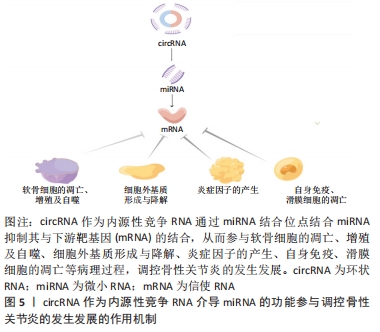
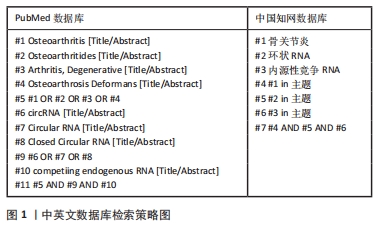
[1] Barbour KE, Helmick CG, Boring M, et al. Vital signs: prevalence of doctor-diagnosed arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation - United States, 2013-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2017;66(9):246-253.
[2] Pereira D, Ramos E, Branco J. Osteoarthritis. Acta Med Port. 2015; 28(1):99-106.
[3] Phillips RE. Review of hip and knee osteoarthritis. JAMA. 2021; 325(24):2504-2505.
[4] Loeser RF, Goldring SR, Scanzello CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[5] Vinatier C, Merceron C, Guicheux J. Osteoarthritis: from pathogenic mechanisms and recent clinical developments to novel prospective therapeutic options. Drug Discov Today. 2016;21(12):1932-1937.
[6] Glyn-Jones S, Palmer AJ, Agricola R et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386(9991):376-387.
[7] Pigeolet M, Jayaram A, Park KB, et al. Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond. Lancet. 2021;397(10279):1059-1060.
[8] Hunter DJ, Bierma-Zeinstra S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2019;393 (10182):1745-1759.
[9] Zhou X, Jiang L, Fan G, et al. Role of the ciRS-7/miR-7 axis in the regulation of proliferation, apoptosis and inflammation of chondrocytes induced by IL-1β. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;71:233-240.
[10] Carr AJ, Robertsson O, Graves S, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2012;379(9823):1331-1340..
[11] Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013;495(7441): 333-338.
[12] Jeck WR, Sharpless NE. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):453-461.
[13] Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495(7441):384-388.
[14] Chen CY, Sarnow P. Initiation of protein synthesis by the eukaryotic translational apparatus on circular RNAs. Science. 1995;268(5209):415-417.
[15] Granados-Riveron JT, Aquino-Jarquin G. The complexity of the translation ability of circRNAs. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016; 1859(10):1245-1251.
[16] Liu C, Ge HM, Liu BH, et al. Targeting pericyte-endothelial cell crosstalk by circular RNA-cPWWP2A inhibition aggravates diabetes-induced microvascular dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019; 116(15):7455-7464.
[17] Aufiero S, Reckman YJ, Pinto YM, et al. Circular RNAs open a new chapter in cardiovascular biology. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019;16(8):503-514.
[18] Chen L, Nan A, Zhang N et al. Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):13.
[19] Liu Q, Zhang X, Hu X, et al. Circular RNA Related to the Chondrocyte ECM Regulates MMP13 Expression by Functioning as a MiR-136 ‘Sponge’ in Human Cartilage Degradation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22572.
[20] Zhou ZB, Du D, Huang GX, et al. Circular RNA Atp9b, a competing endogenous RNA, regulates the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting miR-138-5p. Gene. 2018;646:203-209.
[21] Jeck WR, Sorrentino JA, Wang K, et al. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA. 2013;19(2):141-157.
[22] Salzman J, Gawad C, Wang PL, et al. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e30733.
[23] Guo JU, Agarwal V, Guo H, et al. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014; 15(7):409.
[24] Shen T, Han M, Wei G, et al. An intriguing RNA species-perspectives of circularized RNA. Protein Cell. 2015;6(12):871-880.
[25] Li X, Yang L, Chen LL. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71(3):428-442.
[26] Wilusz JE. A 360° view of circular RNAs: from biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2018;9(4):e1478.
[27] Qu S, Yang X, Li X, et al. Circular RNA: a new star of noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015;365(2):141-148.
[28] Ehrlich GD. Circular RNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2019;23(10):701-702.
[29] Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264.
[30] Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136(2):215-233.
[31] Li BF, Zhang Y, Xiao J, et al. Hsa_circ_0045714 regulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis and extracellular matrix synthesis by promoting the expression of miR-193b target gene IGF1R. Hum Cell. 2017;30(4):311-318.
[32] Zhang Y, Zhang XO, Chen T, et al. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2013;51(6):792-806.
[33] Li Z, Huang C, Bao C, et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015;22(3):256-264.
[34] Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(1):87-97.
[35] Du WW, Zhang C, Yang W, et al. Identifying and Characterizing circRNA-Protein Interaction. Theranostics. 2017;7(17):4183-4191.
