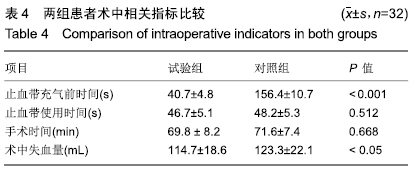
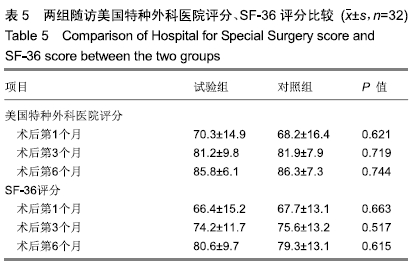
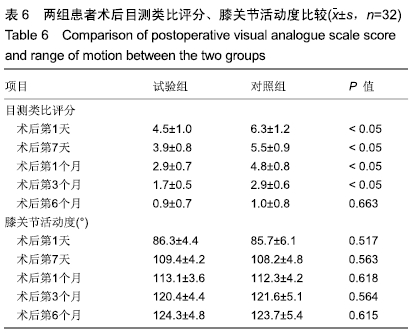
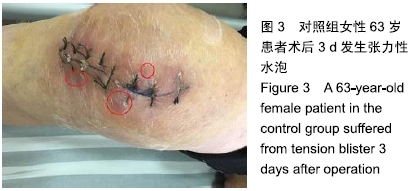
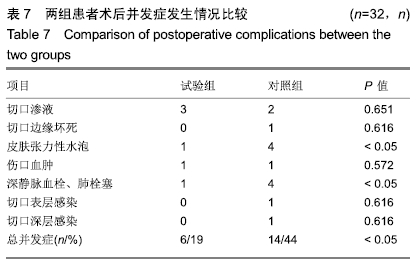
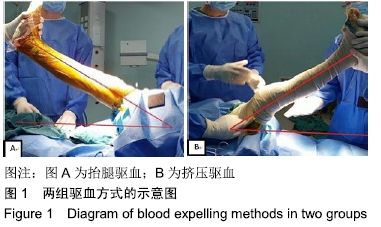
[1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[2] 赵俊涛,郑成胜,王博.全膝关节置换中止血带的优化应用方案[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 3(20):3124-3129.
[3] 谢小伟,岳辰,黄泽宇,等.全膝关节置换术应用与不应用止血带的随机对照研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2017,25(17):1572-1576.
[4] TANPOWPONG T, KITIDUMRONGSOOK P, PATRADUL A. The deleterious effects of exsanguination with a tight bandage on tourniquet tolerance in the upper arm. J Hand Surg Eur. 2012;37(9): 839-841.
[5] MORI N, KIMURA S, ONODERA T, et al. Use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty increases the risk of distal deep vein thrombosis: A prospective, randomized study. Knee. 2016;23(5): 887-889.
[6] TRAN T, LUND SB, NICHOLS MD, et al. Effect of two tourniquet techniques on peripheral intravenous cannulation success: A randomized controlled trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2019.
[7] 王刚,曹晓瑞,陈晓勇,等.膝关节置换术中止血带的使用对术后加速康复的影响[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2017, 10(1): 27-32.
[8] 陈琳,王艳玲,王建珍.骨科手术中帕瑞昔布钠复合地佐辛超前镇痛效果观察[J].山东医药,2015,55(5): 49-51.
[9] 王宏庆,刘祖耀,李珂,等.加速康复外科理念指导下单髁关节置换术后疼痛的相关因素分析[J].临床合理用药杂志, 2017,10(29):134-135.
[10] 谭正玲,陈郡兴,苏志源,等.右美托咪定复合罗哌卡因联合收肌管阻滞用于全膝关节置换后镇痛[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(24): 3798-3804.
[11] LI B, WEN Y, WU H, et al. The effect of tourniquet use on hidden blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5): 1263-1268.
[12] FRANZONE JM, YANG JH, HERZENBERG JE. Reuse of single-use hema clear exsanguination tourniquets: a technique note. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2017;27(1): 59-65.
[13] VAN DE WATER RB, LEICHTENBERG CS, NELISSEN RGHH, et al. Preoperative radiographic osteoarthritis severity modifies the effect of preoperative pain on pain/function after total knee arthroplasty: results at 1 and 2 years postoperatively. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2019; 101(10): 879-887.
[14] LIANG HS, FENG Y. Effect of transcutaneous acupoint electrical stimulation on hemodynamic fluctuation caused by loosing tourniquet in elderly patients undergoing knee joint replacement. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2017;42(6): 522-526.
[15] OZKUNT O, SARIYILMAZ K, GEMALMAZ HC, et al. The effect of tourniquet usage on cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized study of 3 methods. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(4): e9668.
[16] RYU KJ. CORR Insights((R)): does tourniquet use in TKA affect recovery of lower extremity strength and function? a randomized trial. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(1): 78-80.
[17] TIE K, HU D, QI Y, et al. Effects of tourniquet release on total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2016;39(4): e642-650.
[18] 黄家谷,张克,田华,等.单侧初次全膝关节置换后隐性失血的因素分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(26): 3823-3829.
[19] JAWHAR A, SKEIREK D, STETZELBERGER V, et al. No effect of tourniquet in primary total knee arthroplasty on muscle strength, functional outcome, patient satisfaction and health status: a randomized clinical trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019.
[20] ZHANG M, LIU G, ZHAO Z, et al. Comparison of lower limb lifting and squeeze exsanguination before tourniquet inflation during total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1): 35.
[21] FARBOOD A, SHAHBAZI S. Comparison of two different methods of limb exsanguination (Esmarch bandage and limb elevation) in intravenous regional anesthesia. J Clin Anesth. 2008;20(3): 196-199.
[22] ISSA K, PIERCE TP, HARWIN SF, et al. No decrease in knee survivorship or outcomes scores for patients with HIV infection who undergo TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2): 465-471.
[23] ARSOY D, GIORI NJ, WOOLSON ST. Mobile compression reduces bleeding-related readmissions and wound complications after THA and TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018; 476(2): 381-387.
[24] PFITZNER T, VON ROTH P, VOERKELIUS N, et al. Influence of the tourniquet on tibial cement mantle thickness in primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc, 2016; 24(1): 96-101.
[25] SCHOONOVER MJ, MOSER DK, YOUNG JM, et al. Effects of tourniquet number and exsanguination on amikacin concentrations in the radiocarpal and distal interphalangeal joints after low volume intravenous regional limb perfusion in horses. Vet Surg. 2017; 46(5): 675-682.
[26] LYON M, JOHNSON D, GORDON R. Use of a novel abdominal aortic and junctional tourniquet to reduce or eliminate flow in the brachial and popliteal arteries in human subjects. Prehosp Emerg Care. 2015;19(3): 405-408.
[27] COLLEONI JL, RIBEIRO FN, MOS PAC, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty (TKA): aspirin vs. rivaroxaban. Rev Bras Ortop. 2018; 53(1): 22-27.
[28] ISHII Y, NOGUCHI H, SATO J, et al. Impact of anesthesia modality and mechanical venous thromboembolism prophylaxis on the incidence of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis after TKA. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018; 9(2): 142-145.
[29] BALA A, HUDDLESTON JI 3RD, GOODMAN SB, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after TKA: aspirin, warfarin, enoxaparin, or factor xa inhibitors? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017; 475(9): 2205-2213.
|