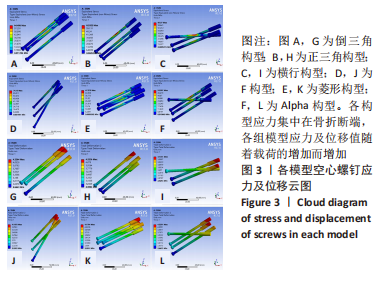
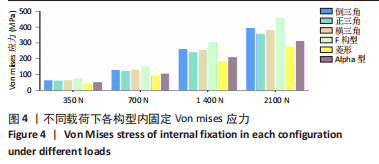
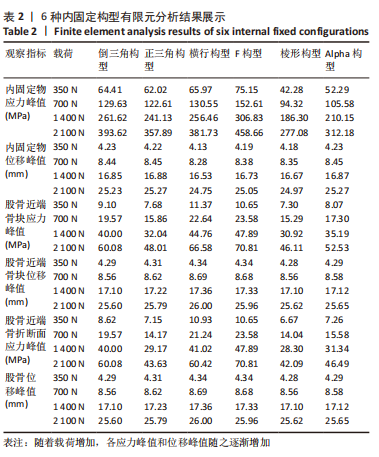
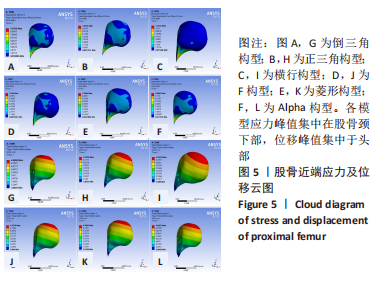
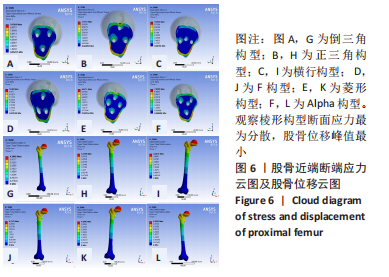
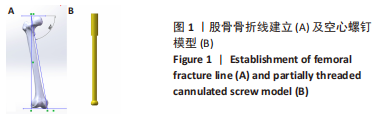
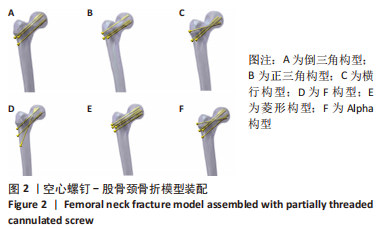
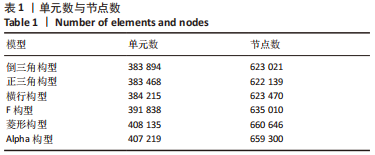
[1] FREITAS A, TORRES GM, SOUZA AC, et al. Analysis on the mechanical resistance of fixation of femoral neck fractures in synthetic bone, using the dynamic hip system and an anti-rotation screw. Rev Bras Ortop. 2014;49(6):586-592.
[2] CHANG SM, HOU ZY, HU SJ, et al. Intertrochanteric Femur Fracture Treatment in Asia: What We Know and What the World Can Learn.Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(2):189-205.
[3] KENMEGNE GR, ZOU C, FANG Y, et al. Femoral neck fractures in non-geriatric patients: femoral neck system versus cannulated cancellous screw. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023;24(1):70.
[4] XU JL, LIANG ZR, XIONG BL, et al. Risk factors associated with osteonecrosis of femoral head after internal fixation of femoral neck fracture:a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):632.
[5] ROBINSON CM, COURT-BROWN CM, MCQUEEN MM, et al. Hip fractures in adults younger than 50 years of age. Epidemiology and results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;(312):238-246.
[6] JACOB G, PAI S, HUGGI V, et al. Lag screw with DHS (LSD) for vertical angle femoral neck fractures in young adults. Injury. 2020;51(11): 2628-2633.
[7] LOWE JA, CRIST BD, BHANDARI M, et al. Optimal treatment of femoral neck fractures according to patient’s physiologic age: an evidence-based review. Orthop Clin North Am. 2010;41(2):157-166.
[8] SENDTNER E, RENKAWITZ T, KRAMNY P, et al. Fractured neck of femur--internal fixation versus arthroplasty. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2010;107(23): 401-407.
[9] LY TV, SWIONTKOWSKI MF. Treatment of femoral neck fractures in young adults. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(10):2254-2266.
[10] ZHANG YZ, LIN Y, LI C, et al. A Comparative Analysis of Femoral Neck System and Three Cannulated Screws Fixation in the Treatment of Femoral Neck Fractures: A Six-Month Follow-Up. Orthop Surg. 2022; 14(4):686-693.
[11] SLOBOGEAN GP, STOCKTON DJ, ZENG B, et al. Femoral Neck Fractures in Adults Treated With Internal Fixation: A Prospective Multicenter Chinese Cohort. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25(4):297-303.
[12] 张健,汤欣.青壮年Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的内固定治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(6):502-506.
[13] AUGAT P, BLIVEN E, HACKL S. Biomechanics of Femoral Neck Fractures and Implications for Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1: S27-S32.
[14] LUTTRELL K, BELTRAN M, COLLINGE CA. Preoperative decision making in the treatment of high-angle “vertical” femoral neck fractures in young adult patients. An expert opinion survey of the Orthopaedic Trauma Association’s (OTA) membership. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(9): e221-e225.
[15] ASNIS SE, WANEK-SGAGLIONE L. Intracapsular fractures of the femoral neck. Results of cannulated screw fixation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994; 76(12):1793-1803.
[16] 王伯珉,杨永良,贾宏磊,等.股骨颈骨折的手术治疗进展[J].创伤外科杂志,2022,24(7):539-543+549.
[17] LI L, ZHAO X, YANG X, et al. Dynamic hip screws versus cannulated screws for femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):352.
[18] VAN EMBDEN D, ROUKEMA GR, RHEMREV SJ, et al. The Pauwels classification for intracapsular hip fractures: is it reliable? Injury. 2011; 42(11):1238-1240.
[19] FAN Z, HUANG Y, SU H, et al. How to choose the suitable FNS specification in young patients with femoral neck fracture: A finite element analysis. Injury. 2021;52(8):2116-2125.
[20] SOMMERS MB, FITZPATRICK DC, MADEY SM, et al. A surrogate long-bone model with osteoporotic material properties for biomechanical testing of fracture implants. J Biomech. 2007;40(15):3297-3304.
[21] EBERLE S, GERBER C, VON OLDENBURG G, et al. A biomechanical evaluation of orthopaedic implants for hip fractures by finite element analysis and in-vitro tests. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2010;224(10):1141-1152.
[22] GREENWALD AS, HAYNES DW. Weight-bearing areas in the human hip joint. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1972;54(1):157-163.
[23] VAN HOUCKE J, SCHOUTEN A, STEENACKERS G, et al. Computer-based estimation of the hip joint reaction force and hip flexion angle in three different sitting configurations. Appl Ergon. 2017;63:99-105.
[24] GOFFIN JM, PANKAJ P, SIMPSON AH. The importance of lag screw position for the stabilization of trochanteric fractures with a sliding hip screw: a subject-specific finite element study. J Orthop Res. 2013; 31(4):596-600.
[25] ZHANG RY, LI JT, ZHAO JX, et al. Comparison of oblique triangular configuration and inverted equilateral triangular configuration of three cannulated screws in treating unstable femoral neck fracture: A finite element analysis. Injury. 2022;53(2):353-361.
[26] LI M, COLE PA.Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures: how anatomy influences the treatment issues? Injury. 2015; 46(3):453-458.
[27] 张雅文,侯国进,周方,等.Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折闭合复位内固定术后缺血性股骨头坏死的多因素分析[J].中国微创外科杂志, 2020,20(12):1057-1062.
[28] 严坤,牟利民,杨晓辉,等.三种空心钉构型固定Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(18):2807-2811.
[29] 陈宇峰,任栋,耿林丹,等.菱形构型空心钉固定PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折生物力学特性的有限元分析[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020, 22(12):1080-1085.
[30] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimum Configuration of Cannulated Compression Screws for the Fixation of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures: Finite Element Analysis Evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:1271762.
[31] 孙彦豹,金宝城,王静,等.四枚空心钉菱形四壁支撑内固定股骨颈骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(20):1857-1861.
[32] 吴贵佑,于前进,朱红伟,等.三枚与四枚空心螺钉平行固定治疗Pauwels Ⅲ型股骨颈骨折的比较研究[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2021, 10(6):431-436.
[33] LINDEQUIST S, TÖRNKVIST H. Quality of reduction and cortical screw support in femoral neck fractures. An analysis of 72 fractures with a new computerized measuring method. J Orthop Trauma. 1995;9(3): 215-221.
[34] GUIMARÃES JAM, ROCHA LR, NORONHA ROCHA TH, et al. Vertical femoral neck fractures in young adults: a closed fixation strategy using a transverse cancellous lag screw. Injury. 2017;48 Suppl 4:S10-S16. |