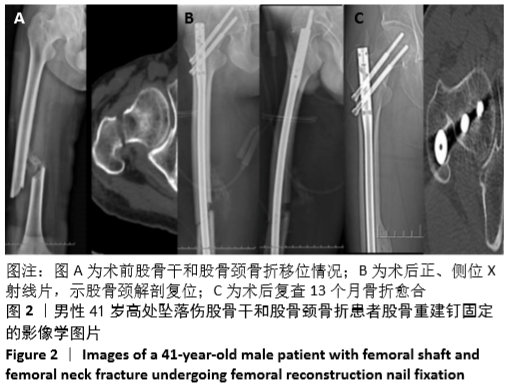
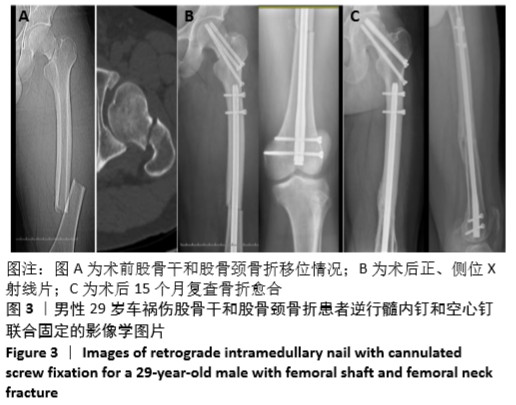
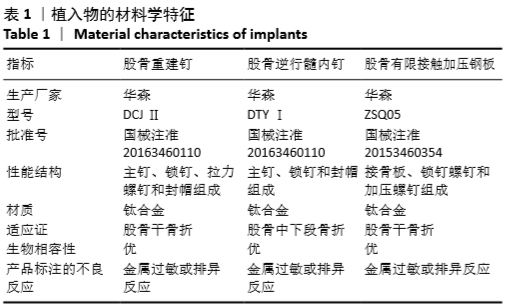
[1] WANG H, LI L H, LIU Z, et al. Reconstruction intramedullary nailing for treatment of ispsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures.Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015;28(9):808-810.
[2] 石振,成昊,焦志坚,等.不同内固定在股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折的疗效分析[J].临床外科杂志,2017,25(8):598-601.
[3] 吴翼飞, 冯旭, 陈旭宏.逆向髓内钉联合空心螺钉内固定治疗股骨颈合并股骨干骨折的临床疗效分析[J].浙江创伤外科, 2019,24(2): 224-227.
[4] 吴进, 郭小微, 宋伟,等.接骨板系统治疗同侧股骨干合并股骨近端骨折[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(8):617-621.
[5] MOHAN K, ELLANTI P, FRENCH H, et al.Single versus separate implant fixation for concomitant ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: A systematic review. Ortho Rev. 2019;11(2):7963-7970.
[6] BOULTON CL, POLLAK AN.Special topic: Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures--does evidence give us the answer? Injury. 2015; 46(3): 478-483.
[7] DU CG, ZHANG YZ, CHEN W. Progress in diagnosis and treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fracture. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2016;54(7):553-557.
[8] 王秋根.髓内钉固定治疗成人股骨干骨折的相关问题[J].中华创伤杂志,2017,33(1):6-9.
[9] FRIEDL L, CLAXTON AG, WALKER CS, et al.Femoral neck and shaft structure in Homo naledi from the Dinaledi Chamber (Rising Star System, South Africa). J Hum Evol. 2019;133(7):61-77.
[10] PARK YC, UM KS, HONG SP, et al. Preoperative “Computed tomography capsular sign” for the detection of occult ipsilateral femoral neck fractures associated with femoral shaft fractures.Injury. 2020;51(4): 1051-1056.
[11] ROGERS NB, HARTLINE BE, ACHOR TS, et al.Improving the diagnosis of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures: a new imaging protocol. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(4):309-314.
[12] 高嘉锴,陈钊,毕龙,等.顺向长髓内钉和逆向髓内钉联合空心钉治疗股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折的比较[J].中华骨科杂志, 2017, 37(17):1081-1087.
[13] SPITLER C A, KINER D, SWAFFORD R, et al.Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures with cannulated screws and antegrade reconstruction nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(5):e176-e180.
[14] 赵毅, 夏永宁, 于铁成.一种治疗股骨颈骨折合并同侧股骨干骨折的新方法:加长Gamma3加压交锁髓内钉联合交叉空心螺钉[J].转化医学电子杂志,2017,4(3):38-42.
[15] 邓怀明.股骨干骨折合并同侧股骨颈骨折的临床治疗分析[J].浙江创伤外科,2019,24(6):1157-1158.
[16] IYENGAR KP, MATAR HE, NADKARNI JB. Retrograde intramedullary nailing for femoral shaft fractures in elderly patients with previous ipsilateral dynamic hip screw fixation. Gerontology. 2015;62(1):16-21.
[17] WU KT, LIN SJ, CHOU YC, et al. Ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures fixation with proximal femoral nail antirotation II (PFNA II): technical note and cases series. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):20.
[18] 牛庆飞, 夏凡, 贾乐生,等.加长PFNA治疗Winquist Ⅲ,Ⅳ型股骨干骨折合并股骨颈骨折13例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017, 25(8):66-68.
[19] 刘立云, 刘又文, 邢庆胜, 等.InterTAN与逆行髓内钉结合空心钉治疗股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折的疗效比较[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2016,24(5):17-20,24.
[20] GANSSLEN A, GOSLING T, HILDEBRAND F, et al. Femoral shaft fractures in adults: treatment options and controversies. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2014;81(2):108-117.
[21] BISACCIA M, CARAFFA A, RINONAPOLI G, et al. Feasibility and value of non-locking retrograde nail vs. locking retrograde nail in fixation of distal third femoral shaft fractures: radiographic, bone densitometry and clinical outcome assessments. Med Glas (Zenica).2020;17(1). DOI:10.17392/1097-20.
[22] ROLLO G, BISACCIA M, RINONAPOLI G, et al. Radiographic, bone densitometry and clinic outcomes assessments in femoral shaft fractures fixed by plating or locking retrograde nail. Med Arch. 2019; 73(3):195-200.
[23] HERRERA A, ALBAREDA J, GABARRE S, et al.Comparative analysis of the biomechanical behavior of anterograde/retrograde nailing in supracondylar femoral fractures. Injury. 2020. 51 Suppl 1:S80-S88.
[24] 冯庆虎,王友良.股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折的不同治疗方法[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(10):763-767.
[25] LI YM, XING BR, GUO DH, et al.Application of self-made fine-tuning device in distal locking process of femoral interlocking intramedullary nail. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(2):161-165.
[26] 左康康, 覃巍, 郭青,等.电磁导航交锁髓内钉远端锁钉技术治疗股骨干骨折的初步应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014, 28(10): 1204-1207.
[27] 荆玉峰,刘京敏,叶发刚,等.芯钻髓内钉治疗股骨干骨折的疗效分析[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2017,23(3):265-266.
[28] 任继鑫,张建政,刘智,等.股骨重建钉治疗股骨干合并同侧髋部骨折适应证探讨[J].实用骨科杂志,2014,20(11):982-985.
[29] SHAH S, DESAI P, MOUNASAMY V. Retrograde nailing of femoral fractures: a retrospective study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015; 25(6):1093-1097.
[30] VAN DYKE B, COLLEY R, OTTOMEYER C, et al.Effect of blocking screws on union of infraisthmal femur fractures stabilized with a retrograde intramedullary nail. J Orthop Trauma. 2018;32(5):251-255.
[31] GARY JL, TAKSALI S, REINERT CM, et al.Ipsilateral femoral shaft and neck fractures: are cephalomedullary nails appropriate? J Surg Orthop Adv. 2011;20(2):122-125.
[32] LU Y, WANG Y, SONG Z, et al.Treatment comparison of femoral shaft with femoral neck fracture: a meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020; 15(1):19.
[33] 许永权,张金山,郑勇强.对比股骨重建带锁髓内钉与空心螺钉联合加压钢板治疗股骨干合并同侧股骨颈骨折的效果[J].中外医疗,2018,37(3):49-51. |