中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (6): 904-907.doi: 10.12307/2022.174
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印模型辅助与骨科机器人在脊柱畸形矫形过程中的精准置钉
宋玉鑫1,张同同2,牛建雄2,王增平1,文 杰1,张群立1,薛 文1,刘 林1
- 1甘肃省人民医院骨二科,甘肃省兰州市 730000 ;2甘肃中医药大学第一临床医学院,甘肃省兰州市 730000
Precise screw placement of 3D printing model and orthopedic robot in spinal deformity
Song Yuxin1, Zhang Tongtong2, Niu Jianxiong2, Wang Zengping1, Wen Jie1, Zhang Qunli1, Xue Wen1, Liu Lin1
- 1Second Department of Orthopedics, Gansu Provincial Hospital, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China; 2First School of Clinical Medicine, Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, Lanzhou 730000, Gansu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
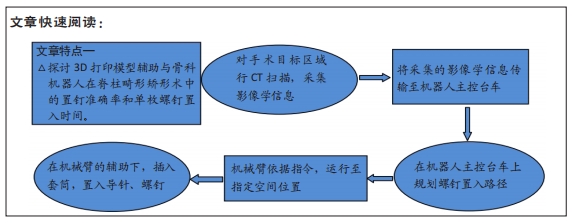
3D打印模型:对手术区域进行螺旋CT扫描,将CT得到的图像信息保存为DICOM格式,接着将数据导入Mimics三维建模软件,重建出三维模型。最后将重建的结果以STL格式导入3D打印机,按照三维模型逐层叠加打印出1∶1解剖模型。在3D打印模型辅助下,手术医师能够获得清晰的三维解剖学信息,并且能够依据术前设计的手术入路、置钉的角度及深度,选择大小合适螺钉,能够提高椎弓根螺钉置入的成功率,降低手术风险。
骨科手术机器人:能够辅助开展脊柱外科手术以及创伤骨科手术,以机械臂辅助完成这些手术中的手术器械或植入物的定位。产品兼容2D与3D模式,独有入钉点及钉道计算智能算法,机械臂精准运动到规划位置,借助骨科引导器,为医生提供精准稳定的导针置入路径。按照术中规划,医生可以精准设计并置入内植入物。
背景:脊柱畸形导致正常的椎弓根解剖结构发生变化,在脊柱畸形矫形术中置入椎弓根螺钉的难度增加。
目的:探讨3D打印模型辅助与骨科机器人在脊柱畸形矫形术中的置钉准确率和单枚螺钉置入时间。
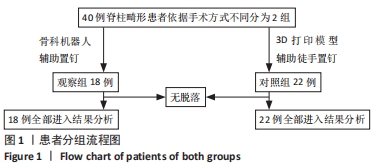
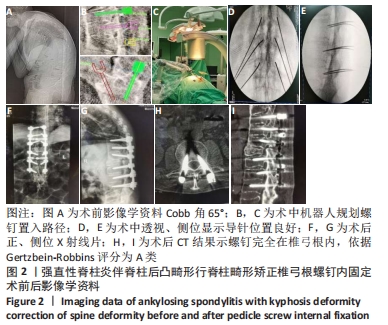
方法:40例脊柱畸形患者依据手术方式不同可分为:观察组18例,采用骨科机器人辅助置入椎弓根螺钉,即在开放手术过程中运用机器人进行椎弓根螺钉路径规划,机械臂到达指定位置,置入导针、螺钉;对照组22例,采用3D模型辅助徒手置入椎弓根螺钉。依据Gertzbein-Robbins分类标准评价置钉准确率,记录两组患者的单枚螺钉置入时间,比较两组之间的置钉准确率及单枚螺钉置入时间。研究方案的实施符合《赫尔辛基宣言》和甘肃省人民医院对研究的相关伦理要求。
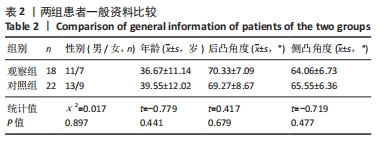
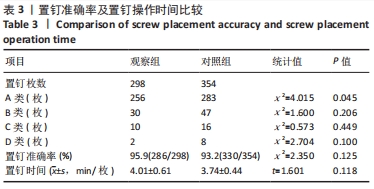
结果与结论:①两组之间置钉准确率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),A类螺钉准确率,观察组85.9%(256/298)高于对照组79.9%(283/354)(P < 0.05),B类、C类、D类螺钉准确率,两组间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②单枚螺钉置入时间两组间比较,差异无显著性意义[(4.01±0.61),(3.74±0.44) min/枚,P > 0.05];③结果说明,骨科机器人辅助脊柱畸形矫形术中椎弓根螺钉置入,显著提高了A类螺钉置入的准确率,准确度高、有效、可行。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4218-4341 (宋玉鑫)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: