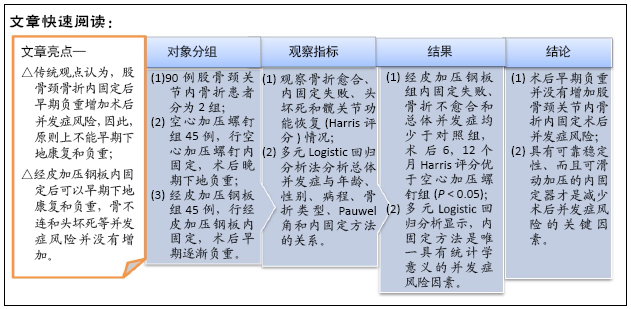
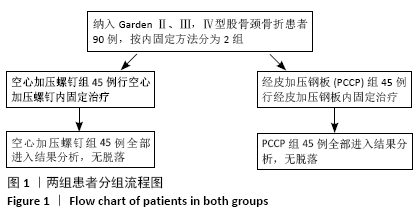
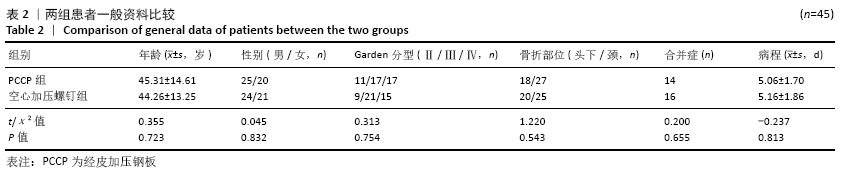
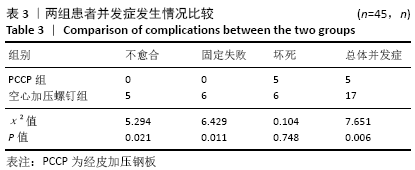
[1] WIDHALM HK, ARNHOLD R, BEIGLBÖCK H, et al. A comparison of dynamic hip screw and two cannulated screws in the treatment of undisplaced intracapsular neck fractures-two-year follow-up of 453 patients. J Clin Med. 2019;8(10):E1670.
[2] 王宝鹏,李光磊,段强民,等.闭合复位经皮空心加压螺钉内固定治疗不稳定头下型股骨颈骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(24): 2296-2297.
[3] SHEHATA MSA, ABOELNAS MM, ABDULKARIM AN, et al. Sliding hip screws versus cancellous screws for femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2019;29(7):1383-1393.
[4] 李伟龙,余霄,庞清江.股骨颈骨折内固定术后股骨颈短缩的相关研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(6):378-384.
[5] 程鹏,王玮琪.骨折内固定术与全髋关节置换术治疗老年股骨颈骨折的临床效果比较[J].中华全科医学,2016,14(4):689-691.
[6] 张华亮,曾剑文,谢建军.两种手术方法治疗青壮年股骨颈骨折的疗效分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(24):2215-2218.
[7] MUKHERJEE P, ASHWORTH MJ. A new device to treat intra-capsular fracture neck of femur nonunion. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2010;5(3):159-162.
[8] BRANDT SE. A new and stable implant in the treatment of intracapsular hip fracture:a case report. Injury Extra. 2008;39(4):137-139.
[9] Parker MJ, Stedtfeld HW. Internal fixation of intracapsular hip fractures with a dynamic locking plate: initial experience and results for 83 patients treated with a new implant. Injury. 2010;41(4):348-351.
[10] 朱锋,徐耀增,耿德春,等.经皮加压钢板治疗股骨颈骨折的早期疗效[J].中华创伤杂志,2014,16(9):909-912.
[11] 朱锋,徐耀增,耿德春,等.经皮加压钢板与空心加压螺钉治疗中青年移位型股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中华创伤骨科志,2014, 30(8):731-733.
[12] 殷渠东,顾三军,王建兵,等.经皮加压钢板治疗移位型股骨颈骨折的前瞻性随机对照研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(8): 951-955.
[13] 林志铝.经皮加压钢板与空心加压螺钉治疗股骨颈骨折患者的临床疗效[J].医疗装备,2019,32(5): 67-68.
[14] 张世明,李海丰,黄轶刚.骨折分类与功能评定[M].北京:人民军医出版社,2008:321-322.
[15] RAJNISH RK, HAQ RU, AGGARWAL AN, et al. Four screws diamond configuration fixation for displaced,comminuted intracapsular fracture neck femur in young adults. Indian J Orthop. 2019;53(1):70-76.
[16] 刘祥,方红育,黄涛,等.股骨颈骨折空心螺钉治疗失败因素的Meta分析[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2018,12(4):523-533.
[17] 刘振东,秦泗河.骨折断端磨损性骨吸收的证据分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015,23(12):1147-1152.
[18] BRANDT E, VERDONSCHOT N, VAN KAMPEN A, et al. Biomechanical analysis of the percutaneous compression plate and sliding hip screw in incapsular hip fractures:experimental assessment using synthetic and cadaver bones. Injury. 2006;37(10):979-983.
[19] KELLY MA, MCSORLEY K, CASEY MC, et al. The long-term outcomes following internal fixation for intracapsular hip fractures in an Irish tertiary referral centre. Ir J Med Sci. 2019;188(4):1227-1231.
[20] THEIN R, HERMAN A, KEDEM P, et al. Osteosynthesis of unstable intracapsular femoral neck fracture by dynamic locking plate or screw fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2014;28(2):70-76.
[21] 孙友强,陈雷雷,刘予豪,等.股骨颈骨折内固定后股骨头坏死发生研究现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(19):3095-3101.
[22] 胡家朗,李绍刚,陈明,等. 新型股骨颈动力加压锁定钉板系统治疗股骨颈骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2019,21(11):939-944.
[23] 赵德伟,马志杰.创伤性股骨颈骨折后股骨头坏死的预防[J].中华显微外科杂志,2019,42(1):3-4.
[24] 李海波,许圣茜,汤雪霞,等.术前牵引对股骨颈骨折术后发生股骨头缺血性坏死的影响研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019, 33(6):671-675.
[25] WU Y, LEU TH, CHUANG TY, et al. Screw trajectory affects screw cut-out risk after fixation for nondisplaced femoral neck fracture in elderly patients. J Orthop Surg. 2019;27(2):2309499019840252.
[26] ESCHLER A, BRANDT S, GIERER P, et al. Angular stable multiple screw fixation (Targon FN) versus standard SHS for the fixation of femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2014;45:S76-S80. |