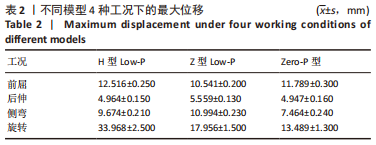
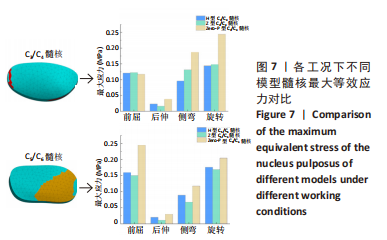
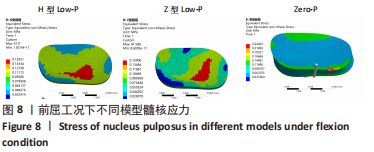
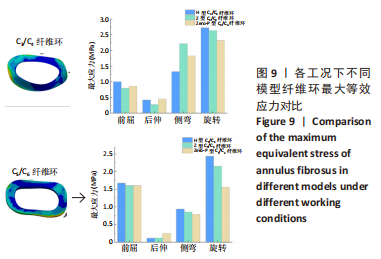
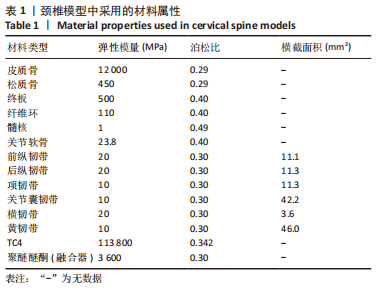
[1] 贾连顺,陈雄生.颈椎病前路融合与非融合手术治疗的历史观[J].脊柱外科杂志,2022,20(3):145-148.
[2] 王立公,常双超.广州市中青年不同人群颈椎病发病率的调查研究[J].中国疗养医学,2010,19(5):473-474.
[3] PATHAK AK, AWASTHI HH, PANDEY AK. Use of Dashamoola in Cervical Spondylosis: Past and Present Perspective. JoAYUSH. 2015;4(1):10-16.
[4] KAISER MG, HAID RW JR, SUBACH BR, et al. Anterior cervical plating enhances arthrodesis after discectomy and fusion with cortical allograft. Neurosurgery. 2002;50(2):229-236.
[5] SONG KJ, TAGHAVI CE, LEE KB, et al. The efficacy of plate construct augmentation versus cage alone in anterior cervical fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(26):2886-2892.
[6] KANDZIORA F, SCHNAKE KJ, HOFFMANN R, et al. A new zeroprofile implant for stand-alone anterior cervical interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):666-673.
[7] FOUNTAS KN, KAPSALAKI EZ, NIKOLAKAKOS LG, et al. Anterior cervical discect to my and fusion associated complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(21):2310-2317.
[8] LEE YS, KIM YB, PARK SW. Does a zero-profile anchored cage offer additional stabilization as anterior cervical plate. Spine. 2015;40(10) : E563-E570.
[9] LEE YS, KIM YB, PARK SW. Risk factors for postoperative subsidence of single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: The significance of the preoperative cervical alignment. Spine. 2014;39(16):1280-1287.
[10] 原芳,薛清华,刘伟强.有限元法在脊柱生物力学应用中的新进展[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):585-590.
[11] 黄嘉华,林峰,姚天平.应用有限元检测植入器械的可行性分析[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(1):1-6.
[12] 原芳,薛清华,刘伟强.有限元法在脊柱生物力学应用中的新进展[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(5):585-590.
[13] 李宝强,于泽,徐志浩,等.颈椎前路单节段减压融合与减压融合联合钢板内固定对相邻节段生物力学效应的有限元分析[J].中国医学工程,2022,30(10):5-17.
[14] LEE MJ, BAZAZ R, FUREY CG, et al. Influence of anterior cervical plate design on Dysphagia: a 2-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Spinal Disorders Tech. 2005;18(5):406-409.
[15] 李龙文. 基于有限元法人体颈椎生物力学分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨理工大学,2015.
[16] 赵齐通. Cage-Plate 颈椎内固定器与两种零切迹固定器的生物力学研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学,2018.
[17] GOEL VK, CLAUSEN JD. Prediction of load sharing among spinal components of a C5-C6 motion segment using the finite element approach. Spine. 1998;23(6):684-691.
[18] KUMARESAN S, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR FA. Finite element modeling of spinal ligaments. Am Soc Mech Eng. 1999;42:281-282.
[19] WHEELDON JA, PINTAR FA, KNOWLES S, et al. Experimental flexion/extension data corridors for validation of finite element models of the young, normal cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006;39(2):375-380.
[20] KUMARESAN S, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR FA. Nonlinear finite element analysis of human cervical spine facet joint. Am Soc Mech Eng. 1997; 35:447-448.
[21] 姜广崇,李学峰,聂林,等.利用 Mimics 和 Abaqus 建立正 常人颈椎的三维有限元模型[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(11):1114-1120.
[22] TEO E, NG H. Evaluation of the role of ligaments, facets and disc nucleus in lower cervical spine under compression and sagittal moments using finite element method. Med Eng Phys. 2001;23(3):155-164.
[23] KUMARESAN S, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR F. Finite element modeling approaches of human cervical spine facet joint capsule. J Biomech. 1998;31(4):371-376.
[24] YOGANANDAN N, KUMARESAN S, PINTARF A. Biomechanics of the cervical spine. Part 2. Cervical spine soft tissue responses and biomechanical modeling. Clin Biomech. 2001;16(1):1-27.
[25] PANJABI MM. Cervical spine models for biomechanical research. Spine. 1998;23(24):2684-2700.
[26] RONG X, WANG B, DING C, et al. The biomechanical impact of the facet tropism on the intervertebral disc and facet joints in the cervical spine. Spine J. 2017;17(12):1926-1931.
[27] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load-displacement curves. Spine. 2001;26(24):2692-2700.
[28] ZHANG QH, TEO EC, NG HW, et al. Finite element analysis of momentrotation relationships for human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006;39(1):189-193.
[29] 罗俊普,何永志,林斌,等.颈前路减压cage与zero-p椎间植骨融合内固定治疗单节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2021,36(9):897-900.
[30] 李鹏飞,危国军,石作为,等.颈前路应用Zero-P椎间融合系统与钛板联合cage融合系统治疗颈椎病的Meta分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2019,29(3):235-246.
[31] 许艺荠,张雪松,孙太存,等.新型Zero-P与cage钛板椎间融合器修复颈椎病:早期稳定性对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(22): 3227-3234.
|