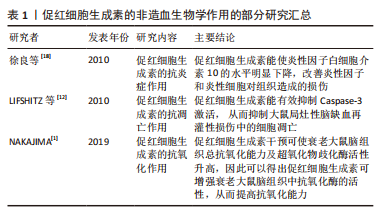
[1] NAKAJIMA Y. Retinoic acid signaling in heart development. Genesis. 2019;57(7-8):e23300.
[2] AWIDA Z, HIRAM-BAB S, BACHAR A, et al. Erythropoietin Receptor (EPOR) signaling in the osteoclast lineage contributes to epo-induced bone loss in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):12051.
[3] BAHLMANN FH. Erythropoietin regulates endothelial progenitor cells. Blood. 2004;103(3):921-926.
[4] SATO T, TAKEDA N. The roles of HIF-1α signaling in cardiovascular diseases. J Cardiol. 2023;81(2):202-208.
[5] LIPSIC E, SCHOEMAKER RG, VAN DER MEER P, et al. Protective effects of erythropoietin in cardiac ischemia: from bench to bedside. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48(11):2161-2167.
[6] PANKRATOVA S, KIRYUSHKO D, SONN K, et al. Neuroprotective properties of a novel, non-haematopoietic agonist of the erythropoietin receptor. Brain. 2010;133(Pt 8):2281-2294.
[7] NAKANO M, SATOH K, FUKUMOTO Y, et al. Important role of erythropoietin receptor to promote VEGF expression and angiogenesis in peripheral ischemia in mice. Circ Res. 2007;100(5):662-669.
[8] TSAI PT, OHAB JJ, KERTESZ N, et al. A critical role of erythropoietin receptor in neurogenesis and post-stroke recovery. J Neurosci. 2006; 26(4):1269-1274.
[9] ELLIOTT S, BUSSE L, MCCAFFERY I, et al. Identification of a sensitive anti-erythropoietin receptor monoclonal antibody allows detection of low levels of EpoR in cells. J Immunol Methods. 2010;352(1-2): 126-139.
[10] MAXWELL P, MELENDEZ-RODRÍGUEZ F, MATCHETT KB, et al. Novel antibodies directed against the human erythropoietin receptor: creating a basis for clinical implementation. Br J Haematol. 2015; 168(3):429-442.
[11] WESTENBRINK BD, LIPSIC E, VAN DER MEER P, et al. Erythropoietin improves cardiac function through endothelial progenitor cell and vascular endothelial growth factor mediated neovascularization. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(16):2018-2027.
[12] LIFSHITZ, TABAK G, GASSMANN M, et al. Macrophages as novel target cells for erythropoietin. Haematologica. 2010;95(11):1823-1831.
[13] REX TS, WONG Y, KODALI K, et al. Neuroprotection of photoreceptors by direct delivery of erythropoietin to the retina of the retinal degeneration slow mouse. Exp Eye Res. 2009;89(5):735-740.
[14] TOBALEM M, HARDER Y, REZAEIAN F, et al. Secondary burn progression decreased by erythropoietin. Crit Care Med. 2013;41(4):963-971.
[15] NAKAMURA S, SHO M, KOYAMA F, et al. Erythropoietin attenuates intestinal inflammation and promotes tissue regeneration. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015;50(9):1094-1102.
[16] LIU QS, CHENG ZW, XIONG JG, et al. Erythropoietin pretreatment exerts anti-inflammatory effects in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion-injured rats via suppression of the TLR2/NF-κB pathway. Transplant Proc. 2015;47(2): 283-289.
[17] GARCIA P, SPEIDEL V, SCHEUER C, et al. Low dose erythropoietin stimulates bone healing in mice. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(2):165-172.
[18] 徐良,周凯.EPO对失血性休克合并内毒素血症兔TNF-α、IL-6、IL-10、MDA影响的研究[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2010;34(2):155-157.
