中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (18): 2789-2793.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3834
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 下一篇
3D打印手术导板在膝关节内外翻畸形患者全膝关节置换中的应用
黄辰宇1,2,3,唐 成1,2,3,魏 波1,2,3,李佳怡1,2,3,李旭祥1,2,3,张惠康2,3,徐 燕2,3,姚庆强1,2,3,王黎明1,2,3
- 1南京医科大学附属南京医院骨科,江苏省南京市 210006;2南京医科大学数字医学研究所,江苏省南京市 210006;3江苏省数字医学与3D打印临床工程研究中心,江苏省南京市 210006
Application of three-dimensional printing guide plate in total knee arthroplasty for patients with varus and valgus deformity
Huang Chenyu1, 2, 3, Tang Cheng1, 2, 3, Wei Bo1, 2, 3, Li Jiayi1, 2, 3, Li Xuxiang1, 2, 3, Zhang Huikang2, 3, Xu Yan2, 3, Yao Qingqiang1, 2, 3, Wang Liming1, 2, 3
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Nanjing Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Institute of Digital Medicine, Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210006, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Jiangsu Digital Medicine and 3D printing Clinical Engineering Research Center, Nanjing 210006, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
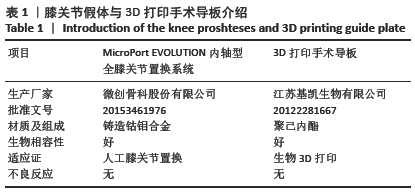
3D 打印个性化截骨导板辅助行全膝关节置换:是术前将患者膝关节的 CT 扫描数据用计算机软件进行处理,在计算机上进行力线的调整,得出最佳的假体横截面对线,再通过三维成像技术制作截骨模板,此截骨模板具有个性化、截骨角度更确切等优点,术中股骨远端及后髁截骨量、胫骨截骨后倾角度与截骨量及术中使用假体的型号都在术前用计算机测定出来。
