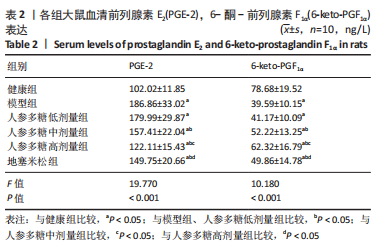
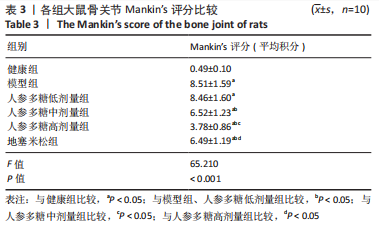
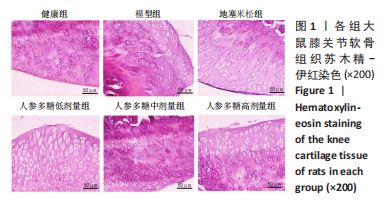
[1] O’BRIEN MS, MCDOUGALL JJ. Neurophysiological assessment of joint nociceptors in the rat medial meniscus transection model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(9):1255-1264.
[2] MENDEZ ME, SEBASTIAN A, MURUGESH DK, et al. LPS-Induced Inflammation Prior to Injury Exacerbates the Development of Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis in Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;1(11):35.
[3] SAITO M, NISHITANI K, KEDA HO, et al. A VCP modulator, KUS121,as a promising therapeutic agent for post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):20787.
[4] HART ML. An Evidence-Based Systematic Review of Human Knee Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis (PTOA): Timeline of Clinical Presentation and Disease Markers, Comparison of Knee Joint PTOA Models and Early Disease Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1996.
[5] KHALIL HE, IBRAHIM H, AHMED EA, et al. Orientin, a Bio-Flavonoid from Trigonella hamosa L.Regulates COX-2/PGE-2 in A549 Cell Lines via miR-26b and miR-146a. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(2):154.
[6] LI JQ,HAO X,SUN ZG, et al. The outcomes of post-traumatic arthritis vs osteoarthritis following primary total knee arthroplasty: A protocol of matched cohort study. Medicine. 2020;99(19):e20077.
[7] 吴鹏,茆军.代谢组学在中医药治疗膝骨关节炎中应用的研究进展[J].中国医药,2021,16(9):1420-1422.
[8] 王璐,孙小虎,刘春娜,等.人参多糖通过下调炎性因子及AKT防治结肠癌的研究[J].重庆医学,2020,49(22):3693-3697.
[9] 陈连旭,傅欣,于长隆,等.内侧副韧带切断合并部分半月板切除对大鼠膝关节软骨、滑膜和细胞因子的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2006,25(6):655-657.
[10] 姚合梅,王政,崔瑾,等.苗药验方皮部熏洗对骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞凋亡与增殖的影响[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2013,37(7):893-896.
[11] BROCKMAN BS, MAUPIN JJ, THOMPSON SF, et al. Complication Rates in Total Knee Arthroplasty Performed for Osteoarthritis and Post-Traumatic Arthritis: A Comparison Study - ScienceDirect. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(2):371-374.
[12] LI EQ, ZHANG JL. Therapeutic effects of triptolide from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. on interleukin-1-beta-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;883:173341.
[13] LIU Y, ZHAO XD, Zhou C, et al. Lingering Risk: A Meta-analysis of Outcomes following Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty for Patients with Post-Traumatic Arthritis. Int J Surg. 2020;77:163-172.
[14] GOMES LMRS, CZECZKO NG, ARAÚJO RLTM, et al. Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on experimental osteoarthritis in rats. PLoS One. 2021;16(1): e0245194.
[15] 徐洋洋,孙成新,丁侃,等.活血化瘀中药多糖的抗癌活性及其机制研究[J]. 上海中医药大学学报,2022,36(4):1-11.
[16] 万浩芳,应佳妮,关旸,等.人参多糖对冠心病大鼠心肌细胞线粒体的保护作用[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(11):24-28+60.
[17] HUANG S, CHEN F, CHEN H. Modification and application of polysaccharide from traditional Chinese medicine such as Dendrobium officinale. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;157:385-393.
[18] 沈哲司,王宏,郭广洋,等.消化性溃疡并发上消化道出血的危险因素及其与血清PGE-2、6-Keto-PGF-(1α)的关系[J].山东医药,2020,60(35):71-74.
[19] 吴弢,高翔,王拥军,等.益气化瘀利水方对骨关节炎兔前列腺素代谢的影响[J].老年医学与保健,2004,1(1):24-26.
[20] 高志.药用植物人参活性成分人参皂苷Rb1对大鼠骨关节炎症和蛋白多糖降解的作用[J].分子植物育种,2022,20(14):4800-4806.
[21] 刘鹏,赵茂盛,曹国定,等.创伤性关节炎手术治疗现状[J].解放军医学杂志,2020,45(5):559-567.
[22] KEENAN CM, RAMOS-MUCCI L, KANAKIS I, et al. Post-traumatic osteoarthritis development is not modified by postnatal chondrocyte deletion of CCN2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020;22(1):57.
[23] MA X, ZHANG Z, SHEN M, et al. Changes of type II collagenase biomarkers on IL-1β-induced rat articular chondrocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(6):582.
[24] 李惠娟,张栋,张晓哲,等.针刀、圆利针干预膝骨关节炎模型大鼠对β-内啡肽及前列腺素E-2水平的影响[J].中国医药导报,2020,17(9):153-155+184.
[25] XU C,NI S, ZHUANG C, et al. Polysaccharide from Angelica sinensis attenuates SNP-induced apoptosis in osteoarthritis chondrocytes by inducing autophagy via the ERK1/2pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):47.
[26] 谭艳,宁丽常,蹇孝丽,等.胶原诱导性关节炎大鼠血清TNF-α、IL-6、IFN-γ及IL-10水平变化[J].贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(1):18-22.
[27] AMERICA MC, RAYMUNDO C,MAGLALENA MS,et al.Latexin expression correlated with mineralization of articular cartilage during progression of post-traumatic osteoarthritis in a rat model. Histol Histopathol. 2020;35(3):269-278.
[28] 董勇勇,段广斌,茹嘉,等.膝关节骨性关节炎患者血清IL-1β、TNF-α表达及其与术后疼痛指标的关系[J].中国实用医刊,2022,49(18):54-57.
[29] CHERY DR, HAN B, LIi Q, et al. Early Changes in Cartilage Pericellular Matrix Micromechanobiology Portend the Onset of Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis. Acta Biomater. 2020;111(1):267-278.
[30] ALONSO B, BRAVO B,MEDIAVILLA L,et al.Osteoarthritis-related biomarkers profile in chronic anterior cruciate ligament injured knee. Knee. 2020;27(1):51-60.
|