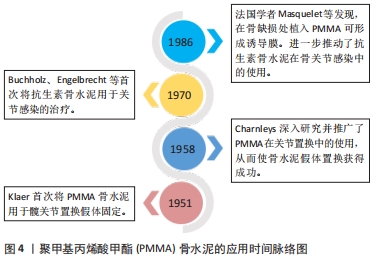
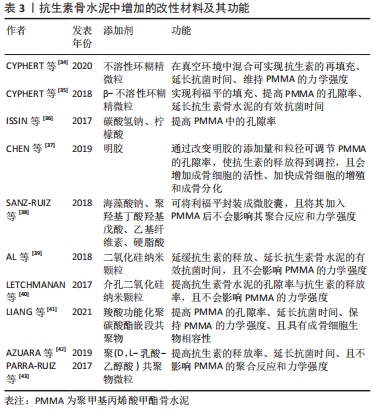
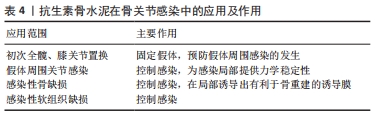
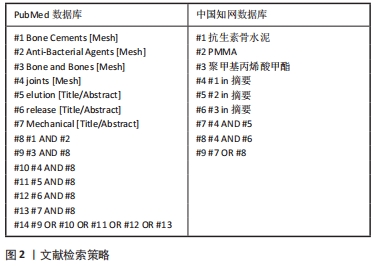
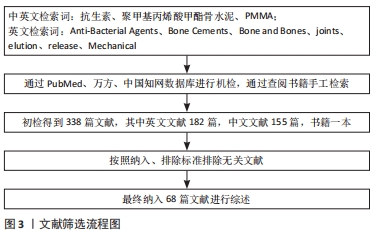
[1] 赵行琪,余斌,胡岩君.感染性骨缺损局部抗生素载体的临床应用[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2019,21(2):173-181.
[2] SCHMITT DR, KILLEN C, MURPHY M, et al. The Impact of Antibiotic-Loaded Bone Cement on Antibiotic Resistance in Periprosthetic Knee Infections. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020;12(3):318-323.
[3] ZIMMERLI W, SENDI P. Orthopaedic biofilm infections. APMIS. 2017; 125(4):353-364.
[4] 斯蒂芬·L·凯特,奥利维尔·波伦斯. AO骨感染治疗原则[M].高秋明,译.上海:上海科学技术出版社.2022:3-4
[5] 徐溢明,彭慧明,翁习生.关节外科用骨水泥性能改善研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(7):592-597.
[6] 任有亮.多中心四肢创伤性骨感染致病菌及其耐药性的流行病学研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2020.
[7] DALL GF, TSANG SJ, GWYNNE PJ, et al. Unexpected synergistic and antagonistic antibiotic activity against Staphylococcus biofilms. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(7):1830-1840.
[8] YUENYONGVIWAT V, INGVIYA N, PATHABUREE P, et al. Inhibitory effects of vancomycin and fosfomycin on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from antibiotic-impregnated articulating cement spacers. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(3):132-136.
[9] BALATO G, ROSCETTO E, VOLLARO A, et al. Bacterial biofilm formation is variably inhibited by different formulations of antibiotic-loaded bone cement in vitro. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(6): 1943-1952.
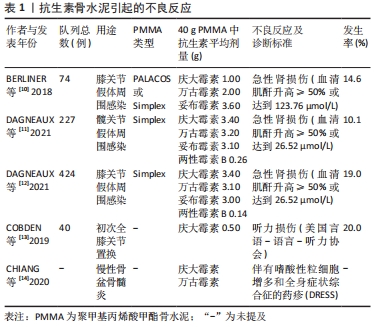
[10] BERLINER ZP, MO AZ, PORTER DA, et al. In-Hospital Acute Kidney Injury After TKA Revision With Placement of an Antibiotic Cement Spacer. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7S):S209-S212.
[11] DAGNEAUX L, LIMBERG AK, OSMON DR, et al. Acute Kidney Injury When Treating Periprosthetic Joint Infections After Total Knee Arthroplasties with Antibiotic-Loaded Spacers: Incidence, Risks, and Outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2021;103(9):754-760.
[12] DAGNEAUX L, LIMBERG AK, OSMON DR, et al. Renal Toxicity Associated With Resection and Spacer Insertion for Chronic Hip PJI. J Arthroplasty. 2021;36(9):3289-3293.
[13] COBDEN A, CAMURCU Y, BULUT CS, et al. Audiometric threshold shifts after total knee arthroplasty by using gentamicin-loaded bone cement. Turk J Med Sci. 2019;49(2):514-518.
[14] CHIANG V, WONG J, YEUNG H, et al. DRESS syndrome induced by antibiotic-loaded bone cements and a diagnostic algorithm for related delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021;9(2):1029-1031.
[15] FERREIRA M, RZHEPISHEVSKA O, GRENHO L, et al. Levofloxacin-loaded bone cement delivery system: Highly effective against intracellular bacteria and Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Int J Pharm. 2017;532(1):241-248.
[16] EICK S, HOFPETER K, SCULEAN A, et al. Activity of Fosfomycin- and Daptomycin-Containing Bone Cement on Selected Bacterial Species Being Associated with Orthopedic Infections. Biomed Res Int. 2017; 2017:2318174.
[17] KILINC S, TUNC T, PAZARCI O, et al. Research into biocompatibility and cytotoxicity of daptomycin, gentamicin, vancomycin and teicoplanin antibiotics at common doses added to bone cement. Jt Dis Relat Surg. 2020;31(2):328-334.
[18] HASEEB A, AJIT SV, TEH C, et al. Addition of ceftaroline fosamil or vancomycin to PMMA: An in vitro comparison of biomechanical properties and anti-MRSA efficacy. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019; 27(2):615510612.
[19] MORIMOTO Y, YO H, OHASHI H. Two-stage revision using antifungal-loaded cement beads for the treatment of Candida infection following revision total hip arthroplasty: A case report. J Orthop Sci. 2021;26(3): 505-509.
[20] RELVAS-SILVA M, PINHO AR, VITAL L, et al. Azole-resistant Candida albicans Spondylodiscitis After Bariatric Surgery:A Case Report. JBJS Case Connect. 2020;10(3):e1900618.
[21] KIM JK, LEE DY, KANG DW, et al. Efficacy of antifungal-impregnated cement spacer against chronic fungal periprosthetic joint infections after total knee arthroplasty. Knee. 2018;25(4):631-637.
[22] ATHANS V, VEVE MP, DAVIS SL.Trowels and Tribulations:Review of Antimicrobial-Impregnated Bone Cements in Prosthetic Joint Surgery. Pharmacotherapy. 2017;37(12):1565-1577.
[23] 袁虎成,马文鑫,王骞,等.载抗结核药骨水泥的筛选、制备及物理性能测定[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(12):2260-2263.
[24] MENSAH LM, LOVE BJ. A meta-analysis of bone cement mediated antibiotic release: Overkill, but a viable approach to eradicate osteomyelitis and other infections tied to open procedures. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;123:111999.
[25] XU YM, PENG HM, FENG B, et al. Progress of antibiotic-loaded bone cement in joint arthroplasty. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020;133(20):2486-2494.
[26] SLANE J, GIETMAN B, SQUIRE M. Antibiotic elution from acrylic bone cement loaded with high doses of tobramycin and vancomycin. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(4):1078-1085.
[27] GANDOMKARZADEH M, MAHBOUBI A, MOGHIMI HR. Release behavior, mechanical properties, and antibacterial activity of ciprofloxacin-loaded acrylic bone cement: a mechanistic study. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2020;46(8):1209-1218.
[28] KIM S, BISHOP AR, SQUIRE MW, et al. Mechanical, elution, and antibacterial properties of simplex bone cement loaded with vancomycin. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;103:103588.
[29] MEEKER DG, COOPER KB, RENARD RL, et al. Comparative Study of Antibiotic Elution Profiles From Alternative Formulations of Polymethylmethacrylate Bone Cement. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(7): 1458-1461.
