仪(型号:51119180,生产企业:赛默飞世尔,S/N:357-705277)。全自动化学发光图像分析系统(型号:Tanon-4600,生产企业:天能,S/N:20T12NP64-12138)。Applied Biosystems PCR热循环仪(型号:EN61326-1,生产企业:赛默飞世尔,SN:2721220120892)。
1.4 方法
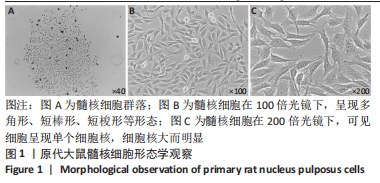
1.4.1 髓核细胞体外培养 采取脱颈法处死大鼠后,浸泡于体积分数75%乙醇溶液中2 min后,转移至生物安全柜,剪开大鼠背部及尾部皮肤,无菌获得大鼠腰椎、骶椎及尾椎,小心切开椎间盘并收集髓核组织。将髓核组织用无菌眼科剪剪碎后,转移至15 mL离心管,加入适量0.25%胰蛋白酶37 ℃消化30 min,期间每5 min摇匀一次,加入含有血清的培养液终止消化。离心去上清后,加入适量Ⅱ型胶原蛋白酶消化37 ℃消化30 min后,期间每5 min摇匀一次,加入血清终止消化。离心去上清后,加入培养液并调整细胞浓度至(3-5)×108 L-1,接种至25 cm2培养瓶中,每瓶接种5 mL,置于CO2培养箱中培养。第3天时进行半量换液,之后每3 d进行全量换液。约2周后,当细胞汇合至90%以上时,即可消化进行传代培养。
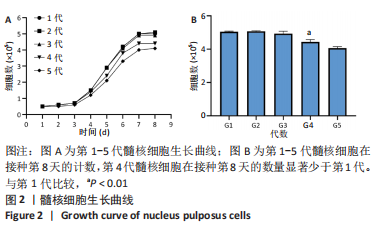
1.4.2 绘制细胞生长曲线 取第1-5代髓核细胞,调整细胞浓度至5.0×108 L-1,等量接种至24孔板,每孔1 mL。接种后第1-8天,每天取3孔细胞进行计数,并计算细胞数量平均值,连续8 d。以时间(d)为横坐标,细胞数量平均值(个)为纵坐标绘制细胞生长曲线。
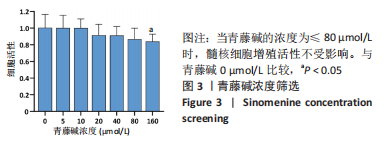
1.4.3 青藤碱浓度筛选 将第3代髓核细胞接种至96孔板,每孔100 μL,待细胞汇合至85%时,弃掉原培养液,加入含有不同浓度青藤碱的培养液。培养液中青藤碱的浓度分别为0,10,20,40,80和160 μmol/L,每组设8孔,置于二氧化碳培养箱中孵育24 h后,采用CCK-8试剂盒检测每组细胞的增殖活性。
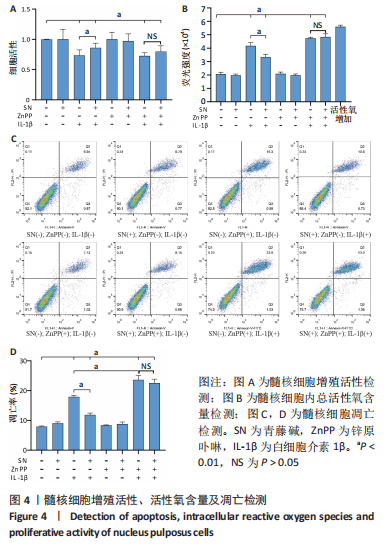
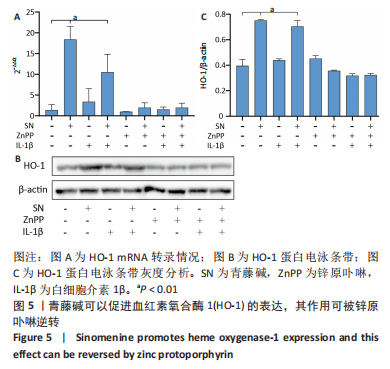
1.4.4 实验分组 将第3代髓核细胞分为以下8组,各组培养液分别5 mL:①对照组:不做处理;②青藤碱组:培养液中含有40 μmol/L青藤碱;③IL-1β组:培养液中含有10 ng/mL IL-1β;④青藤碱+IL-1β组:培养液中含有40 μmol/L青藤碱和10 ng/mL IL-1β;⑤锌原卟啉组:培养液中含有5 μmol/L 锌原卟啉;⑥锌原卟啉+青藤碱组:培养液中含有5 μmol/L锌原卟啉和40 μmol/L 青藤碱;⑦锌原卟啉+IL-1β组:培养液中含有5 μmol/L 锌原卟啉和10 ng/mL IL-1β;⑧青藤碱+锌原卟啉+IL-1β组:培养液中含有40 μmol/L 青藤碱、5 μmol/L锌原卟啉和10 ng/mL IL-1β。在二氧化碳培养箱内孵育8 h后,检测各组细胞的增殖活性、凋亡率、活性氧含量、HO-1的mRNA和蛋白水平。
1.4.5 细胞增殖活性检测 96孔板内的髓核细胞处理结束后,弃掉原培养液。更换不含血清的培养液后,再每孔加入10 µL CCK-8溶液,继续培养2-4 h,酶标仪检测各组细胞在450 nm处的吸光度值。细胞增殖活力计算公式如下:
细胞增殖活力(%)=[A(实验)-A(空白)]/[A(对照)-A(空白)]×100%
式中A(实验)为含有不同药物和CCK-8 溶液孔的吸光度值,A(空白)为含有CCK-8 溶液而没有细胞孔的吸光度值,A(对照)为含有正常培养细胞和CCK-8 溶液孔的吸光度值。
1.4.6 流式细胞术检测髓核细胞凋亡率 各组细胞处理结束后消化收集并用预冷的PBS洗涤2遍。4 ℃离心后弃上清并加入100 µL Binding Buffer重悬细胞。对照组和实验组分别加入5 µL Annexin V-FITC和5 µL PI Staining Solution;Annexin-V组(单阳性组)加入5 µL Annexin V-FITC,PI组(单阳性组)加入5 µL PI Staining Solution,空白组细胞(双阴性组)不做处理,轻轻吹打均匀后,避光、25 ℃孵育10 min;加入400 µL Binding Buffer轻轻吹打混匀后上机检测。
1.4.7 荧光探针DCFH-DA标记法检测髓核细胞内总活性氧含量 96孔荧光酶标板内的髓核细胞处理结束后,弃掉原培养液,加入预先采用DMEM/F12培养液稀释好的10 μmol/L DCFH-DA溶液,每孔100 µL,阳性对照组内加入Rosup作为对照。置于细胞培养箱中20-30 min后,DMEM/F12培养液洗涤3遍后荧光酶标仪检测各种荧光强度(酶标仪设置参数:488 nm激发波长,525 nm发射波长)。
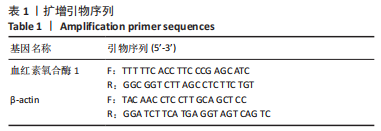
1.4.8 RT-PCR检测HO-1 mRNA转录 引物由生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司合成,序列见表1。
使用Fast Pure Cell/Tissue Total RNA Isolation Kit V2试剂盒提取细胞总RNA,应用HiScript III RT SuperMix for qPCR (+gDNA wiper)试剂盒进行反转录。应用LightCycler®480 System
Real Time PCR扩增仪分析目的基因表达。
1.4.9 Western blot技术检测HO-1的蛋白表达 各组细胞处理结束后采用4 ℃预冷的PBS洗涤3遍,置于冰上加入裂解液,细胞刮刮取细胞后,转入1.5 mL离心管。4 ℃、15 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清采用BCA Protein Quantification Kit检测蛋白样品浓度,加入SDS-PAGE蛋白上样缓冲液(5×)后,金属浴加热至100 ℃,煮沸5 min。等量上样后进行电泳、转膜。取出PVDF膜加入一抗(1∶1 000),4 ℃孵育过夜,TBST溶液清洗3遍后,加入二抗(1∶5 000),室温孵育1 h后,TBST溶液清洗3遍。滴加适量ECL工作液,使ECL工作液覆盖PVDF 膜,室温孵育两三分钟后,采用全自动化学发光图像分析系统进行显影并采集图像。
1.5 主要观察指标 细胞分组处理结束后,分别检测各组髓核细胞的增殖活性、凋亡率、细胞内活性氧含量以及HO-1的表达量。
1.6 统计学分析 实验结果采用SPSS 18.0(美国IBM公司)进行数据分析,应用GraphPad Prism 8(美国GraphPad Software公司)进行统计绘图。计量资料以x±s表示,两组数据之间采用独立样本t检验进行分析,以P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经济宁市第一人民医院生物统计学专家审核。