[19] KERTESZ N, WU J, CHEN TH, et al. The role of erythropoietin in regulating angiogenesis. Dev Biol. 2004;276(1):101-110.
[20] WANG J, FU X, JIANG C, et al. Bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation promotes therapeutic angiogenesis via upregulation of the VEGF-VEGFR2 signaling pathway in a rat model of vascular dementia. Behav Brain Res. 2014;265:171-180.
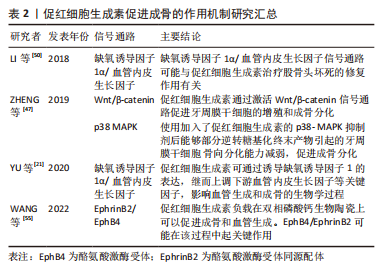
[21] YU Y, MA L, ZHANG H, et al. EPO could be regulated by HIF-1 and promote osteogenesis and accelerate bone repair. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2020;48(1):206-217.
[22] 李杜晨晖,田艾,唐正龙.骨生物支架材料诱导的血管生成[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(22):3602-3608.
[23] TARI K, ATASHI A, KAVIANI S, et al. Erythropoietin induces production of hepatocyte growth factor from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Biologicals. 2017;45:15-19.
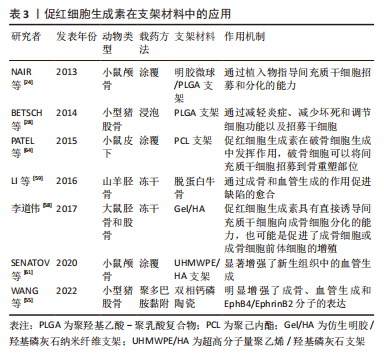
[24] NAIR AM, TSAI YT, SHAH KM, et al. The effect of erythropoietin on autologous stem cell-mediated bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(30):7364-7371.
[25] WAN L, ZHANG F, HE Q, et al. EPO promotes bone repair through enhanced cartilaginous callus formation and angiogenesis. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e102010.
[26] HOLSTEIN JH, ORTH M, SCHEUER C, et al. Erythropoietin stimulates bone formation, cell proliferation, and angiogenesis in a femoral segmental defect model in mice. Bone. 2011;49(5):1037-1045.
[27] RÖLFING JH, BENDTSEN M, JENSEN J, et al. Erythropoietin augments bone formation in a rabbit posterolateral spinal fusion model. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(7):1083-1088.
[28] Betsch M, Thelen S, Santak L, et al. The role of erythropoietin and bone marrow concentrate in the treatment of osteochondral defects in mini-pigs. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92766.
[29] RÖLFING JH, JENSEN J, JENSEN JN, et al. A single topical dose of erythropoietin applied on a collagen carrier enhances calvarial bone healing in pigs. Acta Orthop. 2014;85(2):201-209.
[30] HOLSTEIN JH, MENGER MD, SCHEUER C, et al. Erythropoietin (EPO): EPO-receptor signaling improves early endochondral ossification and mechanical strength in fracture healing. Life Sci. 2007;80(10):893-900.
[31] GARCI P, SPEIDEL V, SCHEUER C, et al. Low dose erythropoietin stimulates bone healing in mice. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(2):165-172.
[32] MIHMANLI A, DOLANMAZ D, AVUNDUK MC, et al. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on mandibular distraction osteogenesis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;67(11):2337-2343.
[33] SINGBRANT S, RUSSELL MR, JOVIC T, et al. Erythropoietin couples erythropoiesis, B-lymphopoiesis, and bone homeostasis within the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood. 2011;117(21):5631-5642.
[34] DESHET-UNGER N, HIRAM-BAB S, HAIM-OHANA Y, et al. Erythropoietin treatment in murine multiple myeloma: immune gain and bone loss. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30998.
[35] HIRAM-BAB S, NEUMANN D, GABET Y. Erythropoietin in bone-Controversies and consensus. Cytokine. 2017;89:155-159.
[36] OIKONOMIDOU PR, CASU C, YANG Z, et al. Polycythemia is associated with bone loss and reduced osteoblast activity in mice. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27(4):1559-1568.
[37] RAUNER M, FRANKE K, MURRAY M, et al. Increased EPO levels are associated with bone loss in mice lacking PHD2 in EPO-producing cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(10):1877-1887.
[38] SURESH S, DE CASTRO LF, DEY S, et al. Erythropoietin modulates bone marrow stromal cell differentiation. Bone Res. 2019;7:21.
[39] JUNG Y, SONG J, SHIOZAWA Y, et al. Hematopoietic stem cells regulate mesenchymal stromal cell induction into osteoblasts thereby participating in the formation of the stem cell niche. Stem Cells. 2008; 26(8):2042-2051.
[40] RÖLFING JH, BAATRUP A, STIEHLER M, et al. The osteogenic effect of erythropoietin on human mesenchymal stromal cells is dose-dependent and involves non-hematopoietic receptors and multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2014;10(1):69-78.
[41] KIM J, JUNG Y, SUN H, et al. Erythropoietin mediated bone formation is regulated by mTOR signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(1):220-228.
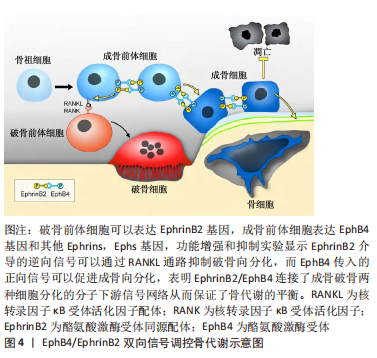
[42] LI C, SHI C, KIM J, et al. Erythropoietin promotes bone formation through EphrinB2/EphB4 signaling. J Dent Res. 2015;94(3):455-463.
[43] RANKIN EB, WU C, KHATRI R, et al. The HIF signaling pathway in osteoblasts directly modulates erythropoiesis through the production of EPO. Cell. 2012;149(1):63-74.
[44] TSIFTSOGLOU AS. Erythropoietin (EPO) as a key regulator of erythropoiesis, bone remodeling and endothelial transdifferentiation of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs): implications in regenerative medicine. Cells. 2021;10(8):2140.
[45] BALAIAN E, WOBUS M, WEIDNER H, et al. Erythropoietin inhibits osteoblast function in myelodysplastic syndromes via the canonical Wnt pathway. Haematologica. 2018;103(1):61-68.
[46] WASHIO K, IWATA T, MIZUTANI M, et al. Assessment of cell sheets derived from human periodontal ligament cells: a pre-clinical study. Cell Tissue Res. 2010;341(3):397-404.
[47] ZHENG DH, WANG XX, MA D, et al. Erythropoietin enhances osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:2543-2552.
[48] JU S, LIM L, WI K, et al. LRP5 Regulates HIF-1α Stability via Interaction with PHD2 in Ischemic Myocardium. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6581
[49] SU J, LI Z, CUI S, et al. The Local HIF-2α/EPO pathway in the bone marrow is associated with excessive erythrocytosis and the increase in bone marrow microvessel density in chronic mountain sickness. High Alt Med Biol. 2015;16(4):318-330.
[50] LI D, HU Q, TAN G, et al. Erythropoietin enhances bone repair effects via the hypoxia-inducible factor signal pathway in glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Am J Med Sci. 2018;355(6): 597-606.
[51] 丁月峰, 王学娟, p38信号通路在牙周膜细胞成骨分化中的调控作用[J].口腔医学,2015,35(9):726-729.
[52] KIM MH, CHO GW, HUH YM, et al. Transduction of human EPO into human bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells synergistically enhances cell-protective and migratory effects. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2010; 44(4):656-663.
[53] 李琛, EphrinB2/EphB4介导促红细胞生成素调控骨重塑的实验研究[D].长春:吉林大学,2014.
[54] WANG Q, LIU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Research progress on the expression and function of erythropoietin-producing hepatomocellular receptors and their receptor-interacting proteins in oral-related diseases. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020;38(2):218-223.
[55] WANG Y, WANG P, WU Q, et al. Loading of erythropoietin on biphasic calcium phosphate bioceramics promotes osteogenesis and angiogenesis by regulating EphB4/EphrinB2 molecules. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2022;33(2):19.
[56] 顾中一.载EPO壳聚糖水凝胶促牙周组织再生的研究[J].口腔生物医学,2017,8(3):127-131.
[57] KARPOV TE, PELTEK OO, MUSLIMOV AR, et al. Development of optimized strategies for growth factor incorporation onto electrospun fibrous scaffolds to promote prolonged release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(5):5578-5592.
[58] 李道伟.载EPO仿生Gel/HA纳米纤维促骨再生研究[J].口腔生物医学,2017,8(3):117-121.
[59] LI D, DENG L, XIE X, et al. Evaluation of the osteogenesis and angiogenesis effects of erythropoietin and the efficacy of deproteinized bovine bone/recombinant human erythropoietin scaffold on bone defect repair. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(6):101.
[60] KIRKEBY A, TORUP L, BOCHSEN L, et al. High-dose erythropoietin alters platelet reactivity and bleeding time in rodents in contrast to the neuroprotective variant carbamyl-erythropoietin (CEPO). Thromb Haemost. 2008;99(4):720-728.
[61] SENATOV F, AMANBEK G, ORLOVA P, et al. Biomimetic UHMWPE/HA scaffolds with rhBMP-2 and erythropoietin for reconstructive surgery. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:110750.
[62] SUN H, JUNG Y, SHIOZAWA Y, et al. Erythropoietin modulates the structure of bone morphogenetic protein 2-engineered cranial bone. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(19-20):2095-2105.
[63] 张广德.重组腺病毒介导BMP-9及促红细胞生成素双基因共转染促进脂肪来源干细胞体外成骨的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(3):272-278.
[64] PATEL JJ, MODES JE, FLANAGAN CL, et al. Dual delivery of EPO and BMP2 from a novel modular poly-ɛ-caprolactone construct to increase the bone formation in prefabricated bone flaps. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2015;21(9):889-897. |
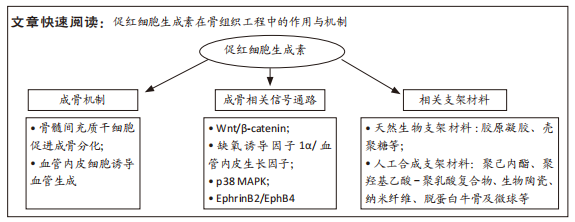

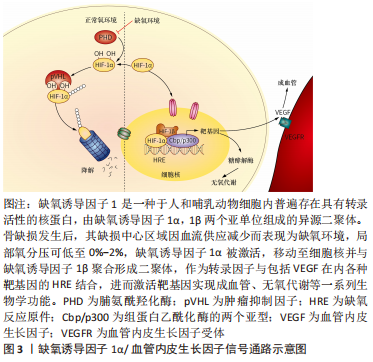

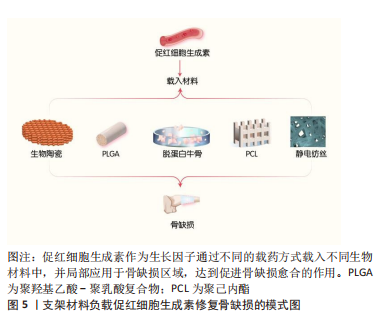

 因此,文章拟综述促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用进展并初步阐述其可能的分子生物学机制,为构建新型组织工程骨提供新思路。
因此,文章拟综述促红细胞生成素在骨组织工程中的应用进展并初步阐述其可能的分子生物学机制,为构建新型组织工程骨提供新思路。