[36] Wang Y, Wang Z. Efficient backsplicing produces translatable circular mRNAs. RNA. 2015;21(2):172-179.
[37] Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, et al. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011;146(3):353-358.
[38] Guo LL, Song CH, Wang P, et al. Competing endogenous RNA networks and gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21(41):11680-11687.
[39] Gong Z, Yang Q, Zeng Z, et al. An integrative transcriptomic analysis reveals p53 regulated miRNA, mRNA, and lncRNA networks in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3683-3695.
[40] Yu J, Liu Y, Gong Z, et al. Overexpression long non-coding RNA LINC00673 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes invasion and metastasis in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(10):16621-16632.
[41] Cheng DL, Xiang YY, Ji LJ, et al. Competing endogenous RNA interplay in cancer: mechanism, methodology, and perspectives. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(2):479-488.
[42] Mukherji S, Ebert MS, Zheng GX, et al. MicroRNAs can generate thresholds in target gene expression. Nat Genet. 2011;43(9):854-859.
[43] Maas S. Posttranscriptional recoding by RNA editing. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 2012;86:193-224.
[44] Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505(7483):344-352.
[45] Ala U, Karreth FA, Bosia C, et al. Integrated transcriptional and competitive endogenous RNA networks are cross-regulated in permissive molecular environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110(18):7154-7159.
[46] Wang S, Su TT, Tong H, et al. CircPVT1 promotes gallbladder cancer growth by sponging miR-339-3p and regulates MCL-1 expression. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1):191.
[47] Zhang S, Song G, Yuan J, et al. Circular RNA circ_0003204 inhibits proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cell in atherosclerosis via miR-370-3p/TGFβR2/phosph-SMAD3 axis. J Biomed Sci. 2020;27(1):11.
[48] Han B, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, et al. Novel insight into circular RNA HECTD1 in astrocyte activation via autophagy by targeting MIR142-TIPARP: implications for cerebral ischemic stroke. Autophagy. 2018; 14(7):1164-1184.
[49] Zhou Z, Ma J, Lu J, et al. Circular RNA CircCDH13 contributes to the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis via CircCDH13/miR-296-3p/PTEN axis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(5):3521-3535.
[50] Wang Q, Luo S, Yang J, et al. Circ_0114876 promoted IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury by targeting miR-671/TRAF2 axis. Biotechnol Lett. 2021;43(4):791-802.
[51] Liu Y, Zhang Y. Hsa_circ_0134111 promotes osteoarthritis progression by regulating miR-224-5p/CCL1 interaction. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(16):20383-20394.
[52] Ouyang X, Ding Y, Yu L, et al. Circ_SPG11 plays contributing effects on IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and ECM degradation via miR-665 inhibition-mediated GREM1 upregulation. Clin Immunol. 2021;233:108889.
[53] Fu Q, Li L, Wang B, et al. CircADAMTS6/miR-431-5p axis regulate interleukin-1β induced chondrocyte apoptosis. J Gene Med. 2021; 23(2):e3304.
[54] Zhang J, Cheng F, Rong G, et al. Hsa_circ_0005567 Activates Autophagy and Suppresses IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Apoptosis by Regulating miR-495. Front Mol Biosci. 2020;7:216.
[55] Mouw JK, Ou G, Weaver VM. Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(12):771-785.
[56] Feng M, Jing L, Cheng J, et al. Circ_0020093 ameliorates IL-1β-induced apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation of human chondrocytes by upregulating SPRY1 via targeting miR-23b. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(10):3623-3633.
[57] Wu Y, Hong Z, Xu W, et al. Circular RNA circPDE4D Protects against Osteoarthritis by Binding to miR-103a-3p and Regulating FGF18. Mol Ther. 2021;29(1):308-323.
[58] Wang T, Hao Z, Liu C, et al. LEF1 mediates osteoarthritis progression through circRNF121/miR-665/MYD88 axis via NF-кB signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(8):689.
[59] Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ŁA, Szukiewicz D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:561459.
[60] Chen G, Liu T, Yu B, et al. CircRNA-UBE2G1 regulates LPS-induced osteoarthritis through miR-373/HIF-1a axis. Cell Cycle. 2020;19(13): 1696-1705.
[61] Zhang M, Mou L, Liu S, et al. Circ_0001103 alleviates IL-1β-induced chondrocyte cell injuries by upregulating SIRT1 via targeting miR-375. Clin Immunol. 2021;227:108718.
[62] Liu W, Yang H, Feng X, et al. Circular RNA circCTNNA1 is downregulated in osteoarthritis and sponges miR-29a to suppress LPS-induced apoptosis of synoviocytes. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(1):1-6.
[63] Zhang J, Cheng F, Rong G, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8920-8930.
[64] Zhang W, Qi L, Chen R, et al. Circular RNAs in osteoarthritis: indispensable regulators and novel strategies in clinical implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):23.
|