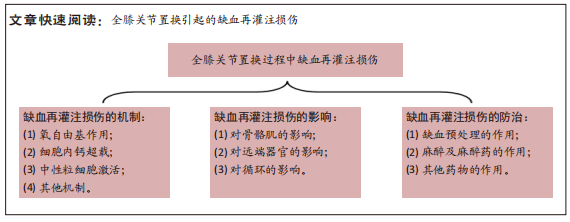
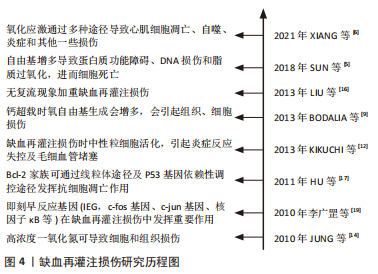
[1] BAKKER SMK, KOSSE NM, CMIC S, et al. Influence of a Tourniquet on Opioid Consumption After Local Infiltration Analgesia for Total Knee Arthroplasty. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019;47(2):107-111.
[2] PARADIS S, CHARLES AL, MEYER A, et al. Chronology of mitochondrial and cellular events during skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(11):C968-C982.
[3] KUMAR K, RAILTON C, TAWFIC Q. Tourniquet application during anesthesia: “What we need to know?”. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2016;32(4):424-430.
[4] JAGANJAC M, CIPAK A, SCHAUR RJ, et al. Pathophysiology of neutrophil-mediated extracellular redox reactions. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2016;21(4):839-855.
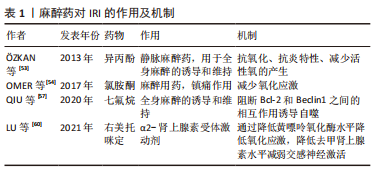
[5] SUN MS, JIN H, SUN X, et al. Free Radical Damage in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: An Obstacle in Acute Ischemic Stroke after Revascularization Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3804979.
[6] XIAMG M, LU Y, XIN L, et al. Role of Oxidative Stress in Reperfusion following Myocardial Ischemia and Its Treatments. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021: 6614009.
[7] GRANGER DN, KVIETYS PR. Reperfusion injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept. Redox Biol. 2015;6:524-551.
[8] BOMPOTIS GC, DEFTEREOS S, ANGELIDIS C, et al. Altered Calcium Handling in Reperfusion Injury. Med Chem. 2016;12(2):114-130.
[9] BODALIA A, LI H, JACKSON MF. Loss of endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ homeostasis: contribution to neuronal cell death during cerebral ischemia. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(1):49-59.
[10] NICOUD IB, KNOX CD, JONES CM, et al. 2-APB protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by reducing cellular and mitochondrial calcium uptake. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007;293(3): G623-G630.
[11] KAMINSKI KA, BONDA TA, KORECKI J, et al. Oxidative stress and neutrophil activation--the two keystones of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Cardiol. 2002; 86(1):41-59.
[12] KIKUCHI K, MIURA N, KAWAHARA KI, et al. Edaravone (Radicut), a free radical scavenger, is a potentially useful addition to thrombolytic therapy in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Rep. 2013;1(1):7-12.
[13] OLIVEIRA THC, MARQUES PE, PROOST P, et al. Neutrophils: a cornerstone of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Lab Invest. 2018;98(1):51-62.
[14] JUNG JE, KIM GS, CHEN H, et al. Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol Neurobiol. 2010;41(2-3):172-179.
[15] KHANNA A, COWLED PA, FITRIDGE RA. Nitric oxide and skeletal muscle reperfusion injury: current controversies (research review). J Surg Res. 2005; 128(1):98-107.
[16] LIU X, TAO GZ. Effects of tirofiban on the reperfusion-related no-reflow in rats with acute myocardial infarction. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2013; 10(1):52-58.
[17] HU H, BATTEUX F, CHEREAU C,et al. Clopidogrel protects from cell apoptosis and oxidative damage in a mouse model of renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. 2011;225(2):265-275.
[18] KO JS, GWAK MS, KIM GS, et al. The protective effect of ischemic preconditioning against hepatic ischemic-reperfusion injury under isoflurane anesthesia in rats. Transplant Proc. 2013;45(5):1704-1707.
[19] 李广罡,韩文斌,陈飞.即刻早期基因c-fos,c-jun在缺血再灌注大鼠肝脏中的表达[J].中国热带医学,2010,10(9):1048-1049.
[20] GILLANI S, CAO J, SUZUKI T, et al. The effect of ischemia reperfusion injury on skeletal muscle. Injury. 2012;43(6):670-675.
[21] BARNIG C, LUTZWEILER G, GIANNINI M, et al. Resolution of Inflammation after Skeletal Muscle Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Focus on the Lipid Mediators Lipoxins, Resolvins, Protectins and Maresins. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(6):1213.
[22] RATCHFORD SM, BAILEY AN, SENESAC HA, et al. Proteins regulating cap-dependent translation are downregulated during total knee arthroplasty. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2012;302(6): R702-R711.
[23] JAWHAR A, HERMANNS S, PONELIES N, et al. Tourniquet-induced ischaemia during total knee arthroplasty results in higher proteolytic activities within vastus medialis cells: a randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10):3313-3321.
[24] DREYER HC. Tourniquet Use During Knee Replacement Surgery May Contribute to Muscle Atrophy in Older Adults. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2016;44(2):61-70.
[25] MUYSKENS JB, HOCKER AD, TURNBULL DW, et al. Transcriptional profiling and muscle cross-section analysis reveal signs of ischemia reperfusion injury following total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Physiol Rep. 2016;4(1):e12671.
[26] TSUI JC, BAKER DM, BIECKER E, et al. Altered endothelin-1 levels in acute lower limb ischemia and reperfusion. Angiology. 2004;55(5):533-539.
[27] TSUI JC, BAKER DM, SHAW SG, et al. Alterations in nitric oxide synthase isoforms in acute lower limb ischemia and reperfusion. Angiology. 2007;58(5):586-592.
[28] YANG Q, HE GW, UNDERWOOD MJ, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of endothelial ischemia/reperfusion injury: perspectives and implications for postischemic myocardial protection. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):765-777.
[29] ABU-SALEH N, OVCHARENKO E, AWAD H, et al. Involvement of the endothelin and nitric oxide systems in the pathogenesis of renal ischemic damage in an experimental diabetic model. Life Sci. 2012;91(13-14):669-675.
[30] JAWHAR A, PONELIES N, SCHILD L. Effect of limited ischemia time on the amount and function of mitochondria within human skeletal muscle cells. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2016;42(6):767-773.
[31] APPELL HJ, GLOSER S, DUARTE JA, et al. Soares JM. Skeletal muscle damage during tourniquet-induced ischaemia. The initial step towards atrophy after orthopaedic surgery? Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1993;67(4):342-347.
[32] LEE HL, CHEN CL, YEH ST, et al. Chen YR. Biphasic modulation of the mitochondrial electron transport chain in myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;302(7):H1410-H1422.
[33] SANCHEZ-HERNANDEZ CD, TORRES-ALARCON LA, GONZALEZ-CORTES A, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Pathophysiology, Current Clinical Management, and Potential Preventive Approaches. Mediators Inflamm. 2020;2020:8405370.
[34] YASSIN MM, HARKIN DW, BARROS D’SA AA, et al. Lower limb ischemia-reperfusion injury triggers a systemic inflammatory response and multiple organ dysfunction. World J Surg. 2002;26(1):115-121.
[35] LAISALMI-KOKKI M, PESONEN E, KOKKI H, et al. Potentially detrimental effects of N-acetylcysteine on renal function in knee arthroplasty. Free Radic Res. 2009; 43(7):691-696.
