中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (4): 633-638.doi: 10.12307/2023.862
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
股骨骨缺损动物模型制备现状及特点
周世博1,关健斌1,俞 兴2,赵 赫2,杨永栋2,刘 涛1
- 1北京中医药大学第一临床医学院,北京市 100029;2北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100070
-
收稿日期:2022-10-31接受日期:2023-01-10出版日期:2024-02-08发布日期:2023-07-14 -
通讯作者:俞兴,博士,主任医师,北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100070 -
作者简介:周世博,男,1994年生,河南省洛阳市人,汉族,在读博士,医师,主要从事脊柱脊髓损伤、椎间盘退变及骨组织工程研究。
Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics
Zhou Shibo1, Guan Jianbin1, Yu Xing2, Zhao He2, Yang Yongdong2, Liu Tao1
- 1First Clinical School of Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 2Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China
-
Received:2022-10-31Accepted:2023-01-10Online:2024-02-08Published:2023-07-14 -
Contact:Yu Xing, MD, Chief physician, Dongzhimen Hospital Affiliated to Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China -
About author:Zhou Shibo, MD candidate, Physician, First Clinical School of Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China
摘要:
文题释义:
临界性骨缺损:骨发生缺损后,不经任何处理在自然状态下不能自行愈合的最小骨缺损的尺寸。动物模型:是基于实验动物建立的模拟人类疾病或满足研究的动物,是实验治疗方式走向临床的一个重要过程。
背景:骨缺损的修复及后期临床转归仍是临床研究中的热点和难点,是困扰临床医师的常见问题。构建合适、可重复性及无限接近临床的动物实验模型及科学的评估对进一步的临床治疗相关疾病至关重要。
目的:回顾性分析文献中股骨骨缺损常用实验动物模型制备方法及不同模型特点,评估优势与不足,为相关研究者选择合适的股骨骨缺损动物模型提供一定的参考。方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science、Medline数据库及CNKI数据库,设定英文检索词为:bone defect,bone,bones,defect,defects,defective,animal model,animal,model,laboratory,laboratory animal,animal laboratory;中文检索词为:骨缺损,动物模型,实验。检索时限为2000-01-01/2022-08-01。
结果与结论:①对入选的27篇随机对照动物实验进行了分析和评估,实验动物包含大鼠、小鼠、新西兰兔及羊,骨缺损类型主要包含圆柱形骨缺损和节段性截骨骨缺损,部位以股骨中段及远端居多。多用于评估骨修复材料、药物、载药活性物质及物理治疗等方法对骨缺损修复的影响及缺损愈合机制研究,尤其是负重骨缺损修复机制的研究。②不同缺损类型及不同实验动物股骨骨缺损值的范围不同,研究者可结合实验目的,选择合适的动物及骨缺损类型,并设置合理的骨缺损值。③目前的研究表明,股骨骨缺损模型以圆柱形及节段截骨骨缺损为主,主要是在股骨远端及中段,手术方法及术后处理较为成熟,可操作性强,能够提供成熟的实验动物模型。④就圆柱形骨缺损而言,大鼠及新西兰兔更适合,而节段性截骨则无特殊要求,各种动物均能满足实验要求。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1260-0807(周世博)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
周世博, 关健斌, 俞 兴, 赵 赫, 杨永栋, 刘 涛. 股骨骨缺损动物模型制备现状及特点[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 633-638.
Zhou Shibo, Guan Jianbin, Yu Xing, Zhao He, Yang Yongdong, Liu Tao. Animal models of femoral bone defects: preparation status and characteristics[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(4): 633-638.
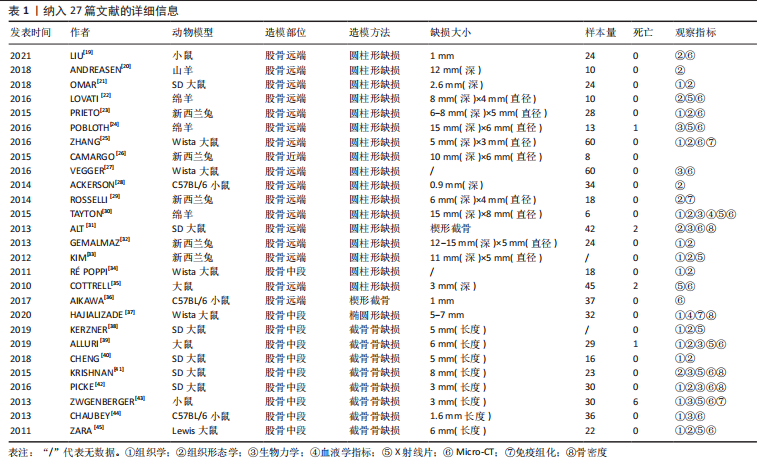
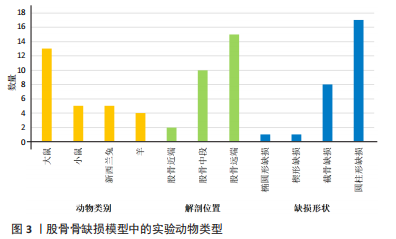
2.2.1 动物类别 27篇文献中共涉及动物模型4种,大鼠最常用,占比48.15%,其次为新西兰兔(18.52%)、小鼠(18.52%)及羊(14.81%),详见图3。
2.2.2 缺损模型 纳入的文献中,股骨远端出现频率最高,占比55.56%,其次为股骨中段(37.04%)、股骨近端(7.41%);其中圆柱形缺损为62.96%、节段性截骨骨缺损为29.63%、楔形截骨为3.70%、椭圆形为3.70%。详见图3。
2.2.3 动物模型 大鼠、小鼠及兔来源广泛,具备较强的抗感染能力,围术期便于集中管理,整体死亡率较低。但啮齿类动物适合短期内骨修复材料及其生物相容性的初步研究,不适合做长期评估;同时,啮齿类动物模型缺乏固有的哈佛管系统,不能完全模仿临床中骨的修复过程。兔介于啮齿类动物和大型动物模型之间,生命周期较长,且具备与人类相似的哈佛氏管,是临床常见的动物模型选择[46-47]。山羊和绵羊作为不同的物种,在实验中也被用来制备骨缺损动物模型。相比山羊,绵羊更加温顺,且绵羊的骨再生率与骨重塑能力与人类较为相似,故可以更加客观地评估骨缺损修复能力或相关修复材料的再生作用 [48-49]。理论上讲动物模型越大,骨缺损愈合机制越接近临床,缺损的模型也越容易制备,但实验成本、操作的可控性及实验样本量难以保证[50-51]。相比之下虽然不同动物之间有不同的解剖学、生物化学、生物力学及相关基因表达的差异[52],但仍有一定的共性。
圆柱形骨缺损大部分以股骨远端外侧髁为手术部位,于股骨外侧髁行纵向切口,在股四头肌和肌腱的外侧通过钝性剥离暴露股骨外侧髁,之后骨科钻或牙科钻形成单皮质圆柱形的骨缺损。在建模的过程中生理盐水局部降温,清理骨屑后根据实验目的选择填充或不填充内容物,止血、缝合及包扎。此模型制备的优点在于股骨外髁层次较为清楚且周围没有重要的神经、血管等解剖结构,便于操作。
节段性截骨骨缺损以股骨中段为手术部位,沿股骨外侧大转子和髌骨之间作一长度合适的切口,切开外侧筋膜,肌间隙钝性分离,暴露股骨外侧,保留大转子臀肌止点,避免损伤神经血管束。根据术者不同习惯及实验目的选用钢板螺钉、克氏针或外固定架固定,之后截骨。KERZNER等[38]暴露股骨外侧后,1.0 mm克氏针打通骨道,之后放置外固定架,4支带纹1.0 mm克氏针分别于股骨近端及远端固定,之后在骨干中部制造一个5 mm节段性骨缺损;PICKE等[42]使用四孔钢板在股骨近端及远端分别固定2枚螺钉,在股骨中轴处形成3 mm的节段性截面缺损;ALLURI等[39]首先将聚乙烯四孔板通过钢丝固定于大鼠股骨近端及远端,之后用高速磨钻形成一长约6 mm的节段性骨缺损,之后3D打印的TCP支架填充缺损处。上述节段性骨缺损模型制备后经过适应性治疗后均允许动物进行负重,在实验期间未出现内固定物的松动。
2.2.4 骨缺损动物模型应用 股骨缺损动物模型主要集中在大鼠[23,25,27,31,34-35,37-43,45]、新西兰兔及小鼠[19,23,26,28-29,32-33,36,43-44];造模方法以圆柱形骨缺损及节段性截骨缺损为主[19-35,38-45];造模方法决定了股骨造模部位,圆柱形骨缺损动物模型主要集中在实验对象的股骨远端,而节段性截骨骨缺损的动物模型主要集中在股骨中段;观察指标主要集中在生物力学[24,27,30-31,39,41-44]、影像学及组织学的相关评价[19,21-25,27,30-45]。大鼠股骨节段性骨缺损模型制备范围在3-8 mm;圆柱形骨缺损范围在(3-5) mm(深度)×(2.6-3) mm(直径)[21,25,35];小鼠节段性骨缺损模型制备范围在1.6-3 mm之间;兔股骨远端圆柱形骨缺损范围在(6-15) mm(深度)×(5-6) mm (直径);羊股骨远端圆柱形骨缺损缺损范围(12-15) mm(深度)×(4-8) mm(直径) [23,32-33]。纳入文献中,有3篇文献对动物实验过程中的不良反应进行了报道[31,35,39],包括感染、应力性骨折;4篇文献报道了分别因麻醉过量及其他原因导致的动物死亡[31,35,39,43],整体安全性尚可。基于上述不良反应,在达到手术造模目的的同时,及时止血,减少创伤,特别是骨缺损制备使用器械的过程中更应该精细操作;同时根据不同麻醉剂的特点,精确计算麻醉剂量,尽量避免由于人为因素导致的实验动物的死亡。
2.3 实验目的 文献中股骨骨缺损动物模型多用于骨修复材料、药物、物理疗法等治疗骨缺损的疗效评价,同时也用于骨缺损愈合机制的相关研究,对于骨缺损形状的选择标准未作特殊说明。圆柱形、节段性截骨及楔形骨缺损动物模型均可评估上述治疗方法的有效性与安全性。对于评估特殊类型骨缺损而言则需要相对特殊的骨缺损模型,例如文献中评估松质骨或骨质疏松骨缺损愈合机制多选用股骨远端圆柱形骨缺损模型;同时,如果实验需要,股骨远端缺损可以同时造成骨与软骨损伤,在有限的实验时间内同时观察骨与软骨损伤的修复过程。而对皮质骨缺损及髓腔再通机制的研究则多选用股骨中段截骨骨缺损,且节段性截骨骨缺损也适用于大段骨缺损愈合机制及生理状态下载荷能力的研究,根据实验目的选择合适的骨缺损模型可以更加客观评估不同治疗方法对骨缺损干预的有效性。颅骨骨缺损从第一例临床报道至今已有百年历史,而颅骨骨缺损动物模型也以其标准化的骨缺损模型、组织学和放射学易于评估,在骨缺损动物模型中占据了相当高的比例。但是作为非负重区域,无法在生理状态下评估力学载荷实验,也无法同时评估骨与软骨修复过程,在一定程度上限制了该模型的应用。因此在上述方面股骨骨缺损可能是更好的骨缺损模型。
2.4 骨缺损范围的选择 动物实验过程中,良好的空白对照对实验结果的观察具有重要作用,不同实验对象本身具备不同的自我修复能力,因此骨缺损模型制备过程中骨缺损大小如何限定是需要考虑的问题。若缺损过小的骨缺损自行愈合会影响实验结果,对骨缺损修复材料的治疗效果、是否具有促成骨作用以及促成骨作用机制的评估产生误判,进而失去研究的意义。因此在1986年有学者提出临界性骨缺损(bone size defect,CSD)的概念,SCHMITZ等[53]提出动物一生中不会自动愈合的最小尺寸的骨缺损即为CSD,将CSD定义为周径的1.5-2.5倍或缺损长度为模型对象的1/10以上,超过此范围就会出现缺损不愈合;1990年HOLLINGER等[54]进一步定义了CSD,他认为在动物生命周期内愈合率小于10%的骨缺损即可定义为CSD。CSD超出了机体自然状态下的再生极限,需要借助材料才能促进骨缺损的愈合。若实验目的用于骨组织材料促成骨性能的评估,则设置大于CSD的骨缺损动物模型对于实验的指导就具有至关重要的意义,缺损范围小于临界性骨缺损值,在观察期内自行愈合,进而影响最终的实验结果。不同动物模型、不同模型制备方法及不同动物自我愈合能力不同,CSD值也不同,甚至部分文献并未叙述CSD的取值范围。作者认为CSD与动物模型、模型制备方法以及实验目的密切相关,而是否需要设定临界性骨缺损的实验动物模型在很大程度上取决于实验目的。
骨缺损特别是大段骨缺损是临床工作中的重点和难点,不同动物自我修复能力不同,故CSD值也有所差异。文献中大鼠股骨节段性骨缺损模型制备范围在3-8 mm之间。T?LLI等[55]、SKALICZKI等[56]学者通过股骨节段性截骨、钢板螺钉固定构建骨缺损模型,结果发现给予活性物质治疗后,8 mm和6 mm并未出现骨重建,产生了稳定的临界性骨缺损,因此认为6-8 mm可以作为大鼠节段性截骨临界性骨缺损值。ZWINGENBERGER等[43]分别制备了长度1,2,3 mm的小鼠节段性骨缺损模型,治疗后发现,3 mm骨缺损组最终产生了稳定的骨缺损不愈合;TAZAWA等[57]和ALAEE等[58]发现2 mm的小鼠节段性截骨不给予活性物质干预的情况下没有表现出愈合趋势,国内学者靳慧勇等[59]分别制备了长度1,2及2.5 mm的股骨干中段骨缺损模型,3个月后经过影像学发现2 mm及2.5 mm的骨缺损没有发生愈合。通过上述研究可以发现,小鼠2 mm节段性骨缺损应该可以作为临界性骨缺损值,在实验设计过程中可以作为参考。圆柱形骨缺损动物模型较少用于节段骨缺损愈合机制的研究,多用于评估材料的成骨性及骨诱导能力或其他研究目的,有报道称10 mm(深度)×6/7 mm(直径)兔股骨髁圆柱骨缺损模型,可以作为临界性骨缺损模型进行实验研究[60-61]。羊是大型动物的代表,有研究认为其根据部位的不同CSD值也不尽相同,约等于相对应骨干直径的3倍[62],但仍需进一步考证。同时受困于动物体型、实验场地、实验经费以及管理所存在的不便性,选择大型动物作为实验观察对象较少。综上,临界性骨缺损需要综合考虑实验对象及实验目的的不同,同时结合既往报道进行设定。与此同时,可视化软件的应用也为骨缺损值的量化提供了一定的可行性。参照SCHMITZ等[53]及HOLLINGER等[54]的论述,结合可视化软件的应用,对不同性别、不同月龄动物的股骨进行量化,做好术前规划,选取合适的骨缺损部位及大小,既可以避免动物资源的浪费,又可以为临床提供可靠的数据支持。可视化软件应用于动物手术过程中已有报道,ABO,STAMM等[63-64]通过将放射学数据对骨骼模型进行重建,模拟手术过程进行精确截骨;SINGH,LOHRE等[65-66]通过显微CT重建模拟大鼠肝叶精确切除手术。因此在后期的发展过程中,完好的术前规划、精细化管理也是发展的方向所在,但是此种方法的不足之处在于会增加实验成本。
2.5 骨缺损与骨骺损伤 既往文献较少论述骨缺损制备过程中如何避免骨骺损伤,对骨损伤与骨骺损伤如何划分也未作过多说明。SUN等 [67]以成年大鼠为研究对象,通过3D解剖和虚拟手术,将大鼠股骨分为Ⅰ-Ⅲ共6个区域,其中认为当缺损部位靠近Ⅲ区特别是Ⅲb区时所形成的损伤更接近骨骺损伤而非骨缺损或损伤,继而影响骨的生长;同时Ⅲ区操作有可能出现骨折,进而造成关节、韧带以及滑膜损伤,以至于出现关节的早期退化与不稳定,对骨愈合造成不良影响[68]。对于其他动物模型,有关骨损伤和骨骺损伤的描述较少。同时啮齿类动物的生长过程似乎终生留有生长软骨板,因此在实验过程中,需要综合考虑,可以结合既往研究,尽可能远离骨骺与关节区域。
2.6 缺损部位的干预及固定方式的选择 圆柱形骨缺损模型通常以填充的方式填充缺损处,而节段性、楔形骨缺损模型的固定方式包括钢板螺钉、钢丝困扎及外固定架等。
骨缺损特别是节段性骨缺损和楔形骨缺损的修复,必须在稳定状态下才能实现,因此在股骨骨缺损模型制备过程中,必须重建稳定性,才能客观全面观察骨缺损的愈合,对愈合时间及愈合机制做出合理、客观的评价。常用的固定方式包括外固定(如外固定架)和内固定(如钢板螺钉) [69-71]。外固定架在一定程度上保留骨膜和软组织,对局部血液供应影响较小,且外固定对植骨材料影响较小,可最大程度避免外在因素对骨愈合的干扰;但是钉道易感染,外固定术后动物如何护理是实验设计者需要考虑的问题,如动物是否会撕咬固定器进而对实验结果造成影响。钢板内固定易实现缺损部位的刚性固定,可以较好地重建骨缺损区域的稳定性,但是钢板固定会在一定程度上破坏了骨组织的血液供应,由此是否会影响自然状态下骨的修复及对骨材料是否造成影响文献中并未提及[72-74]。一项大型动物骨缺损固定方式回顾性分析显示[75],认为外固定较内固定而言更具有优势。由于重建缺损部位稳定性的干扰因素较多,因此有学者选择非负重长骨进行骨缺损动物实验,动物实验中大多认为新西兰兔的前肢骨和鼠的胫骨属于非负重骨,缺损后不需要额外固定,一定程度上解决了固定方式不同给研究者造成的困扰。但是实验中仍存在因过度运动或其他原因导致骨折的发生。似乎没有哪一种固定方式是完美的,可以结合实验目的及实验条件对骨缺损进行合适的固定。
2.7 评价指标 骨缺损动物模型主要为临床骨组织工程、生物活性支架以及基于此所构建的复合材料的临床应用提供支持,评价指标主要集中在影像学、生物力学、骨组织形态及组织学[76-80]。
X射线片可以从成骨、连接及髓腔改建各方面对新生骨组织进行评估。双能X射线还可以对骨密度进行评估,骨密度主要作为骨质疏松模型的常用指标,用来观察对骨质疏松模型干预效果的评估,对于常规动物模型骨密度检测并不作为常规指标使用。骨小梁的微观结构较小,X射线片并不能得到清晰可辨的骨小梁结构图。随着医学影像技术的发展,骨形态计量学在骨科领域的应用逐渐增加。Micro-CT除了能对骨密度进行评估外,还可以客观反映骨缺损在填充不同修复材料后,新生骨小梁的生长变化特点,通过三维模式直观反映填充材料的吸收降解状况,对骨小梁面积百分比、骨小梁厚度、骨小梁密度及骨小梁的分离度等进行量化,从多个方面评估新生骨的生成情况[81-83]。由于治疗骨缺损材料需要植入承重部位,对未缺损的骨骼起到连接和支撑等作用,故需要一定的力学强度。临床中可以通过多种方式对植入材料的力学性能进行评估,比如压缩试验、三点弯曲试验及复合载荷加载试验等,可以根据不同的实验设计及现有条件,选择合适的检测方法,系统评估植入材料的生物力学性能[84-85];除此之外用于骨缺损修复的材料大都具备一定的生物活性,因此材料植入后观察其成骨活性及相关骨代谢指标也有一定的必要性,如碱性磷酸酶、Ⅰ型原胶原羧基端前肽等,用于评估骨材料的成骨情况[86-87]。总之,临床现有检测手段可以对骨缺损植入后材料的转归及骨组织的再生情况进行观察,从静态到动态,从宏观到微观,通过检测手段可以做到良好的追踪,进而全面评估治疗手段的有效性与安全性。
2.8 存在的不足 无论是圆柱形骨缺损还是节段性骨缺损动物模型,文献中尚存在一定不足。第一、文献中并未提及圆柱形骨缺损模型制备过程中如何区别骨缺损与骨骺损伤,也未说明不同骨缺损模型及不同的固定方式对最终的实验结果是否存在影响;第二、骨缺损范围的大小并未进行规范的量化;第三、未说明内植物位置是否需要评估,是否需要影像学的监测及监测时间点如何选择;第四、文中未说明动物性别及月龄选择标准,这两种因素对实验结果存在一定影响[88-89]。除非特别需要(如绝经后骨质疏松骨缺损),建议在实验过程中对不同性别及月龄同时进行评估,避免由此造成的差异;第五、纳入文献中动物样本量参差不齐;第六、文献中仅涉及正常动物模型,未评价炎性、病理性骨缺损等其他情况。

| [1] EASTMAN BL. XII. Two Cases of Bone-Grafting for Cranial Defect. Ann Surg. 1895; 22(6):787-791. [2] GALLARDO-CALERO I, BARRERA-OCHOA S, MANZANARES MC, et al. Vascularized Periosteal Flaps Accelerate Osteointegration and Revascularization of Allografts in Rats. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019;477(4):741-755. [3] WANG H, FU X, SHI J, et al. Nutrient Element Decorated Polyetheretherketone Implants Steer Mitochondrial Dynamics for Boosted Diabetic Osseointegration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(20):e2101778. [4] MIGLIORINI F, LA PADULA G, TORSIELLO E, et al. Strategies for large bone defect reconstruction after trauma, infections or tumour excision: a comprehensive review of the literature. Eur J Med Res. 2021;26(1):118. [5] FREEMAN E, TURNBULL RS. The value of osseous coagulum as a graft material. J Periodontal Res. 1973;8(4):229-236. [6] CUTTING CB, MCCARTHY JG, BERENSTEIN A. Blood supply of the upper craniofacial skeleton: the search for composite calvarial bone flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984;74(5):603-610. [7] RYU DJ, JUNG EY, HONG DH, et al. Efficacy of bone formation of microporous sphere-shaped biphasic calcium phosphate in a rabbit skull bone defect model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2021;109(2):294-307. [8] OKUMUS A, GUVEN E, ERMIS I, et al. Comparative Analysis of Using Bone Graft, Hydroxyapatite Coralline (Biocoral®) and Porous Polyethylene (Medpor®) Implants for Cranioplasty in a Rat Model of Cranial Bone Defect. Turk Neurosurg. 2020;30(2):263-270. [9] HILTUNEN A, VUORIO E, ARO HT. A standardized experimental fracture in the mouse tibia. J Orthop Res. 1993;11(2):305-312. [10] HOLSTEIN JH, GARCIA P, HISTING T, et al. Advances in the establishment of defined mouse models for the study of fracture healing and bone regeneration. J Orthop Trauma. 2009;23(5 Suppl):S31-S38. [11] WANG H, FU X, SHI J, et al. Nutrient Element Decorated Polyetheretherketone Implants Steer Mitochondrial Dynamics for Boosted Diabetic Osseointegration. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(20):e2101778. [12] GHAMOR-AMEGAVI EP, YANG X, QIU J, et al. Composition control in biphasic silicate microspheres on stimulating new bone regeneration and repair of osteoporotic femoral bone defect. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020; 108(2):377-390. [13] AKYOL U, GÜNGÖRMÜŞ M. Er:YAG laser ablation of bone in experimental diabetics. Photomed Laser Surg. 2010;28(4):477-482. [14] PEARSON HB, MASON DE, KEGELMAN CD, et al. Effects of Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on Neovascularization During Large Bone Defect Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(23-24):1623-1634. [15] KLEIN A, BARANOWSKI A, RITZ U, et al. Effect of bone sialoprotein coating on progression of bone formation in a femoral defect model in rats. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020;46(2):277-286. [16] KUMAWAT VS, BANDYOPADHYAY-GHOSH S, GHOSH SB. An overview of translational research in bone graft biomaterials. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2022; 29:1-44. [17] MARYCZ K, ŚMIESZEK A, KORNICKA-GARBOWSKA K, et al. Novel Nanohydroxyapatite (nHAp)-Based Scaffold Doped with Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IO), Functionalized with Small Non-Coding RNA (miR-21/124) Modulates Expression of Runt-Related Transcriptional Factor 2 and Osteopontin, Promoting Regeneration of Osteoporotic Bone in Bilateral Cranial Defects in a Senescence-Accelerated Mouse Model (SAM/P6). PART 2. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:6049-6065. [18] SHUAI C, YU L, FENG P, et al. Interfacial reinforcement in bioceramic/biopolymer composite bone scaffold: The role of coupling agent. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2020;193:111083. [19] LIU H, LIU S, JI H, et al. An adiponectin receptor agonist promote osteogenesis via regulating bone-fat balance. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(6):e13035. [20] ANDREASEN CM, DING M, ANDERSEN TL, et al.Effects of substitute coated with hyaluronic acid or poly-lactic acid on implant fixation: Experimental study in ovariectomized and glucocorticoid-treated sheep. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):e1122-e1130. [21] OMAR O, DAHLIN A, GASSER A, et al. Tissue dynamics and regenerative outcome in two resorbable non-cross-linked collagen membranes for guided bone regeneration: A preclinical molecular and histological study in vivo. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29(1):7-19. [22] LOVATI AB, LOPA S, RECORDATI C, et al. In Vivo Bone Formation Within Engineered Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds in a Sheep Model. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;99(2):209-223. [23] PRIETO EM, TALLEY AD, GOULD NR, et al. Effects of particle size and porosity on in vivo remodeling of settable allograft bone/polymer composites. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;103(8):1641-1651. [24] POBLOTH AM, JOHNSON KA, SCHELL H, et al. Establishment of a preclinical ovine screening model for the investigation of bone tissue engineering strategies in cancellous and cortical bone defects. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:111. [25] ZHANG Y, WEI L, MIRON RJ, et al. Bone scaffolds loaded with siRNA-Semaphorin4d for the treatment of osteoporosis related bone defects. Sci Rep. 2016;6:26925. [26] CAMARGO AF, BAPTISTA AM, NATALINO R, et al. Bioactive glass in cavitary bone defects: a comparative experimental study in rabbits. Acta Ortop Bras. 2015; 23(4):202-207. [27] VEGGER JB, BRÜEL A, SØRENSEN TG, et al. Systemic Treatment with Strontium Ranelate Does Not Influence the Healing of Femoral Mid-shaft Defects in Rats. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016;98(2):206-214. [28] ACKERSON RM, SHUM LC, BERRY AR, et al. In vivo model to measure bone repair efficacy of nanoparticle-based drug delivery. Orthopedics. 2014;37(8):e707-e711. [29] ROSSELLI JE, MARTINS DM, MARTINS JL, et al. The effect of simvastatin on the regeneration of surgical cavities in the femurs of rabbits. Acta Cir Bras. 2014; 29(2):87-92. [30] TAYTON E, PURCELL M, SMITH JO, et al. The scale-up of a tissue engineered porous hydroxyapatite polymer composite scaffold for use in bone repair: an ovine femoral condyle defect study. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(4):1346-1356. [31] ALT V, THORMANN U, RAY S, et al. A new metaphyseal bone defect model in osteoporotic rats to study biomaterials for the enhancement of bone healing in osteoporotic fractures. Acta Biomater. 2013;9(6):7035-7042. [32] GEMALMAZ HC, BOLUKBASI S, ESEN E, et al. Periosteal adventitia is a valuable bone graft alternative. Int J Artif Organs. 2013;36(5):341-349. [33] KIM J, MCBRIDE S, TELLIS B, et al. Rapid-prototyped PLGA/β-TCP/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite scaffolds in a rabbit femoral defect model. Biofabrication. 2012; 4(2):025003. [34] RÉ POPPI R, DA SILVA AL, NACER RS, et al. Evaluation of the osteogenic effect of low-level laser therapy (808 nm and 660 nm) on bone defects induced in the femurs of female rats submitted to ovariectomy. Lasers Med Sci. 2011;26(4): 515-522. [35] COTTRELL JA, VALES FM, SCHACHTER D, et al. Osteogenic activity of locally applied small molecule drugs in a rat femur defect model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2010;2010:597641. [36] AIKAWA T, MATSUBARA H, UGAJI S, et al. Contribution of methylglyoxal to delayed healing of bone injury in diabetes. Mol Med Rep. 2017;16(1):403-409. [37] HAJIALIZADE M, MOGHTADAEI M, MIRZAEI A, et al. Significant effect of simvastatin and/or ezetimibe-loaded nanofibers on the healing of femoral defect: An experimental study. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:110861. [38] KERZNER B, MARTIN HL, WEISER M, et al. A Reliable and Reproducible Critical-Sized Segmental Femoral Defect Model in Rats Stabilized with a Custom External Fixator. J Vis Exp. 2019;(145):10.3791/59206. [39] ALLURI R, SONG X, BOUGIOUKLI S, et al. Regional gene therapy with 3D printed scaffolds to heal critical sized bone defects in a rat model. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(10):2174-2182. [40] CHENG P, LI D, GAO Y, et al. Prevascularization promotes endogenous cell-mediated angiogenesis by upregulating the expression of fibrinogen and connective tissue growth factor in tissue-engineered bone grafts. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):176. [41] KRISHNAN L, PRIDDY LB, ESANCY C, et al. Hydrogel-based Delivery of rhBMP-2 Improves Healing of Large Bone Defects Compared With Autograft. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(9):2885-2897. [42] PICKE AK, GORDALIZA ALAGUERO I, CAMPBELL GM, et al. Bone defect regeneration and cortical bone parameters of type 2 diabetic rats are improved by insulin therapy. Bone. 2016;82:108-115. [43] ZWINGENBERGER S, NIEDERLOHMANN E, VATER C, et al. Establishment of a femoral critical-size bone defect model in immunodeficient mice. J Surg Res. 2013;181(1):e7-e14. [44] CHAUBEY A, GRAWE B, MEGANCK JA, et al. Structural and biomechanical responses of osseous healing: a novel murine nonunion model. J Orthop Traumatol. 2013;14(4):247-257. [45] ZARA JN, SIU RK, ZHANG X, et al. High doses of bone morphogenetic protein 2 induce structurally abnormal bone and inflammation in vivo. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(9-10):1389-1399. [46] BINSALAH MA, RAMALINGAM S, ALKINDI M, et al. Guided Bone Regeneration of Femoral Segmental Defects using Equine Bone Graft: An In-Vivo Micro-Computed Tomographic Study in Rats. J Invest Surg. 2019;32(5):456-466. [47] HETTWER W, HORSTMANN PF, BISCHOFF S, et al. Establishment and effects of allograft and synthetic bone graft substitute treatment of a critical size metaphyseal bone defect model in the sheep femur. APMIS. 2019;127(2):53-63. [48] CHU W, GAN Y, ZHUANG Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and porous β-tricalcium phosphate composites prepared through stem cell screen-enrich-combine(-biomaterials) circulating system for the repair of critical size bone defects in goat tibia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):157. [49] MCGOVERN JA, GRIFFIN M, HUTMACHER DW. Animal models for bone tissue engineering and modelling disease. Dis Model Mech. 2018;11(4):dmm033084. [50] SAMADIAN H, MOBASHERI H, AZAMI M, et al. Osteoconductive and electroactive carbon nanofibers/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite tailored for bone tissue engineering: in vitro and in vivo studies. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):14853. [51] SCHALLER B, MATTHIAS BURKHARD JP, CHAGNON M, et al. Fracture Healing and Bone Remodeling With Human Standard-Sized Magnesium Versus Polylactide-Co-Glycolide Plate and Screw Systems Using a Mini-Swine Craniomaxillofacial Osteotomy Fixation Model. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76(10):2138-2150. [52] BIGHAM-SADEGH A, ORYAN A. Selection of animal models for pre-clinical strategies in evaluating the fracture healing, bone graft substitutes and bone tissue regeneration and engineering. Connect Tissue Res. 2015;56(3):175-194. [53] SCHMITZ JP, HOLLINGER JO. The critical size defect as an experimental model for craniomandibulofacial nonunions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1986;(205):299-308. [54] HOLLINGER JO, KLEINSCHMIDT JC. The critical size defect as an experimental model to test bone repair materials. J Craniofac Surg. 1990;1(1):60-68. [55] TÖLLI H, KUJALA S, JÄMSÄ T, et al. Reindeer bone extract can heal the critical-size rat femur defect. Int Orthop. 2011;35(4):615-622. [56] SKALICZKI G, SCHANDL K, WESZL M, et al. Serum albumin enhances bone healing in a nonunion femoral defect model in rats: a computer tomography micromorphometry study. Int Orthop. 2013;37(4):741-745. [57] TAZAWA R, UCHIDA K, MINEHARA H, et al. Poly(POG)n loaded with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 accelerates new bone formation in a critical-sized bone defect mouse model. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):471. [58] ALAEE F, SUGIYAMA O, VIRK MS, et al. Suicide gene approach using a dual-expression lentiviral vector to enhance the safety of ex vivo gene therapy for bone repair. Gene Ther. 2014;21(2):139-147. [59] 靳慧勇,侯天勇,罗飞,等.小鼠股骨临界骨缺损模型的构建及评估[J].第三军医大学学报,2011,33(22):2331-2334. [60] LIU J, MAO K, LIU Z, et al. Injectable biocomposites for bone healing in rabbit femoral condyle defects. PLoS One. 2013;8(10):e75668. [61] 徐石庄,王进,潘文振,等.兔股骨髁临界性骨缺损动物模型制备及临界骨缺损值[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(20):3191-3195. [62] KIRBY GTS, WHITE LJ, STECK R, et al. Microparticles for Sustained Growth Factor Delivery in the Regeneration of Critically-Sized Segmental Tibial Bone Defects. Materials (Basel). 2016;9(4):259. [63] ABO SHARKH H, MAKHOUL N. In-House Surgeon-Led Virtual Surgical Planning for Maxillofacial Reconstruction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;78(4):651-660. [64] STAMM T, BÖTTCHER D, KLEINHEINZ J. The University Münster model surgery system for orthognathic surgery - The digital update. Head Face Med. 2021; 17(1):31. [65] SINGH GD, SINGH M. Virtual Surgical Planning: Modeling from the Present to the Future. J Clin Med. 2021;10(23):5655. [66] LOHRE R, WARNER JJP, ATHWAL GS, et al. The evolution of virtual reality in shoulder and elbow surgery. JSES Int. 2020;4(2):215-223. [67] SUN Y, HELMHOLZ H, WILLUMEIT-RÖMER R. Surgical Classification for Preclinical Rat Femoral Bone Defect Model: Standardization Based on Systematic Review, Anatomical Analysis and Virtual Surgery. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022;9(9):476. [68] KIM JE, SONG DH, KIM SH, et al. Development and characterization of various osteoarthritis models for tissue engineering. PLoS One. 2018;13(3):e0194288. [69] BADWELAN M, ALKINDI M, RAMALINGAM S, et al. The Efficacy of Recombinant Platelet-Derived Growth Factor on Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate to Regenerate Femoral Critical Sized Segmental Defects: Longitudinal In Vivo Micro-CT Study in a Rat Model. J Invest Surg. 2020;33(5):476-488. [70] PAN Z, JIANG P, XUE S, et al. Repair of a critical-size segmental rabbit femur defect using bioglass-β-TCP monoblock, a vascularized periosteal flap and BMP-2. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(6):2148-2156. [71] KUROIWA Y, NIIKURA T, LEE SY, et al. Escherichia coli-derived BMP-2-absorbed β-TCP granules induce bone regeneration in rabbit critical-sized femoral segmental defects. Int Orthop. 2019;43(5):1247-1253. [72] HORNER EA, KIRKHAM J, WOOD D, et al. Long bone defect models for tissue engineering applications: criteria for choice. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(2): 263-271. [73] GARSKE DS, SCHMIDT-BLEEK K, ELLINGHAUS A, et al. Alginate Hydrogels for In Vivo Bone Regeneration: The Immune Competence of the Animal Model Matters. Tissue Eng Part A. 2020;26(15-16):852-862. [74] KRAUS T, FISCHERAUER S, TREICHLER S, et al. The influence of biodegradable magnesium implants on the growth plate. Acta Biomater. 2018;66:109-117. [75] JEWELL E, RYTLEWSKI J, ANGLE JO, et al. Surgical Fixation Hardware for Regeneration of Long Bone Segmental Defects: Translating Large Animal Model and Human Experiences. Clin Rev Bone Miner Metab. 2015;13(4). doi: 10.1007/s12018-015-9195-8 [76] HERTEN M, ZILKENS C, THOREY F, et al. Biomechanical Stability and Osteogenesis in a Tibial Bone Defect Treated by Autologous Ovine Cord Blood Cells-A Pilot Study. Molecules. 2019;24(2):295. [77] PATEL PP, BUCKLEY C, TAYLOR BL, et al. Mechanical and biological evaluation of a hydroxyapatite-reinforced scaffold for bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(4):732-741. [78] ZHA Y, LI Y, LIN T, et al. Progenitor cell-derived exosomes endowed with VEGF plasmids enhance osteogenic induction and vascular remodeling in large segmental bone defects. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):397-409. [79] MABILLEAU G, MIECZKOWSKA A, LIBOUBAN H, et al. Comparison between quantitative X-ray imaging, dual energy X-ray absorptiometry and microCT in the assessment of bone mineral density in disuse-induced bone loss. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2015;15(1):42-52. [80] CLARK DP, BADEA CT. Advances in micro-CT imaging of small animals. Phys Med. 2021;88:175-192. [81] NEGRI AL, DEL VALLE EE, ZANCHETTA MB, et al. Evaluation of bone microarchitecture by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT) in hemodialysis patients. Osteoporos Int. 2012;23(10): 2543-2550. [82] PERMUY M, GUEDE D, LÓPEZ-PEÑA M, et al. Comparison of various SYSADOA for the osteoarthritis treatment: an experimental study in rabbits. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:120. [83] WU Y, ADEEB S, DOSCHAK MR. Using Micro-CT Derived Bone Microarchitecture to Analyze Bone Stiffness - A Case Study on Osteoporosis Rat Bone. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015;6:80. [84] ALBERT CI, JAMESON J, HARRIS G. Design and validation of bending test method for characterization of miniature pediatric cortical bone specimens. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013;227(2):105-113. [85] SCHWIEDRZIK J, RAGHAVAN R, BÜRKI A, et al. In situ micropillar compression reveals superior strength and ductility but an absence of damage in lamellar bone. Nat Mater. 2014;13(7):740-747. [86] KIM HK, PARK KS, LEE JS, et al. Salicylideneamino-2-thiophenol enhances osteogenic differentiation through the activation of MAPK pathways in multipotent bone marrow stem cell. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(6):1833-1841. [87] GASIŃSKA T, BOROWSKA A, WICHARY H, et al. Effect of methylprednisolone pulse therapy with and without alendronate on biochemical markers of bone turnover in patients with Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2012;122(7-8): 341-347. [88] BIGUETTI CC, COUTO MCR, SILVA ACR, et al. New Surgical Model for Bone-Muscle Injury Reveals Age and Gender-Related Healing Patterns in the 5 Lipoxygenase (5LO) Knockout Mouse. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:484. [89] MCCABE IC, FEDORKO A, MYERS MG JR,et al. Novel leptin receptor signaling mutants identify location and sex-dependent modulation of bone density, adiposity, and growth. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(3):4398-4408. |
| [1] | 薛晓峰, 魏永康, 乔晓红, 杜玉勇, 牛建军, 任立新, 杨慧峰, 张治民, 郭 媛, 陈维毅. 股骨颈骨折空心钉内固定后股骨近端骨质疏松的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 862-867. |
| [2] | 黄培镇, 董 航, 蔡群斌, 林梓凌, 黄 枫. 顺行和逆行髓内钉治疗不同部位股骨干骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 868-872. |
| [3] | 谭能贤, 吴文正, 郑楚荣, 罗列良, 古 鹏, 欧阳崇志, 郑晓辉. 不同空心加压螺钉固定方式对股骨颈垂直型骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 873-878. |
| [4] | 吴钟汉, 王景坤, 李 涛, 许新忠, 余水生, 程 里, 田大胜, 汤 健, 荆珏华. 股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗外侧壁完整型和外侧壁危险型股骨转子间骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 911-916. |
| [5] | 赵汝顺, 郝阳泉, 许 鹏, 郑 鑫, 姜永宏, 张玉婷, 王孟飞, 鲁 超. 不同坏死病灶位置对非创伤性股骨头坏死自然病程的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 917-921. |
| [6] | 胡智星, 李 群, 杨 超, 王潇潇, 方罗昌婷, 侯吴琼, 林 娜, 陈卫衡, 刘春芳, 林 雅. 不同因素影响激素性股骨头坏死家兔模型成模效果的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 976-984. |
| [7] | 杨雨晴, 陈志宇. 早期短暂M1巨噬细胞在骨组织工程中的作用及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 594-601. |
| [8] | 张乾龙, 买合木提•亚库甫, 宋晨辉, 刘修信, 任 政, 刘宇哲, 木牙沙尔•阿布都沙拉木, 萨吉旦•艾克拜尔, 冉 建. 骨水泥分布位置与含量对股骨反转子间骨折应力、位移影响的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 336-340. |
| [9] | 戴 京, 刘沙沙, 沈明敬. 负载外泌体的可注射水凝胶修复种植体周围骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 347-354. |
| [10] | 谷明西, 王常成, 田丰德, 安 宁, 郝瑞胡, 郭 林. 丝素蛋白/明胶/壳聚糖三维多孔软骨组织支架的制备及体外评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 366-372. |
| [11] | 高雪钰, 张文涛, 孙天泽, 张 警, 李忠海. 金属离子在骨组织工程中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 439-444. |
| [12] | 龙智睿, 黄 雷, 肖 放, 王 琳, 王晓蓓. 骨组织工程中研究水凝胶微球的特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 472-478. |
| [13] | 孔祥宇, 王 兴, 裴志伟, 常家乐, 李斯琴, 郝 廷, 何万雄, 张葆鑫, 贾燕飞. 生物支架材料及打印技术修复骨缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 479-485. |
| [14] | 林天烨, 吴智明, 张文胜, 何晓铭, 何敏聪, 张庆文, 何 伟, 魏秋实, 李子祺. 复方生脉成骨胶囊修复激素性股骨头坏死的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 200-207. |
| [15] | 冉 磊, 韩海慧, 徐 博, 王建业, 沈 军, 肖涟波, 施 杞. 补骨脂-淫羊藿对类风湿关节炎抗炎机制的分子对接分析:动物实验验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 208-215. |
因此构建合适、可重复性及无限接近临床的动物实验模型对临床应用前的评估至关重要[15-18]。故作者阅读并总结了相关文献,目的在于为学者提供稳定的、可以客观评估骨缺损修复过程的股骨骨缺损动物模型,为相关研究者选择合适的股骨骨缺损动物模型提供参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年8月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2000-01-01/2022-08-01。
1.1.3 检索数据库 检索Pubmed、Web of Science、Medline数据库及CNKI数据库。
1.1.4 检索途径 全文检索。
1.1.5 检索词 英文检索词:bone defect,bone,bones,defect,defects,defective,animal model,animal,model,Laboratory,Laboratory animal,animal Laboratory;检索范围为“All fields”;中文检索词:骨缺损,动物模型,实验。
1.1.6 检索文献类型 研究原著,动物实验。
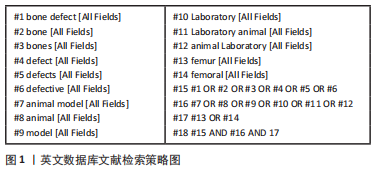
1.1.7 检索策略 检索策略以图片形式展现,以英文检索为例,详见图1。
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①随机对照动物实验;②骨缺损模型;③造模部位为股骨。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①软骨缺损模型;②股骨头坏死模型;③骨关节炎模型;④非原创性研究;⑤多节段骨缺损;⑥数据重复或不完整;⑦体外动物实验;⑧基因变异动物模型;⑨综述;⑩单纯骨折,非骨缺损动物模型。
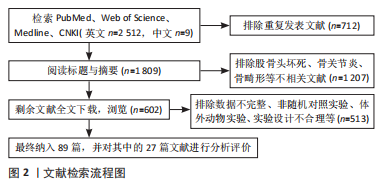
1.3 质量评估与数据提取 阅读文献及摘要后根据纳入与排除标准,剔除研究内容重复、设计不合理等文献。最终纳入89篇,其中中文2篇,英文87篇。文献检索流程见图2。
总之,没有哪一种动物模型是完美契合临床的,研究者应根据实验目的及动物的自身特点,选择合适的动物类型、骨缺损部位,并确定缺损范围的大小,这样可以获得经济、重复性好、并且能够客观评价骨缺损修复过程的较为理想的实验动物模型。与此同时,目前存在的骨缺损动物模型不应该作为终点,为了进一步研究骨缺损,今后需要纳入更高质量的文献,逐步形成模型制备标准,更好地为临床服务。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
临界性骨缺损:骨发生缺损后,不经任何处理在自然状态下不能自行愈合的最小骨缺损的尺寸。动物模型:是基于实验动物建立的模拟人类疾病或满足研究的动物,是实验治疗方式走向临床的一个重要过程。
最早的骨缺损动物模型可以追溯到1973年,FREEMAN和TURNBULL构建大鼠颅骨骨缺损模型,用于骨填充修复材料的评估。但颅骨骨缺损模型无法评估大段骨缺损及髓腔是否再通的修复效果。因此长骨骨缺损模型逐渐出现,1993年HILTUNEN等首次报道了小鼠胫骨骨缺损模型,但胫骨呈三角形且靠近腓骨,在一定程度会影响骨修复过程。股骨作为管状骨,内外径相对一致,与胫骨和颅骨相比可以提供如骨质疏松、感染性以及其他更复杂的骨缺损模型,且股骨作为负重骨,可以更加客观评价骨修复过程中生理状态下力学载荷的评估。构建合适、可重复性及无限接近临床的动物实验模型对临床应用前的评估至关重要。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||