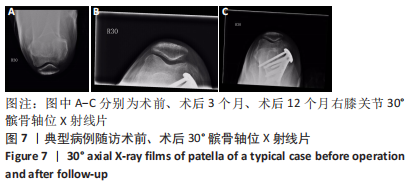
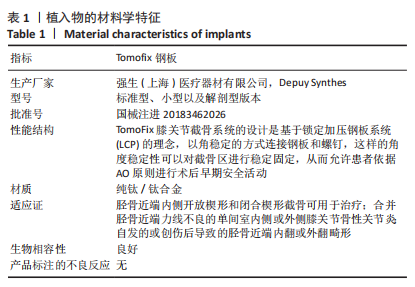
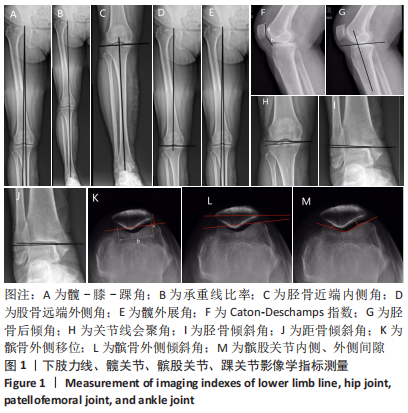
[1] COVENTRY MB. Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report. 1965. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(248):4-8.
[2] HERNIGOU P, MEDEVIELLE D, DEBEYRE J, et al. Proximal tibial osteotomy for osteoarthritis with varus deformity. A ten to thirteen-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69(3):332-354.
[3] 王兴山,黄野.开放楔形胫骨高位截骨术的研究进展[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(5):525-529.
[4] GOSHIMA K, SAWAGUCHI T, SHIGEMOTO K, et al. Comparison of Clinical and Radiologic Outcomes Between Normal and Overcorrected Medial Proximal Tibial Angle Groups After Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(10):2898-2908.
[5] CHOI GW, YANG JH, PARK JH, et al. Changes in coronal alignment of the ankle joint after high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(3):838-845.
[6] ISHIMATSU T, TAKEUCHI R, ISHIKAWA H, et al. Hybrid closed wedge high tibial osteotomy improves patellofemoral joint congruity compared with open wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(4):1299-1309.
[7] CHO WJ, KIM JM, KIM WK, et al. Mobile-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty in old-aged patients demonstrates superior short-term clinical outcomes to open-wedge high tibial osteotomy in middle-aged patients with advanced isolated medial osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2018;42(10):2357-2363.
[8] HUANG SC, CHEN YF, LIU XD, et al. The efficacy and safety of opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy in treating unicompartmental knee osteoarthritis: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(12):e14927.
[9] ROBERSON TA, MOMAYA AM, ADAMS K, et al. High Tibial Osteotomy Performed With All-PEEK Implants Demonstrates Similar Outcomes but Less Hardware Removal at Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Compared With Metal Plates. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(3):2325967117749584.
[10] MARTAY JL, PALMER AJ, BANGERTER NK, et al. A preliminary modeling investigation into the safe correction zone for high tibial osteotomy. Knee. 2018;25(2):286-295.
[11] WEIDENHIELM L, SVENSSON OK, BROSTRÖM LÅ. Change of adduction moment about the hip, knee and ankle joints after high tibial osteotomy in osteoarthrosis of the knee. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 1992;7(3):177-180.
[12] TAKEUCHI R, SAITO T, KOSHINO T. Clinical results of a valgus high tibial osteotomy for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee and the ipsilateral ankle. Knee. 2008;15(3):196-200.
[13] JINGBO C, MINGLI F, GUANGLEI C, et al. Patellar Height Is Not Altered When the Knee Axis Correction Is Less than 15 Degrees and Has Good Short-Term Clinical Outcome. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(6):536-546.
[14] OTSUKI S, MURAKAMI T, OKAMOTO Y, et al. Risk of patella baja after opening-wedge high tibial osteotomy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2018;26(3):2309499018802484.
[15] OZKAYA U, KABUKÇUOĞLU Y, PARMAKSIZOĞLU AS, et al. Changes in patellar height and tibia inclination angle following open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2008;42(4):265-271.
[16] YANG JH, LEE SH, NATHAWAT KS, et al. The effect of biplane medial opening wedge high tibial osteotomy on patellofemoral joint indices. Knee. 2013;20(2):128-132.
[17] KIM GB, KIM KI, SONG SJ, et al. Increased Posterior Tibial Slope After Medial Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy May Result in Degenerative Changes in Anterior Cruciate Ligament. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(9): 1922-1928.
[18] NHA KW, KIM HJ, AHN HS, et al. Change in Posterior Tibial Slope After Open-Wedge and Closed-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy: A Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. 2016;44(11):3006-3013.
[19] JO HS, PARK JS, BYUN JH, et al. The effects of different hinge positions on posterior tibial slope in medial open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2018;26(6):1851-1858.
[20] LEE SS, NHA KW, LEE DH. Posterior cortical breakage leads to posterior tibial slope change in lateral hinge fracture following opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(3): 698-706.
[21] OZEL O, YUCEL B, MUTLU S, et al. Changes in posterior tibial slope angle in patients undergoing open-wedge high tibial osteotomy for varus gonarthrosis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(1): 314-318.
|