[36] LEE JY, KIM CJ, CHUNG MY. Effect of high-dose vitamin C on oxygen free radical production and myocardial enzyme after tourniquet ischaemia-reperfusion injury during bilateral total knee replacement. J Int Med Res. 2010;38(4):1519-1529.
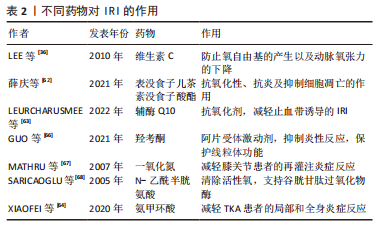
[37] OH CS, KIM SH, LEE J, et al. Impact of remote ischaemic preconditioning on cerebral oxygenation during total knee arthroplasty. Int J Med Sci. 2017;14(2): 115-122.
[38] MEMTSOUDIS SG, GONZALEZ DELLA VALLE A, BESCULIDES MC, et al. In-hospital complications and mortality of unilateral, bilateral, and revision TKA: based on an estimate of 4,159,661 discharges. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(11):2617-2627.
[39] GARCIA-DE-LA-ASUNCION J, PEREZ-SOLAZ A, CARRAU M, et al. Different oxidative stress marker levels in blood from the operated knee or the antecubital vein in patients undergoing knee surgery: a tourniquet-induced ischemia-reperfusion model. Redox Rep. 2012;17(5):194-199.
[40] CLEMENTSEN T, REIKERAS O. Cytokine patterns after tourniquet-induced skeletal muscle ischaemia reperfusion in total knee replacement. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2008;68(2):154-159.
[41] LIALIARIS T, KOUSKOUKIS A, TIAKA E, et al. Cytogenetic damage after ischemia and reperfusion. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2010;14(4):471-475.
[42] TSUNODA K, SONOHATA M, KUGISAKI H, et al. The Effect of Air Tourniquet on Interleukin-6 Levels in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Open Orthop J. 2017;11:20-28.
[43] PAC-SOO CK, MATHEW H, MA D. Ischaemic conditioning strategies reduce ischaemia/reperfusion-induced organ injury. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114(2):204-216.
[44] MURPHY T, WALSH PM, DORAN PP, et al. Transcriptional responses in the adaptation to ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a study of the effect of ischaemic preconditioning in total knee arthroplasty patients. J Transl Med. 2010;8:46.
[45] SHA Y, XU YQ, ZHAO WQ, et al. Protective effect of ischaemic preconditioning in total knee arthroplasty. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(10):1559-1566.
[46] MEMTSOUDIS SG, STUNDNER O, YOO D, et al. Does limb preconditioning reduce pain after total knee arthroplasty? A randomized, double-blind study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(5):1467-1474.
[47] LEURCHARUSMEE P, SAWADDIRUK P, PUNJASAWADWONG Y, et al. Ischemic preconditioning upregulates Mitofusin2 and preserves muscle strength in tourniquet-induced ischemia/reperfusion. J Orthop Translat. 2022;35:113-121.
[48] AKTAS E, ATAY Ç, DEVECI MA, et al. Impact of oxidative stress on early postoperative knee function and muscle injury biochemical markers: Is it possible to create an ischemic preconditioning effect in sequential ischemic surgical procedures? Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2015;49(4):387-393.
[49] 陈彬,胡雨,陶建平,等.远端肢体缺血预处理对AMI患者的心肌保护作用及对远期预后的影响[J].心血管康复医学杂志,2022,31(1):19-22.
[50] HAUSENLOY DJ, YELLON DM. Ischaemic conditioning and reperfusion injury. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2016;13(4):193-209.
[51] GILL R, KURIAKOSE R, GERTZ ZM, et al. Remote ischemic preconditioning for myocardial protection: update on mechanisms and clinical relevance. Mol Cell Biochem. 2015;402(1-2):41-49.
[52] GANJIFARD M, KOUZEGARAN S, ABDI R, et al. The Comparison of Inflammatory Cytokines between Spinal and General Anesthesia following Changes in Ischemic Reperfusion due to Tourniquet during Lower Limb Surgery. Adv Orthop. 2021; 2021:2027421.
[53] ÖZKAN D, AKKAYA T, YALCINDAG A, et al. Propofol sedation in total knee replacement : effects on oxidative stress and ischemia-reperfusion damage. Anaesthesist. 2013;62(7):537-542.
[54] OMER K, NERMIN G, ALI A, et al. Lesão de isquemia‐reperfusão induzida por torniquete: comparação dos efeitos antioxidantes de propofol e cetamina em doses baixas [Tourniquet-induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury: the comparison of antioxidative effects of small-dose propofol and ketamine]. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 2017;67(3):246-250.
[55] FANG H, ZHANG FX, LI HF, et al. PRR34-AS1 overexpression promotes protection of propofol pretreatment against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a mouse model after total knee arthroplasty via blockade of the JAK1-dependent JAK-STAT signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(3):2545-2556.
[56] AGARWAL B, STOWE DF, DASH RK, et al. Mitochondrial targets for volatile anesthetics against cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. Front Physiol. 2014;5:341.
[57] QIU S, LIU B, MO Y, et al. MicroRNA-153-3p increases autophagy in sevoflurane-preconditioned mice to protect against ischaemic/reperfusion injury after knee arthroplasty. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(9): 5330-5340.
[58] ARNAOUTOGLOU H, VRETZAKIS G, SOULIOTIS D, et al. The effects of propofol or sevoflurane on free radical production after tourniquet induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury during knee arthroplasty. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2007;58(1):3-6.
[59] MAS E, BARDEN AE, CORCORAN TB, et al. Effects of spinal or general anesthesia on F₂-isoprostanes and isofurans during ischemia/reperfusion of the leg in patients undergoing knee replacement surgery. Free Radic Biol Med. 2011;50(9): 1171-1176.
[60] LU S, CHEN X, CHEN Q, et al. Effects of dexmedetomidine on the function of distal organs and oxidative stress after lower limb ischaemia-reperfusion in elderly patients undergoing unilateral knee arthroplasty. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021;87(11):4212-4220.
[61] HALLSTROM L, FROSTELL C, HERRLIN A, et al. No signs of inflammation during knee surgery with ischemia: a study involving inhaled nitric oxide. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:620281.
[62] 薛庆,童梁成,杨智伟,等.表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯可减轻大鼠骨骼肌缺血再灌注损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(26):4145-4149.
[63] LEURCHARUSMEE P, SAWADDIRUK P, PUNJASAWADWONG Y, et al. CoenzymeQ10 and Ischemic Preconditioning Potentially Prevent Tourniquet-Induced Ischemia/Reperfusion in Knee Arthroplasty, but Combined Pretreatment Possibly Neutralizes Their Beneficial Effects. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(2):419.
[64] XIAOFEI L, XUAN W, JINLIANG W. Effect of tranexamic acid on ischemia-reperfusion injury caused by application of tourniquet in the surgery of total knee arthroplasty. Orthop J Sports Med. 2020;8(9 suppl7):2325967120S00532.
[65] CAO Q, HE Z, FAN Y, et al. Effects of tourniquet application on enhanced recovery after surgery (ERAS) and ischemia-reperfusion post-total knee arthroplasty: Full- versus second half-course application. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2020;28(1): 2309499019896026.
[66] GUO YX, WANG GY, CHENG WJ, et al. Activation of Opioid Receptors Attenuates Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Skeletal Muscle Induced by Tourniquet Placement. Mediators Inflamm. 2021;2021:6699499.
[67] MATHRU M, HUDA R, SOLANKI DR, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide attenuates reperfusion inflammatory responses in humans. Anesthesiology. 2007;106(2):275-282.
[68] SARICAOGLU F, DAL D, SALMAN AE, et al. Effect of low-dose N-acetyl-cysteine infusion on tourniquet-induced ischaemia-reperfusion injury in arthroscopic knee surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005;49(6):847-851. |