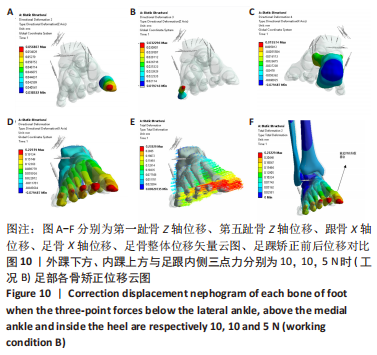
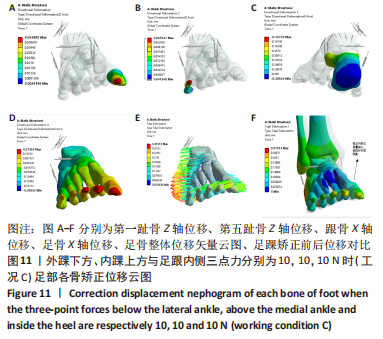
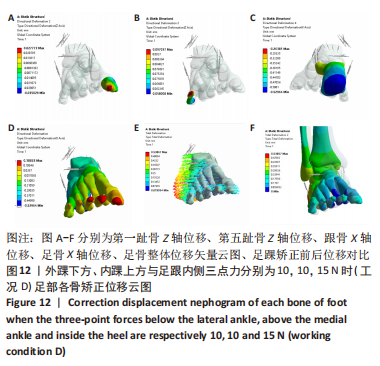
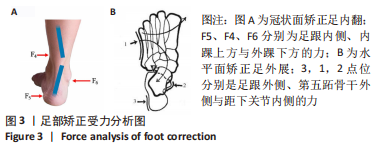
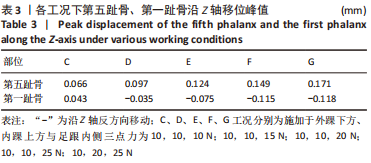
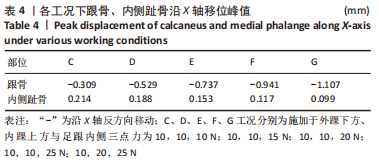
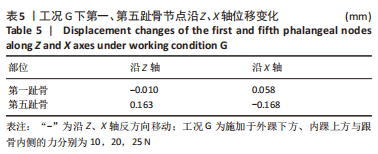
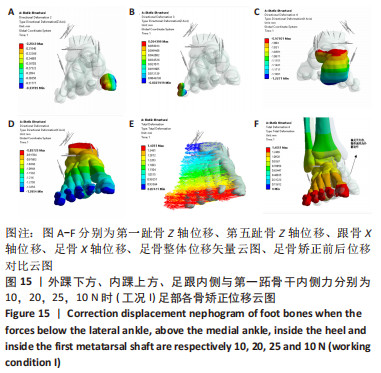
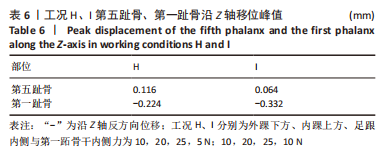
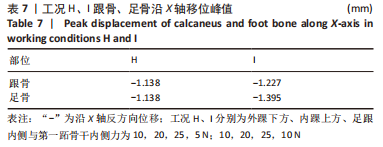
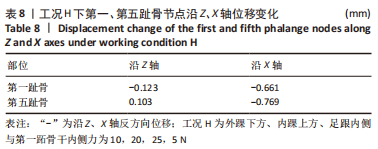
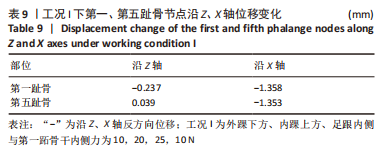
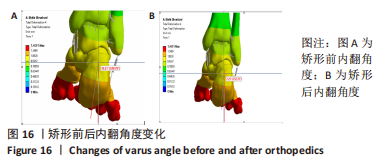
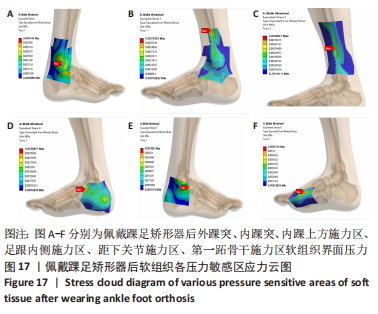
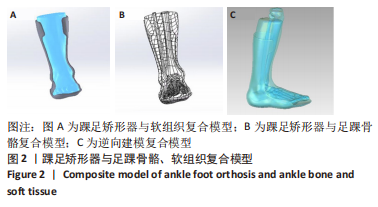
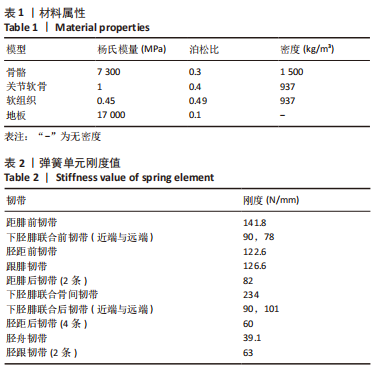
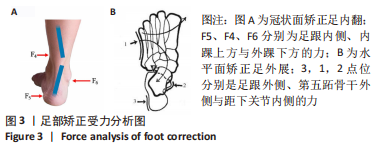
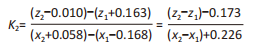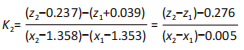[1] KIRIAKI T, CHRISTOS I, PETROS O, et al. Forefoot Varus (FV) in Children. International Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences. 2016;3(4):102-104.
[2] GÖK H, KÜÇÜKDEVECI A, ALTINKAYNAK H, et al. Effects of ankle-foot orthoses on hemiparetic gait. Clin Rehabil. 2003;17(2):137-139.
[3] ZHANG Y, LIU HW, FU CH, et al. The biomechanical effect of acupuncture for poststroke cavovarus foot: study protocol for a randomized controlled pilot trial. Trials. 2016;17(1):146.
[4] WARD AB. A literature review of the pathophysiology and onset of post-stroke spasticity. Eur J Neurol. 2012;19(1):21-27.
[5] 胡金鲁,陈彦.中西医康复治疗中风后足内翻研究进展[J].中医药临床杂志, 2020,32(2):383-386.
[6] MENG X, REN M, ZHUANG Y, et al. Application Experience and Patient Feedback Analysis of 3D Printed AFO with Different Materials: A Random Crossover Study. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8493505.
[7] KHAN SF, RADZMI I. Design and Analysis of Various Thermoplastic for Optimized Ankle Foot Orthosis. J Phys Conf Ser. 2021;2051(1): 012034.
[8] 刘震,张盘德,容小川,等.脑卒中踝足矫形器的3D打印研究[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(8):874-878.
[9] KEMAL SH, ZIYA AY. Evaluation of various design concepts in passive ankle-foot orthoses using finite element analysis. Eng Sci Technol. 2021;24(6):1301-1307.
[10] 王岩,张明.足踝矫形器及其生物力学研究进展[J].科技导报,2019,37(22): 60-68.
[11] 路鹏程.3D打印踝足紧密接触型外固定支具的数字化设计、计算机仿真分析及临床应用[D].广州:南方医科大学,2021.
[12] LIU X, YUE Y, WU X, et al. Analysis of transient response of the human foot based on the finite element method.Technol Health Care. 2022;30(1):79-92.
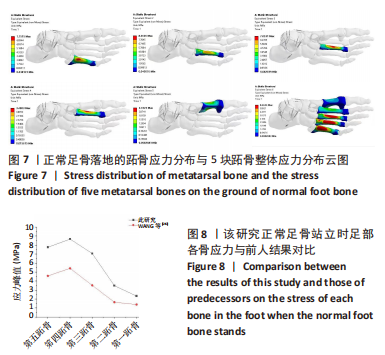
[13] GU YD, REN XJ, LI JS, et al. Computer simulation of stress distribution in the metatarsals at different inversion landing angles using the finite element method. Int Orthop. 2010;34(5):669-676.
[14] 彭志鑫,闫文刚,王坤,等.3D打印前臂外固定支具的有限元分析与结构优化设计[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(9):1340-1345.
[15] CHO JR, LEE DY, AHN YJ. Finite element investigation of the biomechanical responses of human foot to the heel height and a rigid hemisphere cleat. J Mech Sci Technol. 2016;30(9):4269-4274.
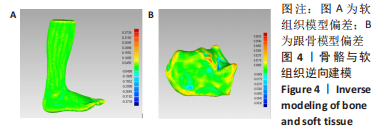
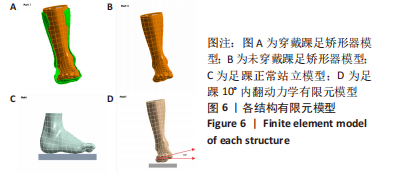
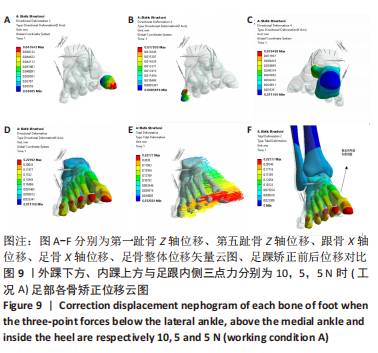
[16] 何晓宇,王朝强,周之平,等.三维有限元方法构建足部健康骨骼与常见疾病模型及生物力学分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1410-1415.
[17] DARWICH A, NAZHA H, NAZHA A, et al. Bio-Numerical Analysis of the Human Ankle-Foot Model Corresponding to Neutral Standing Condition. J Biomed Phys Eng. 2020;10(5):645-650.
[18] WANG D, CAI P. Finite Element Analysis of the Expression of Plantar Pressure Distribution in the Injury of the Lateral Ligament of the Ankle. Nano Biomed Eng. 2019;11(3):290-296.
[19] 弓太生,康路平,李姝,等.足部有限元模型静态分析及验证[J].中国皮革, 2022,51(4):61-66.
[20] 刘清华.数字化人体足踝部三维有限元模型的建立及分析[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.
[21] KATHIRGAMANATHAN B, SILVA P, FERNANDEZ J. Implication of obesity on motion, posture and internal stress of the foot: an experimental and finite element analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2019;22(1):47-54.
[22] CHEUNG JT, ZHANG M, AN KN. Effect of Achilles tendon loading on plantar fascia tension in the standing foot. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2006;21(2):194-203.
[23] 胡航帆.基于有限元分析的3D打印踝关节矫形器的设计与制作[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2019.
[24] 赵辉三.假肢与矫形器学[M].北京:华夏出版社,2005.
[25] 喻洪流.假肢矫形器原理与应用[M].南京:东南大学出版社,2011.
[26] WANG CQ, HE XY, ZHANG ZN, et al. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis and Biomechanical Analysis of Midfoot von Mises Stress Levels in Flatfoot, Clubfoot, and Lisfranc Joint Injury. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e931969.
[27] 樊瑜波,张明.康复工程与生物力学[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社,2017.
[28] 吴云成,许苑晶,鲁德志,等.增材制造脊柱侧弯矫形器治疗效果的有限元分析[J].医用生物力学,2022,37(3):492-497.
[29] 王晓辉,王坤,胡志勇,等.假肢接受腔设计及界面应力的有限元分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(6):862-868.
[30] BANGA HK, KALRA P, BELOKAR RM, et al. Customized design and additive manufacturing of kids’ ankle foot orthosis. Rapid Prototyping J. 2020;26(10): 1677-1685.
[31] FU JC, CHEN YJ, LI CF, et al. The effect of three dimensional printing hinged ankle foot orthosis for equinovarus control in stroke patients. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2022;94:105622.
[32] SANAD DA. Moderate effect of ankle foot orthosis versus ground reaction ankle foot orthosis on balance in children with diplegic cerebral palsy. Prosthet Orthot Int. 2022;46(1):2-6.
[33] FAHAD MOHANAD KADHIM, MUHAMMAD SAFA AL-DIN TAHIR. Design and Analysis of Three-Point Pressure for Varus Foot Deformity. J Biomim Biomater BI. 2020;4739: 1-11.
[34] SHINICHI E, JUNG HC, TSUTAO K. Design/Manufacturing System for Composite Ankle Foot Orthosis. Key Eng Mater. 2014;627:261-264.
[35] TELFER S, PALLARI J, MUNGUIA J, et al. Embracing additive manufacture: implications for foot and ankle orthosis design. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:84.
[36] MASO AD, COSMI F. 3D-printed ankle-foot orthosis: a design method. Mater Today: Proc. 2019;12:252-261.
[37] PANDEY R, SINGH R. Experimental Analysis of Various Materials on Custom-Fit Ankle Foot Orthosis. J Phys Conf Ser. 2021;1950(1):1-7.
[38] 王坤,张振江,赵卫国.3D打印外固定支具参数化反求建模方法[J].机械设计,2021,38(5):121-126. |