[30] ATICI T, SAHIN N, CAVUN S, et al. Antibiotic release and antibacterial efficacy in cement spacers and cement beads impregnated with different techniques: In vitro study. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2018;29(2):71-78.
[31] FREW NM, CANNON T, NICHOL T, et al. Comparison of the elution properties of commercially available gentamicin and bone cement containing vancomycin with ‘home-made’ preparations. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(1):73-77.
[32] AJIT SV, CHUN HB, HASEEB A, et al. Hand-mixed vancomycin versus commercial tobramycin cement revisited: A study on mechanical and antibacterial properties. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2019;27(2): 615499904.
[33] SUNDBLAD J, NIXON M, JACKSON N, et al. Altering polymerization temperature of antibiotic-laden cement can increase porosity and subsequent antibiotic elution. Int Orthop. 2018;42(11):2627-2632.
[34] CYPHERT EL, LEARN GD, MARQUES DW, et al. Antibiotic Refilling, Antimicrobial Activity, and Mechanical Strength of PMMA Bone Cement Composites Critically Depend on the Processing Technique. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(7):4024-4035.
[35] CYPHERT EL, LEARN GD, HURLEY SK, et al. An Additive to PMMA Bone Cement Enables Postimplantation Drug Refilling, Broadens Range of Compatible Antibiotics, and Prolongs Antimicrobial Therapy. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(21):e1800812.
[36] ISSIN A, KOCKARA N. Simple method for increasing drug elution from polymethylmethacrylate bone cement. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2017; 28(2):100-106.
[37] CHEN L, TANG Y, ZHAO K, et al. Fabrication of the antibiotic-releasing gelatin/PMMA bone cement. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;183: 110448.
[38] SANZ-RUIZ P, CARBO-LASO E, DEL RJ, et al. Microencapsulation of rifampicin: A technique to preserve the mechanical properties of bone cement. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(1):459-466.
[39] AL TY, YANG L, JONES SA, et al. LbL-assembled gentamicin delivery system for PMMA bone cements to prolong antimicrobial activity. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e207753.
[40] LETCHMANAN K, SHEN SC, NG WK, et al. Mechanical properties and antibiotic release characteristics of poly(methyl methacrylate)-based bone cement formulated with mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;72:163-170.
[41] LIANG ZC, YANG C, DING X, et al. Carboxylic acid-functionalized polycarbonates as bone cement additives for enhanced and sustained release of antibiotics. J Control Release. 2021;329:871-881.
[42] AZUARA G, GARCIA-GARCIA J, IBARRA B, et al. Experimental study of the application of a new bone cement loaded with broad spectrum antibiotics for the treatment of bone infection. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol (Engl Ed). 2019;63(2):95-103.
[43] PARRA-RUIZ FJ, GONZALEZ-GOMEZ A, FERNANDEZ-GUTIERREZ M, et al. Development of advanced biantibiotic loaded bone cement spacers for arthroplasty associated infections. Int J Pharm. 2017;522(1-2):11-20.
[44] FARHAN-ALANIE MM, BURNAND HG, WHITEHOUSE MR. The effect of antibiotic-loaded bone cement on risk of revision following hip and knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2021;103-B(1):7-15.
[45] JAMESON SS, ASAAD A, DIAMENT M, et al. Antibiotic-loaded bone cement is associated with a lower risk of revision following primary cemented total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 731,214 cases using National Joint Registry data. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(11):1331-1347.
[46] BENDICH I, ZHANG N, BARRY JJ, et al. Antibiotic-Laden Bone Cement Use and Revision Risk After Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in U.S. Veterans. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(22):1939-1947.
[47] NAMBA RS, PRENTICE HA, PAXTON EW, et al. Commercially Prepared Antibiotic-Loaded Bone Cement and Infection Risk Following Cemented Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020; 102(22):1930-1938.
[48] LENGUERRAND E, WHITEHOUSE MR, BESWICK AD, et al. Risk factors associated with revision for prosthetic joint infection after hip replacement: a prospective observational cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(9):1004-1014.
[49] KONG L, CAO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection following primary total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Int Wound J. 2017;14(3):529-536.
[50] BLANCO JF, DIAZ A, MELCHOR FR, et al. Risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020;140(2):239-245.
[51] GRUBHOFER F, IMAM M A, WIESER K, et al. Staged Revision With Antibiotic Spacers for Shoulder Prosthetic Joint Infections Yields High Infection Control. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(1):146-152.
[52] ORTOLA DJ, FENGA D, MARCELLINO S, et al. Peri-Prosthetic Knee Infection Management: Spacers Loaded with Two or Three Antibiotic Agents. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2017;18(5):619-624.
[53] JIA C, WANG X, YU S, et al. An antibiotic cement-coated locking plate as a temporary fixation for treatment of infected bone defects: a new method of stabilization. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):44.
[54] WANG X, WANG S, XU J, et al. Antibiotic cement plate composite structure internal fixation after debridement of bone infection. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):16921.
[55] CHO JW, KIM J, CHO WT, et al. Antibiotic coated hinged threaded rods in the treatment of infected nonunions and intramedullary long bone infections. Injury. 2018;49(10):1912-1921.
[56] RUPP M, WALTER N, ISMAT A, et al. Polymethyl methacrylate cement coating of intramedullary implants: A new technique for revision surgery with the example of a temporary knee arthrodesis. Video article. Orthopade. 2021;50(9):758-762.
[57] BEAUPRE LA, STAMPE K, MASSON E, et al. Health-related quality of life with long-term retention of the PROSthesis of Antibiotic Loaded Acrylic Cement system following infection resolution in low demand patients. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017;25(2):613376545.
[58] ELMARSAFI T, OLIVER NG, STEINBERG JS, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Permanent Cement Spacers in the Infected Foot. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2017;56(2):287-290.
[59] 张宝成,元玲,蔡贤华,等.抗生素骨水泥联合负压封闭引流术治疗软组织感染[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(23):2190-2192.
[60] 叶远坚,郭子诚,刘沛辰,等.抗生素骨水泥在肢体开放性损伤伴软组织缺损创面治疗中的疗效观察[J].医学理论与实践,2021, 34(4):614-615.
[61] 屈增辉,王莎.抗生素骨水泥结合股前外游离皮瓣治疗创伤性胫骨骨髓炎伴皮肤软组织缺损的效果[J].临床医学研究与实践,2021, 6(10):68-70.
[62] 杨焕友,王斌,李瑞国,等.皮瓣联合抗生素骨水泥链珠在手部骨与软组织感染创面的应用研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2021,37(3): 177-179.
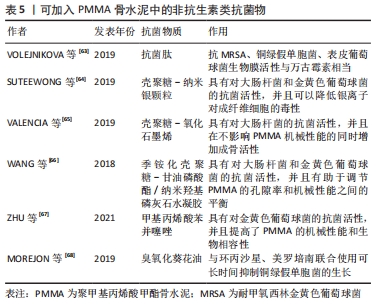
[63] VOLEJNIKOVA A, MELICHERCIK P, NESUTA O, et al. Antimicrobial peptides prevent bacterial biofilm formation on the surface of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement. J Med Microbiol. 2019;68(6): 961-972.
[64] SUTEEWONG T, WONGPREECHA J, POLPANICH D, et al. PMMA particles coated with chitosan-silver nanoparticles as a dual antibacterial modifier for natural rubber latex films. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019;174:544-552.
[65] VALENCIA ZM, MINA HJ, GRANDE TC, et al. Novel Bioactive and Antibacterial Acrylic Bone Cement Nanocomposites Modified with Graphene Oxide and Chitosan. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(12):2938.
[66] WANG M, SA Y, LI P, et al. A versatile and injectable poly (methyl methacrylate) cement functionalized with quaternized chitosan-glycerophosphate/nanosized hydroxyapatite hydrogels. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;90:264-272.
[67] ZHU W, LIU F, YU B, et al. Preparation of antibacterial acrylic bone cement with methacrylate derived from benzothiazole. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;117:104403.
[68] MOREJON AL, FERNANDEZ TI, ZAYAS TA, et al. Antibacterial effect of acrylic bone cements loaded with drugs of different action’s mechanism. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2019;13(6):487-495.
|