[1] MURGIER J, LAFFOSSE JM, CAILLIEZ J, et al. Is the prognosis the same for periprosthetic joint infections due to Staphylococcus aureus versus coagulase-negative staphylococci? A retrospective study of 101 patients with 2- year minimum follow-up. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016;136(10):1357-1361.
[2] DUTTON T, DE-SOUZA R, PARSONS N, et al. The timing of tourniquet release and retransfusion drains in total knee arthroplasty:a stratified randomized pilot investigation. Knee. 2012;19(3):190-192.
[3] YI S, TAN J, CHEN C, et al. The use of pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(10):1469-1476.
[4] OLIVECRONA C, PONZER S, HAMBERG P, et al. Lower tourniquet cuff pressure reduces postoperative wound complications after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled study of 164 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(24):2216-2221.
[5] JIANG FZ, ZHONG HM, HONG YC, et al. Use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Orthop Sci. 2015;20(1):110-123.
[6] ZHANG W, LI N, CHEN S, et al. The effects of a tourniquet used in total knee arthroplasty : a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014;9(1): 13.
[7] OLIVECRONA C, LAPIDUS LJ, BENSON L, et al. Tourniquet time affects postoperative complications after knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2013;37(5):827-832.
[8] PETERS CL, CRAIG MA, MOHR RA, et al. Tibial component fixation with cement: full-versus surface-cementation techniques. Clin Orthop. 2003;409(409):158-168.
[9] PFITZNER T, VON ROTH P, VOERKELIUS N, et al. Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(1):96-101.
[10] ZHANG P, LIANG Y, HE JS, et al. Timing of tourniquet release in total knee arthroplasty: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(17):e6786.
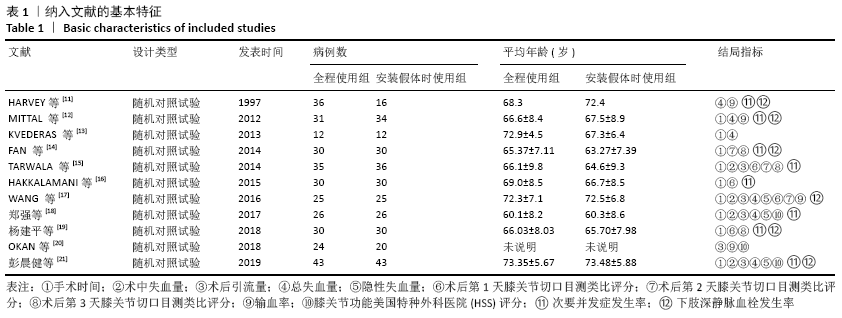
[11] HARVEY EJ,LECLERC J, BROOKS CE, et al. Effect of tourniquet use on blood loss and incidence of deep vein thrombosis in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplast. 1997;12(3):291-296.
[12] MITTAL R, KO V, ADIE S, NAYLOR J, et al. Tourniquet application only during cement fixation in total knee arthroplasty: a double-blind randombed contolled trial. ANZ J Surg. 2012;82(6):428-433.
[13] KVEDERAS G, PORVANECKAS N, ANDRIJAUSKAS A, et al. A randomized double-blind clinical trial of tourniquet application strategies for total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2013;21(12):2790-2799.
[14] FAN Y, JIN J, SUN Z, et al. The limited use of a tourniquet during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee. 2014; 21(6):1263-1268.
[15] TARWALA R, DORR LD, GILBERT PK, et al. Tourniquet use during cementation only during total knee arthroplasty: a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(1):169-174.
[16] HAKKALAMANI S, CLARK V, PRADHAN N. Short versus standard duration tourniquet use during total knee replacement: A pilot study. Acta Orthop Belg. 2015;81(1):52-56.
[17] WANG K, NI S, LI Z, et al. The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9): 2849-2857.
[18] 郑强,尚希福.止血带在全膝关节置换术中不同应用方式的比较研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2017,27(16):86-89.
[19] 杨建平,蒋涛,吕正祥.止血带优化对全膝关节置换术快速康复的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(1):33-37.
[20] OKAN O, KERIM S, HALIL CG, et al. The Effect of Tourniquet Usage on Cement Penetration in total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized study of 3 methods. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(4):e9668.
[21] 彭晨健,杜斌,孙光权,等.人工全膝关节置换加速康复中优化止血带的使用策略[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(28): 4451-4455.
[22] ZHOU K, LING T, WANG H, et al. Influence of tourniquet use in primary total knee arthroplasty with drainage: a prospective randomised controlled trial. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):172.
[23] 马骏,李国庆,曹力.全膝关节置换术中不同压力止血带对术后肿胀及疼痛影响的临床研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013, 21(13):1297-1300.
[24] MUYSKENS JB, HOCKER AD, TURNBULL DW, et al. Transcriptional profiling and muscle cross-section analysis reveal signs of ischemia reperfusion injury following total knee arthroplasty with tourniquet. Physiol Rep. 2016;4(1):e12671.
[25] EJAZ A, LAURSEN AC, KAPPEL A, et al. Tourniquet induced ischemia and changes in metabolism during TKA: a randomized study using microdialysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:326.
[26] SHERMAN OH, FOX JM, SNYDER SJ, et al. Arthroscopy- “no-problem surgery”. An analysis of complications in two thousand six hundred and forty cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986;68(2):256-265.
[27] ISHII Y, MATSUDA Y. Effect of the timing of tourniquet release on perioperative blood loss associated with cementless total knee arthroplasty: a prospetive randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2005;20(8):977-983. |