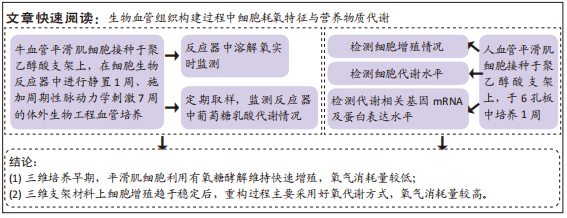
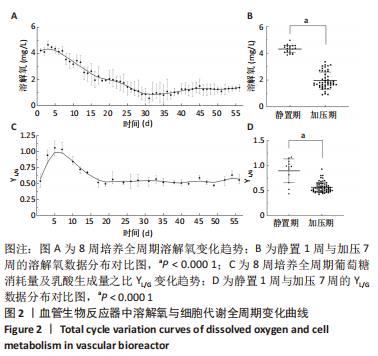
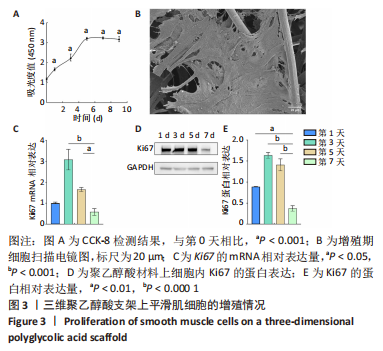
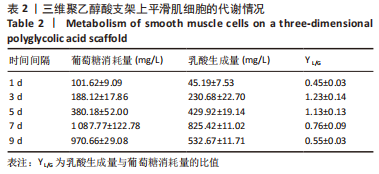
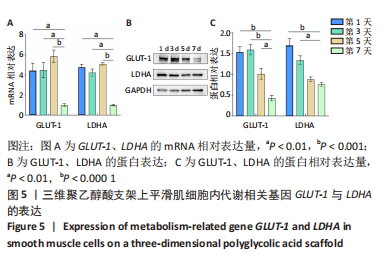
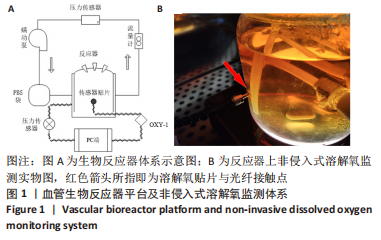
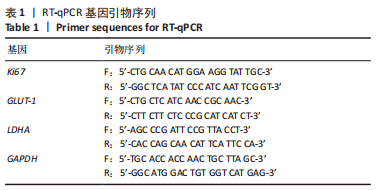
[1] NAEGELI KM, KURAL MH, LI Y, et al. Bioengineering Human Tissues and the Future of Vascular Replacement. Circ Res. 2022;131(1):109-126.
[2] GIWA S, LEWIS JK, ALVAREZ L, et al. The promise of organ and tissue preservation to transform medicine. Nat Biotechnol. 2017;35(6):530-542.
[3] NIKLASON LE, LAWSON JH. Bioengineered human blood vessels. Science. 2020;370(6513):eaaw8682.
[4] SHAH MOHAMMADI M, BUCHEN JT, PASQUINA PF, et al. Critical Considerations for Regeneration of Vascularized Composite Tissues. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021;27(4):366-381.
[5] OBIWELUOZOR FO, EMECHEBE GA, KIM DW, et al. Considerations in the Development of Small-Diameter Vascular Graft as an Alternative for Bypass and Reconstructive Surgeries: A Review. Cardiovasc Eng Technol. 2020;11(5):495-521.
[6] PAPKOVSKY DB, DMITRIEV RI. Imaging of oxygen and hypoxia in cell and tissue samples. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(16):2963-2980.
[7] CASTRO N, RIBEIRO S, FERNANDES MM, et al. Physically Active Bioreactors for Tissue Engineering Applications. Adv Biosyst. 2020; 4(10):e2000125.
[8] 刘江,冯子倍,周嘉辉,等.多孔隙三维环境下细胞接种密度对血管平滑肌细胞增殖行为的影响[J].岭南心血管病杂志,2022,28(3): 264-268.
[9] SOLAN A, MITCHELL S, MOSES M, et al. Effect of pulse rate on collagen deposition in the tissue-engineered blood vessel. Tissue Eng. 2003;9(4):579-586.
[10] SOLAN A, DAHL SL, NIKLASON LE. Effects of mechanical stretch on collagen and cross-linking in engineered blood vessels. Cell Transplant. 2009;18(8):915-921.
[11] TSCHOEKE B, FLANAGAN TC, KOCH S, et al. Tissue-engineered small-caliber vascular graft based on a novel biodegradable composite fibrin-polylactide scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8):1909-1918.
[12] MONIZ I, RAMALHO-SANTOS J, BRANCO AF. Differential Oxygen Exposure Modulates Mesenchymal Stem Cell Metabolism and Proliferation through mTOR Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7): 3749.
[13] 李祯,张磊,孙伟.组织工程血管脉动生物反应器的研制[J].新技术新工艺,2019(7):47-50.
[14] 周浩浩.双层模型结构下生物反应器组织工程血管培养的力学刺激研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2021.
[15] WEN Z, ZHOU H, ZHOU J, et al. Quantitative Evaluation of Mechanical Stimulation for Tissue-Engineered Blood Vessels. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2021;27(5):337-347.
[16] CHANCE B, ITO T. Control of endogenous adenosine triphosphatase activity by energy-linked pyridine nucleotide reduction in mitochondria. Nature. 1962;195:150-153.
[17] ZHU XH, LU M, LEE BY, et al. In vivo NAD assay reveals the intracellular NAD contents and redox state in healthy human brain and their age dependences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(9):2876-2881.
[18] ENGLER AJ, LE AV, BAEVOVA P, et al. Controlled gas exchange in whole lung bioreactors. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1):e119-e129.
[19] ZHAO F, PATHI P, GRAYSON W, et al. Effects of oxygen transport on 3-d human mesenchymal stem cell metabolic activity in perfusion and static cultures: experiments and mathematical model. Biotechnol Prog. 2005;21(4):1269-1280.
[20] CHRISTOFK HR, VANDER HEIDEN MG, HARRIS MH, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452(7184):230-233.
[21] ZHANG T, NIE M, LI Y. Current Advances and Future Perspectives of Advanced Polymer Processing for Bone and Tissue Engineering: Morphological Control and Applications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:895766.
[22] MIRONOV VA, SENATOV FS, KOUDAN EV, et al. Design, Fabrication, and Application of Mini-Scaffolds for Cell Components in Tissue Engineering. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(23):5068.
[23] SAUNDERS SK, COLE SY, ACUNA SIERRA V, et al. Evaluation of perfusion-driven cell seeding of small diameter engineered tissue vascular grafts with a custom-designed seed-and-culture bioreactor. PLoS One. 2022;17(6):e0269499.
[24] ÇELEBI-SALTIK B, ÖTEYAKA MÖ, GÖKÇINAR-YAGCI B. Stem cell-based small-diameter vascular grafts in dynamic culture. Connect Tissue Res. 2021;62(2):151-163.
[25] BARONE PW, WIEBE ME, LEUNG JC, et al. Viral contamination in biologic manufacture and implications for emerging therapies. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38(5):563-572.
[26] DIAMANTOUROS SE, HURTADO-AGUILAR LG, SCHMITZ-RODE T, et al. Pulsatile perfusion bioreactor system for durability testing and compliance estimation of tissue engineered vascular grafts. Ann Biomed Eng. 2013;41(9):1979-1989.
[27] SONG Y, WENNINK JW, KAMPHUIS MM, et al. Dynamic culturing of smooth muscle cells in tubular poly(trimethylene carbonate) scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17(3-4): 381-387.
[28] HUANG AH, BALESTRINI JL, UDELSMAN BV, et al. Biaxial Stretch Improves Elastic Fiber Maturation, Collagen Arrangement, and Mechanical Properties in Engineered Arteries. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2016;22(6):524-533.
[29] BEAMISH JA, HE P, KOTTKE-MARCHANT K, et al. Molecular regulation of contractile smooth muscle cell phenotype: implications for vascular tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(5):467-491.
[30] FERNIE AR, ZHANG Y, SAMPATHKUMAR A. Cytoskeleton Architecture Regulates Glycolysis Coupling Cellular Metabolism to Mechanical Cues. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020;45(8):637-638.
[31] CALDERIN EP, ZHENG JJ, BOYD NL, et al. Exercise-induced specialized proresolving mediators stimulate AMPK phosphorylation to promote mitochondrial respiration in macrophages. Mol Metab. 2022;66: 101637.
[32] PALSSON-MCDERMOTT EM, CURTIS AM, GOEL G, et al. Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates Hif-1α activity and IL-1β induction and is a critical determinant of the warburg effect in LPS-activated macrophages. Cell Metab. 2015;21(1):65-80.
[33] LUNT SY, VANDER HEIDEN MG. Aerobic glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2011;27:441-464.
[34] CACCIATORE M, GRASSO EA, TRIPODI R, et al. Impact of glucose metabolism on the developing brain. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:1047545.
[35] RYBKOWSKA P, RADOSZKIEWICZ K, KAWALEC M, et al. The Metabolic Changes between Monolayer (2D) and Three-Dimensional (3D) Culture Conditions in Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells Derived from Adipose Tissue. Cells. 2023;12(1):178.
[36] BALGUID A, MOL A, VAN VLIMMEREN MA, et al. Hypoxia induces near-native mechanical properties in engineered heart valve tissue. Circulation. 2009;119(2):290-297.
[37] FATHOLLAHIPOUR S, PATIL PS, LEIPZIG ND. Oxygen Regulation in Development: Lessons from Embryogenesis towards Tissue Engineering. Cells Tissues Organs. 2018;205(5-6):350-371.
[38] ZHAO X, TAN F, CAO X, et al. PKM2-dependent glycolysis promotes the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells during atherosclerosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020;52(1):9-17.
[39] JAIN M, DHANESHA N, DODDAPATTAR P, et al. Smooth Muscle Cell-Specific PKM2 (Pyruvate Kinase Muscle 2) Promotes Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching and Neointimal Hyperplasia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021;41(5):1724-1737.
|