3D 打印个性化截骨导板辅助行全膝关节置换的优势:与传统的全膝关节置换相比,其不需要术中使用髓内外导向器反复测量力线,不需要反复测定股骨远端及后髁的截骨量、胫骨截骨的后倾角度与截骨量;也不用反复安放假体试模查看其与关节的匹配程度,尤为重要的是术中无需使用髓内导向器,不需要打开股骨髓腔,这使得术中出血量降低,输血率下降;另外还可以降低由于使用髓内导向器所增加的脂肪栓塞发生率。
背景:近年来 3D打印技术在导航骨折内固定植入、脊柱外科螺钉置入及巨大骨缺损修复重建领域应用较为广泛,但是将3D打印导航模板运用于膝关节内外翻患者全膝关节置换手术的相关报道较少。
目的:对比3D打印手术导板辅助全膝关节置换和传统全膝关节置换治疗膝关节内外翻骨性关节炎的效果。
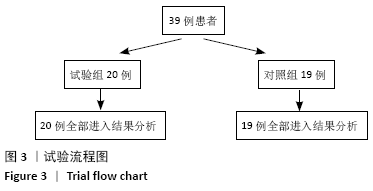
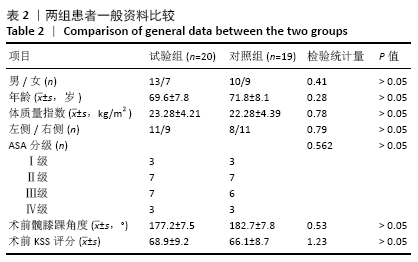
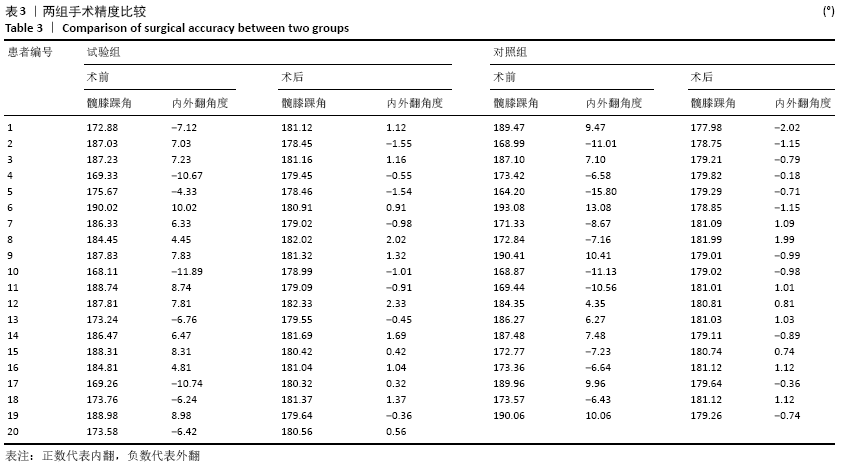
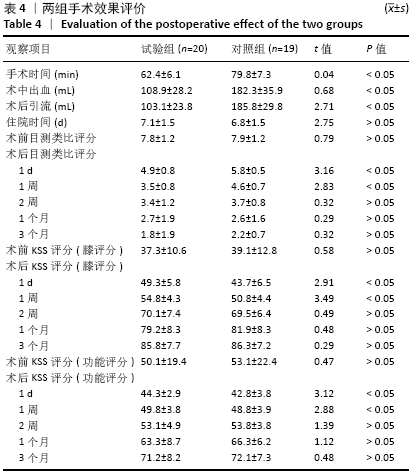
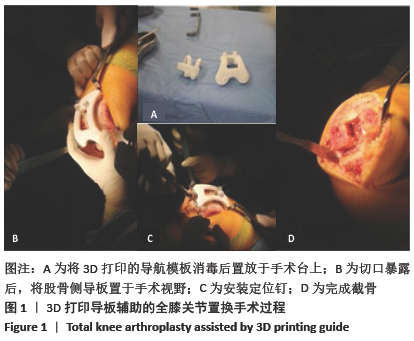
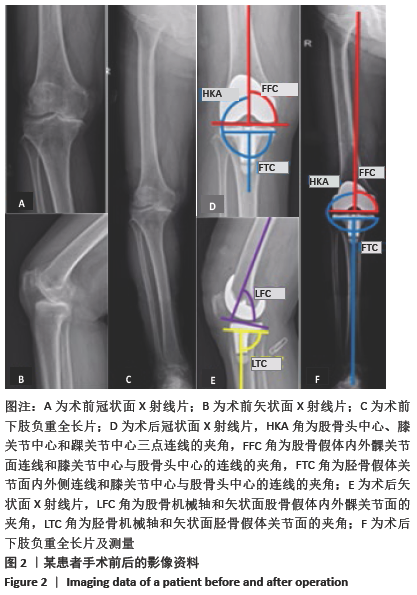
方法:选择2019年1月至2020年2月南京医科大学附属南京医院收治的膝关节内外翻骨性关节炎患者39例,其中女18例,男21例,年龄55-83岁,随机分2组:试验组(n=20)在3D打印手术导板辅助下进行全膝关节置换,对照组(n=19)进行传统的全膝关节置换。术后拍摄X射线片,测量冠状面胫骨组件角、矢状面胫骨组件角、冠状面股骨组件角、矢状面股骨组件角、髋膝踝角度及下肢力线角度;记录两组住院时间、手术时间、术中出血量和术后引流量。术后1 d、1周、2周、1个月、3个月时,进行目测类比评分及美国膝关节协会(KSS)评分。试验通过南京医科大学附属南京医院伦理委员会批准。
结果与结论:①两组术后的冠状面胫骨组件角、矢状面胫骨组件角、冠状面股骨组件角、矢状面股骨组件角及髋膝踝角度偏移值均<3°,试验组对下肢力线角度的调整效果优于对照组(P < 0.05);②试验组的手术时间、术中出血量与术后引流量少于对照组(P < 0.05),两组患者住院时间比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);③试验组术后1 d、1周的目测类比评分低于对照组(P < 0.05),KSS评分高于对照组(P < 0.05);④结果表明,对于膝关节严重内外翻患者,3D打印手术导板辅助下的膝关节置换提高了手术精度,节省了术中时间。
中图分类号: