中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (5): 795-803.doi: 10.12307/2023.979
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨科止血材料临床应用的优势、不适与面临的挑战
刘 闯1,2,单 烁3,于腾波3,周 欢2,杨 磊2
- 河北工业大学,1材料科学与工程学院,2生命科学与健康工程学院,健康科学与工程研究中心,河北省生物医学材料与智能诊疗重点实验室,天津市 300131;3青岛大学附属医院运动医学科,山东省青岛市 266100
-
收稿日期:2022-11-07接受日期:2023-02-14出版日期:2024-02-18发布日期:2023-08-17 -
通讯作者:周欢,博士,副研究员,硕士生导师,河北工业大学生命科学与健康工程学院,健康科学与工程研究中心,河北省生物医学材料与智能诊疗重点实验室,天津市 300131 于腾波,博士,教授,主任医师,副院长,青岛大学附属医院运动医学科,山东省青岛市 266100 杨磊,博士,教授,博士生导师,院长,河北工业大学生命科学与健康工程学院,健康科学与工程研究中心,河北省生物医学材料与智能诊疗重点实验室,天津市 300131 -
作者简介:刘闯,男,1997年生,河南省驻马店市人,汉族,硕士,主要从事生物材料和医疗器械等相关研究。 单烁,男,1995年生,北京市人,汉族,硕士,主要从事运动医学等相关研究。 -
基金资助:科技部重点研发计划(2020YFC1107400),项目参与者:杨磊、周欢;国家自然科学基金杰出青年基金(82025025),项目负责人:杨磊;国家自然科学基金青年科学基金(31802022),项目参与者:于腾波;河北省自然基金绿色通道项目(C2021202003),项目负责人:周欢;河北省自然基金创新研究群体项目(H2022202007),项目负责人:杨磊;天津市多元投入基金项目面上项目(21JCYBJC01030),项目负责人:周欢;国家骨科与运动康复临床医学研究中心创新基金项目(2021-NCRC-CXJJ-ZH-17),项目参与者:杨磊、周欢
Advantages, discomfort and challenges of clinical application of orthopedic hemostatic materials
Liu Chuang1, 2, Shan Shuo3, Yu Tengbo3, Zhou Huan2, Yang Lei2
- 1School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China; 2Center for Health Science and Engineering, Hebei Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Smart Theranostics, School of Health Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China; 3Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266100, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-07Accepted:2023-02-14Online:2024-02-18Published:2023-08-17 -
Contact:Zhou Huan, PhD, Associate researcher, Master’s supervisor, Center for Health Science and Engineering, Hebei Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Smart Theranostics, School of Health Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China Yu Tengbo, PhD, Professor, Chief physician, Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266100, Shandong Province, China Yang Lei, PhD, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Center for Health Science and Engineering, Hebei Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Smart Theranostics, School of Health Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China -
About author:Liu Chuang, Master, School of Materials Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China; Center for Health Science and Engineering, Hebei Key Laboratory of Biomaterials and Smart Theranostics, School of Health Sciences and Biomedical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin 300131, China Shan Shuo, Master, Department of Sports Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266100, Shandong Province, China -
Supported by:Key Research and Development Program of Ministry of Science and Technology, No. 2020YFC1107400 (to YL, ZH [project participant]); National Natural Science Foundation of China for Distinguished Young Scholars, No. 82025025 (to YL); National Natural Science Foundation of China for Youth, No. 31802022 (to YTB [project participant]); Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province of China (Green Channel Project), No. C2021202003 (to ZH); Innovation Research Group Project of Science Foundation of Hebei Province, No. H2022202007 (to YL); Tianjin Multi-Input Fund Project (General Project), No. 21JCYBJC01030 (to ZH); National Center for Orthopedics and Exercise Rehabilitation Clinical Medicine Innovation Fund Project, No. 2021-NCRC-CXJJ-ZH-17 (to YL, ZH [project participant])
摘要:
文题释义:
骨蜡:是骨科手术、胸外科手术及牙科手术中常用的骨科止血填塞剂。它主要是由蜂蜡和凡士林等软化剂或石蜡与棕榈酸异丙酯的混合物组成,其不可降解,具有较强的疏水性。手术中使用时,先放入手心稍作升温后,即可任意搓揉和塑形,并可填塞到骨渗血处实现物理封堵止血。骨骼:是人体运动系统的重要组成部分,含有大量的毛细血管。骨创面的出血往往为渗血,因为骨骼内部的结构松散、血运丰富,所以从表面上看没有血管断裂那样出血迅速,但并不意味出血量少,短时间内如未能有效止血,患者生命安全将难以保证。
背景:骨蜡是可用于骨止血的填塞剂,国内外虽一直在修正骨蜡配方,但无法改变其难以被吸收的核心瓶颈,因此开发具有止血、成骨和抗菌等功能化的骨科止血材料替代骨蜡具有迫切的临床需求。
目的:回顾包括骨蜡和其替代材料在内的骨科止血材料的发展历程。方法:检索PubMed、Web of Science、万方数据库、中国知网及维普数据库中与骨蜡、止血材料、骨科止血材料研究进展相关的文献,并通过阅读文章中的摘要部分初筛,选择了136篇文献纳入综述。
结果与结论:为替代传统骨蜡,研究人员从止血、成骨等实际场景的需求出发,开发出各式骨科止血材料,但相关研究多集中于基础的理化和性能测试,缺乏系统的评价体系,同时欠缺足够的大动物实验和临床试验报道。因此,目前骨蜡依旧是公认的骨科止血材料,其根本原因是已有材料的设计无法适时满足术中止血、术后成骨及临床上的新需求。未来还需要对现有止血和成骨材料的结构、组分和功能进行整合和再设计,以满足不断提高的止血与成骨需求。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3918-6223(刘闯)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘 闯, 单 烁, 于腾波, 周 欢, 杨 磊. 骨科止血材料临床应用的优势、不适与面临的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 795-803.
Liu Chuang, Shan Shuo, Yu Tengbo, Zhou Huan, Yang Lei. Advantages, discomfort and challenges of clinical application of orthopedic hemostatic materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(5): 795-803.
20世纪上半叶,中国的医用骨蜡依赖于进口。直到1959年,武汉医学院使用石膏粉和凡士林混合制备了类骨蜡的骨科止血材料,其可通过改变凡士林和石膏的比例来调节材料的软硬度,且止血性能和骨蜡相近[29]。自此至20世纪末,国内诸多医院纷纷开始摸索各种配方的自制骨蜡,其基本是由蜡状质感材料(蜂蜡、石蜡、白蜡等)、麻油/甘油/石蜡油等赋形剂及水杨酸等材料经过特定工序制备而成,并可在其中掺杂各种药物,使其具备无毒、吸水性、黏合性、均匀性和可塑性的特点。例如,河南人民医院的沈国珍医生[18]报道了由87 g蜂蜡、12 g杏仁油或花生油1 g醋柳酸(阿司匹林)组成的骨蜡,具有止血、消炎、镇痛的优点。但是由于生产条件和工艺的限制,医院自制的骨蜡质量无法保障,如蒋永春[30]发现环境温度差异导致所制的骨蜡软硬程度变化明显,从而在搓揉时有显著颗粒感,且堵塞后与血液混合易松散、脱落,难以达到预期的止血效果。在1990年,中国在《中国医院制剂规范》规定了制备骨蜡的章程,但多数医院反映临床效果不佳[16]。沈阳军区总医院郭涛等[31]参照英国进口骨蜡的标准和国内有关文献,制订了骨蜡相关的原料标准、处方、工艺、质量标准和检测方法,起到了一定的示范指导作用。而随着中国食品药品监督管理局将骨蜡纳入第三类医疗器械进行注册监管,骨蜡才正式进入标准化生产的时代。
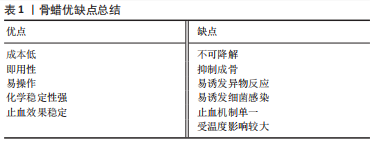
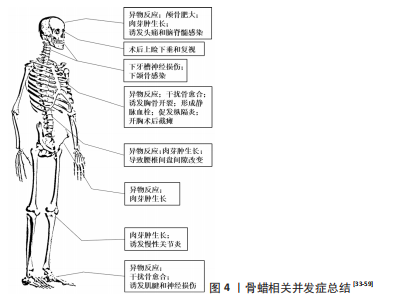
综上所述,国内外骨蜡配方虽一直在改动,但主体材料仍是由石蜡或棕榈酸异丙酯或两者软化的不溶性和不可吸收性蜂蜡组成,这使其优缺点鲜明(表1),虽便于手术操作[32],但易导致术后阻碍骨愈合、材料移位、引发组织感染、异物排斥反应及神经压迫等一系列问题(图4)[33-59]。周大鹏等[60]研究发现,动物实验中使用骨蜡填充出血面时,骨缺损区无骨性愈合,骨蜡无法被吸收,并且随着骨蜡使用剂量的增加,骨创面处发生异物肉芽肿的概率也随之增加。在大鼠颅骨模型中,骨缺损边缘处观察到类似“项圈”的组织包裹着生物惰性骨蜡,延伸至外部骨膜,并在“项圈”外观察到明显的新骨生成,这和“项圈”内情况形成强烈反差[61]。此外,创伤处出现不同程度的炎症、异物反应和纤维化反应。这些观察结果与大鼠胫骨模型中植入骨蜡的实验结果一致[62]。在慢性金黄色葡萄球菌骨髓炎的大鼠模型中,研究人员发现,使用无菌骨蜡的大鼠炎症更严重,具有诱发组织感染的问题[63]。刘锐等[64]追踪了100例开胸手术,发现骨蜡填充后影响胸骨血供和骨质再生,造成胸骨愈合延迟或不愈合及排异反应,较严重者出现伤口处脂肪液化感染。SORRENTI等[65]
使用骨蜡填充人类胫骨,术后6个月时观察到非特异性炎症反应,13个月后炎症反应消失并形成纤维组织。在SOLOMON等[58]的一项临床随机对照研究中,11例用骨蜡控制股骨颈出血的患者组织活检结果显示,全部患有异物性慢性滑膜炎,其中5例患者同时患有淋巴浆细胞性炎症反应,而在髋关节内骨蜡接触的滑膜附近均出现了不同程度的增厚和充血,这些都属于异物感染的表现。除此以外,骨蜡形成的异物肉芽肿在不同解剖部位会表现出类似肿瘤受压的不同临床表现,例如:1例腰痛病史患者并发腿部无力、截瘫等表现,MRI显示硬膜外肿物压迫脊髓,最终组织病理学验证了该肿物为骨蜡肉芽肿[66]。同样,骨蜡的相关并发症在一些颅面手术中也被报道,例如:FAHRADYAN等[46]发现患者于术中在颅骨后下方使用骨蜡后,术后1周出现了记忆丧失、失语症等症状,随访MRI显示颅脑异物占位及感染灶。因此,在临床中使用无菌骨蜡时必须权衡其利弊。
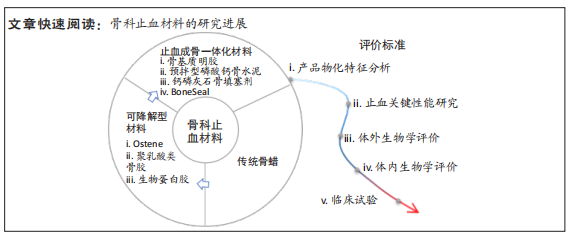
2.2 替代骨蜡的骨科止血材料 骨蜡生物相容性差且难以被机体降解、吸收,对骨愈合造成了很大的阻碍并存在系列的不良反应。尽管研究人员已经从骨蜡的配方、制作工艺等方面进行改进用于减少不良反应发生概率,但由于制备材料本身的限制,难以从根本上解决骨蜡配方中蜂蜡等难以降解的问题,因此,开发新的骨科止血材料成了唯一选项。已知骨渗血创面的修复包括了止血及成骨2个阶段,其中成骨阶段伴随着血管生成,且常出现细菌感染的现象,故国内外骨科止血材料的研究主要围绕这几个方面展开。
2.2.1 止血需求 出血是骨科手术需要面临的一个重要挑战,有效的止血十分必要,如术中不能及时止血,不仅会使患者病情恶化,还会使术者的操作视野模糊不清[67]。松质骨创面的出血往往为渗血,出血后止血困难是因为骨创面组织结构松散,血运丰富形成密布的血窦,组织中血管收缩性差,血凝块难以黏附于创面。虽然骨蜡在骨创面止血手术过程中具有多方面的优势,但在术中、术后存在不可忽视的并发症风险。此外,生理条件下的止血一共分为3个部分,首先是损伤创面反射性的小血管收缩,这一过程不仅受神经调控还受到损伤附近血小板释放的血管活性物质的调节,从而减少局部血流;之后发生一期止血,即血小板受红细胞分泌的腺苷二磷酸和血栓烷A2等物质影响,不断募集更多血小板黏附于损伤附近,形成质地松软的血小板性止血栓;最终机体启动凝血和纤溶系统,大量凝血因子释放,使局部血液凝固完成二期止血[68]。在整个止血过程中,并非按照3部分序贯进行,而是止血、凝血和纤溶3个环节相互协调,最终达到止血的效果[69]。而骨蜡止血仅是机械的物理屏障作用,而且易阻碍血液成分(纤维蛋白和血小板)聚集,不利于自身凝血机制的触发[15]。传统的止血材料,如胶原蛋白和氧化纤维素,虽具备优异的止血机制,但是材料以粉状和片状为主,术中不易操作塑形,而且骨创面黏合性较差、易被血流冲走[70-72]。因此,研究人员以生物可降解和丰富止血机制为切入点,其中止血机制归结为凝血因子引起的血小板凝聚、纤维蛋白产生和材料自身的有效物理封堵,为制备具有如下优点的理想的骨创面止血材料为导向:质地柔软和可塑性强,能够迅速填充创面的裂隙及血窦;具有一定的黏弹性,能够牢固黏附创面,一定时间内不脱落;止血作用完成后可逐渐降解、被机体组织吸收,不影响创面愈合。
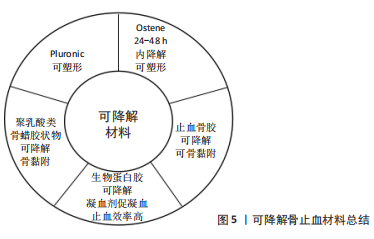
不可降解是传统骨蜡的致命缺陷。为此,在2001年,WANG等[73]使用一种Pluronic可吸收共聚物混合物用于骨止血,共聚物具备亲水性,可以很好地黏附在湿润的骨创面,该类材料处理特性同骨蜡一样,可任意塑形且具有作为抗生素载体的潜力。在此基础上,美国Ceremed公司则于2005年推出了基于环氧烷共聚物的松质骨创面止血材料Ostene,使用方法和骨蜡相似,软化塑形后填塞到骨创面上,该材料可在24-48 h
内完全降解,保证了缺损处的骨愈合可以启动更早[74]。研究表明,该类材料在无组织感染情况下使用,无炎症反应且不阻碍骨愈合,并且在已感染的骨组织中使用既不会增加感染概率,也不会干扰骨愈合[75]。此类材料使用完美地承接了传统骨蜡的临床习惯,但仍未突破材料止血特性单一的缺陷,因此,有研究利用明胶、医用淀粉和抗炎药的混合粉末与生理盐水混合制备了止血骨胶,并通过动物及临床试验验证了该骨胶的骨创面止血效果良好且无不良反应,但需术前再加工且适用骨创面范围小(4-120 mm2),限制了其临床应用。周大鹏等[60]利用低分子量生物可降解材料聚乳酸制备类骨蜡胶状物,可填充松质骨表面裂隙、中止渗血过程,其在动物实验中表现出良好的局部止血作用,但是聚乳酸存在降解后出现局部酸化及炎症的风险。中国医科大学附属第一医院的谷天祥教授团队使用含有高浓度纤维蛋白原及凝血因子ⅩⅢ和含凝血酶原及氯化钙的两种试剂混合后的生物蛋白胶,通过注射治疗胸骨出血,凝血酶及钙离子激活凝血因子ⅩⅢ、裂解纤维蛋白原,最后形成稳定的不溶性纤维蛋白多聚体后,不仅成功止血,而且为创伤组织提供黏合及填充组织的缺损[76]。但目前的研究显示,生物蛋白胶的应用也非绝对安全,国内外均存在生物蛋白胶严重过敏致患者休克的报道[77-78]。可降解骨止血材料总结见图5。
2.2.2 成骨需求 传统骨蜡生物降解能力较差并且在损伤表面形成一层物理屏障,影响了成骨细胞的迁移和血液的供应,严重影响骨愈合[79],因此,在骨蜡替代材料的研究过程中,可吸收性与骨再生之间的联系逐渐紧密,这促使骨科止血材料从单一的止血材料演变为具有止血和成骨一体化的材料。
天然骨生物相容性好,成骨能力强,骨诱导、骨传导活性高,它不仅可以直接与骨结合、促进骨形成,并且可以诱导干细胞向成骨细胞分化[80],因此一直被认为是治疗骨缺损的标准材料[81]。2000年,黄海洋等[82]使用犬骨粉与白芨胶混合制备了骨基质明胶,通过动物实验验证了材料具有优异的止血和成骨能力,但当人体使用时必须使用价格高昂的同种异体骨来构建材料。基于此,研究人员开始探索人工骨材料在骨科止血材料上的可行性。
韦淑玲等[83]报道了由明胶和纳米羟基磷灰石混合制备的止血材料,其中的纳米羟基磷灰石具备优异的骨传导性,可以骨组织的整合和成骨细胞的生长,并且保证了止血材料的质感,使其更加细腻、柔软、易涂。KOKOTT等[84]报道了一种基于氨基化磷酸钙、壳聚糖、氧化淀粉的复合粉体材料,该粉体材料遇水后可以调制成膏状来填充渗血创面,但引入或生成的羟基磷灰石降解速率十分缓慢,有阻碍骨愈合的风险。因此,陈晨等[85]研发出一种纳米生物活性玻璃/壳聚糖/羧甲基纤维素复合材料,以取代传统骨蜡,该材料拥有与骨蜡接近的止血效果,并且其中的生物活性玻璃具有良好的降解性能,降解产生的物质可促进细胞增殖、生长因子的产生、成骨细胞中的基因表达及骨组织的生长。此外,生物活性玻璃是目前唯一既可与骨组织结合的同时,又可与软组织相连的人工合成的生物材料。遗憾的是,这类材料虽具备可降解、止血及成骨功能,但失去了骨蜡的即用性和可操作性,这一理念和传统骨蜡的自身特性及临床习惯是背道而驰。美国的TRISTAN THAM开发了一种由羟基磷灰石和可降解的聚乳酸组成的具有蜡质特性的材料(BoneSeal)[79],它不仅止血能力和操作手感与传统骨蜡相似,而且具备一定的成骨性能,目前已进入市场转化。
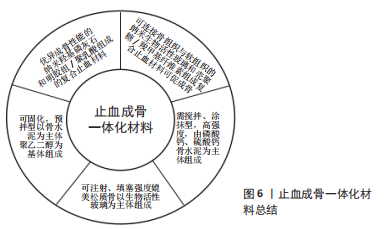
另一种方案是采用生物陶瓷骨水泥用于骨止血。生物陶瓷骨水泥也常称作骨黏固剂,是骨科手术中常用的一种骨修复材料,其具有可注射、可降解、可塑性、生物相容性良好、骨整合、骨传导等特点,可用于复杂松质骨创面的填塞。美国Skeletal Kinetics公司提出了基于磷酸钙骨水泥的Calcium Apatite Bone Tamponade (CAAP)[86-87],CAAP的操作与磷酸钙骨水泥类似,包括将粉末和反应液倒入搅拌器皿后手工混匀形成膏体,后直接用于填充或注射到骨创面固化后形成支架,多余的膏体需在固化前及时移除。ZHOU等[88]以羟丙基甲基纤维素或海藻酸钠为改性剂制备了硫酸钙水泥复合材料,该材料与水接触后会逐渐固化,形成物理屏障及释放Ca2+来止血和促进新骨生成。但由于该类材料主要由降解较快的硫酸钙和凝胶构成,无法在力学和降解上适配骨组织的再生过程。CAO等[89]将硅酸盐三钙水泥、58S生物活性玻璃/壳聚糖/羧甲基纤维素与磷酸二氢钾固化溶液混合开发了一种自固化骨蜡替代物,通过注射到骨创面出血处达到止血及成骨效果,机械强度最高可接近10 MPa。生物陶瓷水泥基材料也有一定的缺点,医生在使用前必须手动混合粉末和固化剂,增加术前操作步骤和感染的风险,而且由于其固化反应启动后难以停止,无法按需随时进行创面填塞。因此,BRüCKNER等[90]基于预拌型磷酸钙骨水泥的设计理念报道了一种基于聚乙二醇、预胶化淀粉、磷酸钙骨水泥的可塑形的复合材料,但是该类复合材料由于磷酸钙骨水泥各反应组分和大量易吸水的聚乙二醇、预胶化淀粉预混在一起,存在储存过程中易引发固化反应,进而有影响产品质量的风险及抗溃散性能不佳等问题。止血成骨一体化材料总结见图6。
2.2.3 抗菌与成血管需求 上述国内外研究进展表明,目前已知的骨科止血材料着重于术前的止血和使用时的可操作性,以及术后的可降解性、生物相容性和促成骨能力,但随着骨组织修复研究领域的不断发展和临床中骨组织感染案例的接连报道,研究人员对消炎抗菌和促进骨中血管生成等功能提出了更高的要求。
骨感染也称之为骨髓炎,它可以累及皮质骨、骨小梁、骨髓和骨膜,多为金黄色葡萄球菌感染,是由复杂的开放性骨损伤或术后感染所致,患者不仅有炎症表现还会有窦道、骨坏死甚至脓毒败血症等临床表现,从而危及生命[91-92]。因骨骼解剖特性较为特殊,松质骨血运丰富,细菌一旦滋生,除非手术干预,否则即使静脉使用大量抗生素,药物在局部病灶组织中也难以达到消灭细菌所需要的有效作用浓度,使得骨感染难以彻底控制[93]。早在1977年,医生们在制备传统骨蜡时就会加入醋柳酸(阿司匹林)、万古霉素等抗炎药物[94]。李振宏等[95]利用骨蜡作为万古霉素的载体混合制备了抗菌骨蜡,并研究了其在体外的释放及抗菌性能。MADSBOELL等[96]使用富含庆大霉素的水溶性聚合物蜡治疗猪胸骨感染,这种水溶性聚合物蜡可以在48 h内通过肾脏代谢,将其与含有庆大霉素的骨蜡进行对比,分别获取实验猪处死前体温、C-反应蛋白、白细胞计数以及组织标本细菌培养等感染指标,这些结果均表明,聚合物组的感染发生率较骨蜡组更低。德国维尔茨堡大学的BRüCKNER等[90]通过磷酸钙骨水泥结合聚乙二醇和万古霉素合成具备止血、成骨及抗菌的亲水性骨蜡,尽管存在药物突释的现象,但这种亲水性骨蜡的抗菌活性仍然能保持大约5 d。虽然载抗生素骨蜡及其替代材料具有明确的临床需求,但以上材料均是简单的把基体材料与抗生素混合使用,因此,骨止血材料的抗菌能力仍面临诸多挑战,例如:大多骨蜡材料中抗生素前期突释现象明显,后期药物释放量较低,难以保证长期的抑菌性[97-98]。
除材料的抗菌能力外,研究人员在关注到了各类功能离子后也进一步开发了具有骨血管修复功能的骨止血材料[99-103]。YAN等[104]使用含铜离子的硫酸钙粉、泊洛沙姆407、乙酸酯维生素E和羧甲基纤维素钠加水调制成了一种可降解的骨蜡,希望通过铜离子赋予骨蜡血管生成和抗感染能力。法国的PONSEN等[105]开发了一种由富含Zn2+和Ca2+的海藻酸盐型止血剂,使用时只需敷于创面出血处,到达止血目的后移除即可,在此期间所释放的离子可促进血管及其他组织的修复和抗组织感染。
2.3 骨科止血材料转化的瓶颈 骨蜡问世以来,已超百年历史,至今仍被用于骨出血治疗。骨蜡优缺点鲜明,如自身性质(如不可降解)引起的诸多临床并发症、价格便宜和易操作等,学者们也以此为鉴,来开发骨科止血材料。此外,根据Transparency Market Research中题为“骨蜡市场-全球行业分析,规模,份额,增长,趋势和预测,2018-2026年”的市场报告,2017年全球骨蜡的市场规模约为6 880万美元,2018-2026年将以2%的复合年增长率增长,2026年将达到8 420万美元。其中美国占据了市场的主要份额,而且将大力研究和开发或向市场推出性能更为优异的新产品。欧洲地区也因外科手术数量的增加、诸多创新型骨科止血材料被获批、骨病和意外骨折病例的增加,而成为了骨蜡的第二大市场。由于印度和中国等发展中国家推动,亚太地区骨蜡的市场也将以3%的增长率快速增长。但距离骨蜡被报道的两个多世纪以来,一系列的骨科止血材料相继面世,其中仅有极少数的材料进入临床,当前骨蜡依旧作为首选的骨科止血材料。原因正如表2中所示,骨科止血材料因各种方面不足而无法在临床应用上获得成功,例如:不易储存、生物安全性未知、易导致过敏反应等。然而要想完成最终的临床转化,临床医生的实际使用体验、是否可以缩短患者的组织修复时间、减少患者术后相关并发症的发生,这些则变得尤为关键。此外,如何证明新材料能有效替代骨蜡的止血功能,是当前基础研究需要解决的必要问题。在满足止血成骨的基本需求的前提下,为最终获准进入市场,骨科止血材料需要根据监管机构要求进行型式检验和临床试验,以保证其安全性与可靠性。监管机构所规定的标准、方法和技术是产品设计的指导原则,在这个过程中骨科止血材料相关的注册指导意见并不明确[106]。由于骨蜡与其替代材料的差异性,骨蜡的注册标准并不适用于其替代材料。已开发的骨科止血材料介绍见表2。为进一步对此进行说明,对骨科止血材料的可能的临床前评价方法进行了汇总。

2.3.1 产品物化特征分析
生物陶瓷类材料:现已被应用在止血成骨材料中的生物陶瓷包括磷酸钙类、硫酸钙类及生物活性玻璃等。借鉴生物陶瓷填充材料的评价标准,以下物化表征是必要的注册资料:①必要的生物陶瓷的相成分、结晶度、显微形貌、亲疏水性;②已知可降解的材料需要进行降解性能的研究,具体标准可参考GB/T 16886.14-2003《医疗器械生物学评价第14部分:陶瓷降解产物的定性与定量》。此外,有必要对降解的浸出液进行pH值记录;③如预期材料会固化成型则应根据美国ASTMC266-15标准进行固化时间的研究;④材料为块或柱状等规则形状时需要进行力学性能研究,可参照国际标准ISO5833-2002标准(如抗压强度、各向异性等);⑤对于双相或多相陶瓷,进行成分配比优选的研究。
高分子类材料:聚乙二醇、聚乳酸、海藻酸钠、淀粉、羧甲基纤维素钠、Pluronic P85、环氧烷共聚物等材料常直接或预处理后被作为类骨蜡的主体材料或改性剂。此类材料除了需要进行同生物陶瓷类材料评价标准中的显微形貌、力学性能、亲疏水性、结晶度等研究外,还需要研究:材料间新化学键的生成等结合键;吸水率;凝胶类复合材料应对材料的流变学性能。
2.3.2 止血关键性能研究
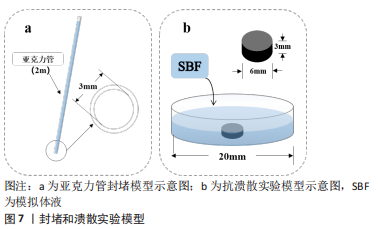
封堵性:到目前为止,封堵性评估实验主要是通过动物模型来实现的,即在动物各个骨部位钻取一定大小和深度的孔作为骨缺损模型,随后使用骨科止血材料观察能否成功封堵、封堵后是否会再次出血和统计一定时间内的出血量研究。动物模型的不足在于,缺少对于打孔的部位、缺损的大小/深度和填塞/止血成功后需观察时间的相关规定。为减少动物的使用,JINTAMAI等[112]提出了体外压力模拟实验,简而言之,在室温下使用填充一定高度水柱的亚克力管(图7a)来模拟骨中毛细血管的压力,当水柱高达1.91 m时,相当于18.68 kPa或140 mmHg,通过监测材料可成功封堵的时间来评估。这一模拟实验设计缺点在于,骨内血液实际上是从骨缺损面扩散渗出,不同于管中的水流动,以及水与血液本就存在巨大差异,无法测试目前具备诸多止血机制的骨科止血材料[113]。
抗溃散性:当前主要通过对材料的抗溃散能力进行研究来评估材料封堵后是否可稳定发挥作用,即不存在脱落或发生渗血现象。此类评估方法是由钙磷灰石骨水泥的研究演变而来,即室温下,在特定大小的容器内加入适当生理盐水等液体来模拟骨科止血材料应用微环境,再将一定大小和形状的骨科止血材料放容器内静止或摇晃一定时间后,观察骨科止血材料的状况,从而评估抗溃散强度[114]。XI等[115]利用此法来直观地评估了掺有支链淀粉磷酸钙水泥体系的抗溃散性能。中国台湾地区的CHIANG等[116]进一步完善了此法,即在37 ℃下,将直径为6 mm、高度为3 mm的材料放入含模拟体液的直径和高度均为20 mm容器中并置于中心(图7b),样品其中材料与模拟体的比率为0.2 g/mL;静止浸泡不同时间后,先直观地评估抗溃散性,再除去模拟体液,加入1 mL 无水乙醇,静置30 s后除去乙醇,将剩余材料在50 ℃下干燥3 d,最终通过计算剩余主体材料质量与初始粉末质量的差值来评估溃散性能。此法的最大争议在于实验中的容器所处环境,即无论是静止还是摇晃状态都难以精确模拟出血部位的实际情况。
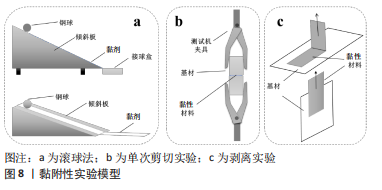
黏附性:组织黏合能力是重要的考察指标,因为它们有助于伤口愈合、止血、组织重建和药物输送[117-118]。黏附力的出现也使得骨科止血材料摆脱了单一的物理封堵性能[82],其与凝胶材料黏附在基材上的机制相似,一是材料直接黏附在粗糙基材上形成“机械性的结合”,另一种方法是材料使用一定相互作用力(氢键、范德华力及化学键等)黏附到基材上[119]。其中黏附力可分为初黏力、持黏力或剥离强度2种[120-121]。
初黏力表示与皮肤轻、快的接触时表现出对皮肤的粘接能力,即所谓的手感黏性;持黏力表示两者间内聚力的大小,即抗持久性剪切外力所引起蠕变破坏的能力,表示黏附力的大小。目前多数研究只报道了持黏力,然而初黏力也是不可忽视的,骨科止血材料在填塞到骨创面的过程中常和多种材料进行短暂的接触,如若初黏力过大将严重干扰医生的手术操作。因此,研究者应根据材料的应用场景去选择是否进行必要的初黏力测试。初黏力的测试法较多,例如滚球法、探针法、快黏法和环黏法等[122]。滚球法虽是最古老的测试方法,也是最为简单直接的,即将不锈钢小球沿特定角度的斜面自由滚下,记录球在材料黏附层移动的距离和球的大小作为评估标准,具体的装置如图8a所示。虽已报道了许多用于表征聚合物持黏力的方法,但结合骨创面止血情景选择以下几种测试方法[123]:①单次剪切实验。美国阿克伦大学的BHAGAT等[122]将打磨后的骨片(2 cm长×0.6 cm宽×0.4 cm厚,使用前1 h将骨骼保存在PBS中)固定在测试机器加持两端,骨黏合剂施加在骨片的一端,操作测试机使两端骨片接触并施压,1 min后以1.3 mm/min的速度拉开,记录失效时的最大载荷(N)作为黏附力。如图8b所示,取两块相同规格的基材,并在其中一块涂上黏合剂,操作测试机压住另一块直至挤出多余的黏合剂后,对两端施加拉伸力,直到2个样品分离,记录最大拉伸力作为黏附力。②剥离实验[124]。如图8c所示,剥离角度分为90°或180°,材料施加一定的压力可以保证材料和基地充分接触。因为材料失效后剥离,所以动态法最为常用。模型90°似乎符合贴剂黏附力的测试的概念,而模型180°更能反映封堵时所受力的场景。此法优点在于可选择不同的基材材料,例如上海大学的WANG等[125]利用2个羟基磷灰石片替代骨片来测试其材料的黏附性。
体外凝血研究:关于体外的凝血性能的测试方法有试管法、玻片法、血凝块法及血小板黏附评价方法。其中,可参考GB/T 14233.2-2005评价标准中的试管法和血小板黏附实验。①试管法:最为直观和简单,取新鲜血液到内径8 mm的聚丙烯试管内后,如测试试样组可参考GB/T 16 886.12规定的浸提比例添加,血液离开动物3 min后,每隔30 s将试管倾斜30°,观察血液是否流动,以试管中血液不再流动、可倒置为截止时间,记录时间作为凝固时间,用以评价凝血能力。玻璃片法简单来说是将0.05 mL新鲜血液滴到已有0.003 4 g样品的洁净玻璃片上,此时开始计时,固定间隔使用针头从血液底部往上缓慢挑起(间隔为15 s),并仔细观察针尖处是否有纤维蛋白丝出现,观察到立即结束计时。实验重复不可低于20次。②凝血血块法:将50 μL新鲜血液滴到载有材料的孔板后,在特定时间点使用1 mL生理盐水反复清洗每个孔以保证血液停止凝结,直至洗出液体变清,表明所有的可溶性血液成分被去除,此时可拍照或测量保留在孔中的血凝块的大小,代表材料促凝的能力。③血小板黏附实验:取新鲜血液,离心(100×g离心10 min);血液将分3层,先把上两层转移到另一试管中,再次离心(1 000×g离心10 min),将近3/4的上清液分离后,剩余液体吹打均匀后得到富血小板血浆;将富血小板血浆依次滴加到样品表面上,并进一步转移到37 ℃环境下培养30 min;结束后用PBS冲洗样品表面未黏附的血小板,并使用戊二醛进行固定(4 ℃,1-2.5 h),最后进行梯度乙醇脱水;脱水完成后自然风干,进一步使用电子扫描电镜观察血小板黏附情况,以血小板形状、是否出现伪足及周围是否生成纤维蛋白等情况作为促进凝血的能力。
2.3.3 体外生物学评价 作为骨止血材料,需要根据GB/T 16886系列标准选择合适的生物学评价方法外,例如骨填充物一般需要进行细胞毒性实验、致敏实验、全身毒性实验、刺激或皮内反应实验、遗传毒性、热源、骨植入实验。同时,还应根据GB/T 14233.2-2005评价标准中的溶血率实验进行材料的血液相容性测试。这里值得注意的是进行生物学评价所使用的应是最终的产品而非实验室的原型,应完成产品的封装、灭菌等步骤后以最终品进行测试。
2.3.4 体内动物实验
体内止血实验:骨出血为松质骨间渗血,所以在选择模型时应尽可能的还原真实出现的场景。髂骨处的松质骨面较大,并且具有丰富的骨孔网络,是生物骨创面出血概率最高的部位,因此,选择此部位评估骨科止血材料的综合止血性能是非常具有代表性的。此外,大鼠模型是可能的评价模型。苏州大学葛隽[126]设计了大鼠的股骨出血模型,选择适当大小的手持电钻在股骨中远端沿股骨冠状位方向钻取直径1.0-
2.0 mm的非贯通孔(仅打穿一层骨皮质),分别使用术前称量的无菌干燥棉球、市售骨蜡和自主设计的类骨蜡材料立即填塞出血处,并不断用干棉球擦拭渗出血液,并拍照记录5 min时的出血情况,运用量差法测定大鼠股骨缺损出血量。这一模型的设计成功还原了松质骨的出血情景,但大鼠的出血量有限,还难以实际模拟人体场景。使用大动物模型,在出血创面系统评价样品的黏附牢固程度、抗溃散及渗血情况等将更接近真实场景,但目前还没有相关报道。
体内成骨实验:首先,在设计成骨实验的动物实验时应考虑如下几个方面:①充分的排除动物自身修复能力的影响,故在选择动物时应选择骨骼已成熟的动物。②实验分组:合理分组,确保结果的科学性。在此建议应设计实验组、同类产品对照组、假手术组。③选择对照样品:首选境内已上市的同类产品。其中,对照样品的尺寸、质量和形状等应尽量与实验样品保持一致。假手术组的动物模型的骨缺损可以不进行处理。④选择合适的观察期:时间的长短应考虑产品的促成骨效果、动物自身的骨生长情况以及材料的降解速率,观察时间点应不少于2个。⑤选择合适的观察指标:需要在观察时间点通过影像学、组织学以及新生骨生物力学性能等方式,以评估产品植入后的降解情况和缺损处的骨再生情况。
2.3.5 新使用场景 伴随临床治疗手段以及内镜技术的蓬勃发展,使得止血材料在骨科领域有越来越多的跨界应用场景,不仅要求材料具备优良的止血特性,还需要具备卓越的成骨能力以及其他适应临床需求的新功能。在年轻患者单侧间室骨关节炎病变中,胫骨高位截骨术已成为主要术式,该手术的目的是将机械轴从膝关节中线的内侧移至略外侧,以最大限度延缓骨关节炎的发展进程,从而推迟骨关节炎患者的膝关节置换时间[127-128]。胫骨高位截骨术在胫骨干骺端做一楔形截骨并使用TomoFix钢板对截骨近端和远端固定从而纠正下肢力线,但这会造成胫骨干骺端楔形骨缺损、骨膜不能闭合,同时干骺端血运丰富易造成截骨平面出血[129]。已有报道称,胫骨高位截骨术后出血的减少可以促进伤口愈合和早期康复[130]。这也就要求具有止血性能的骨科用材料在胫骨高位截骨术中不仅有良好的封堵止血功能,更应具备良好的成骨能力,促进新骨爬行,从而在术后早期为患者下肢提供更良好的力学支撑,达到早期康复的目的。除此以外,骨科与腔镜技术的关系越来越密切,关节镜下前交叉韧带重建术具有创伤小、恢复快等优势[131],该术式需在外侧股骨髁内侧壁上的前交叉韧带覆盖区中心钻取一个骨隧道,从而将选取的重建肌腱穿过其中进行固定[132]。在这一操作过程中,可以使用骨蜡填塞在骨隧道中,这需要骨蜡替代物除止血功能外还应具有更高的黏附性、可塑性以及成骨能力,以此促进腱骨愈合;同时关节镜操作还需时刻保持关节腔内有流动性生理盐水充盈,以保证手术视野,因此,关节镜下应用的骨蜡替代物还应有更强的抗溃散性,以保证其在一定水流冲击强度下仍能保证不脱落。单侧双门内镜近年来在脊柱外科中的应用,使以前需要开放式手术才能治疗的腰椎间盘突出、腰椎管狭窄等疾病可以采用微创治疗且术后康复时间更短[133]。单侧双门内镜技术不仅可以在同侧进行操作,而且对侧椎间孔区域也有良好的视野,同时单独的手术通道也增加了手术操作的可移动范围[134-135]。行微创经椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术时,在植入工作套管后需用咬骨钳切除棘突和椎板以及部分小关节突,从而达到充分的椎管减压并为椎间融合器的植入做准
备[136]。因为椎板和关节突均为松质骨,极易渗血,因此纱布填塞止血往往效果欠佳,此时需要尽快使用骨蜡封闭渗血创面,为后续操作提供良好视野;同时在患者康复期,也需要止血材料有较强的成骨再生能力,使脊柱尽早恢复稳定性。这些止血材料在临床中更为广泛的应用场景也就意味着未来需要新的评价方法和模型适时的与其相适应,例如:在有水流冲击下手术时就需要止血材料符合更高的黏附性评价标准以及抗溃散性标准,从而达到临床需求。

| [1] 秦岭,陈启明,梁国穗.体育运动与骨骼--骨密度和结构与生物力学适应性[J].中国运动医学杂志,2004,23(5):532-536,551. [2] 赵文礼,孙丽丹.64排螺旋CT动脉造影在意外创伤多发骨盆骨折合并盆腔出血诊断中的应用[J].中国现代医药杂志,2021,23(12):76-78. [3] 曹奇勇,王满宜,吴新宝,等.骨盆骨折出血及其治疗[J].国外医学(骨科学分册),2003,24(4):214-216. [4] HICKMAN DA, PAWLOWSKI CL, SEKHON UDS, et al. Biomaterials and Advanced Technologies for Hemostatic Management of Bleeding. Adv Mater. 2018;30(4).10.1002/adma.201700859. doi: 10.1002/adma.201700859. [5] 李保强,方一帆,杨传瑞,等.新型快速止血材料的止血评价与止血机制[J].实验技术与管理,2007,24(7):51-54. [6] 徐浩昌.高频电刀粘贴式负极板及负极板回路垫的安全使用[J].医疗装备,2018,31(7):106-107. [7] 宋立为,李晓亮,苏庆.超声切割止血刀与高强度聚焦超声刀的比较[J].医疗设备信息,2007,22(10): 32-34. [8] 吕晓丹,李勤,胡晓明.激光止血刀匀光系统设计[J].生命科学仪器, 2017,15(5):35-40,55. [9] 李健,赵家宏.新型外用生物止血剂--纤维蛋白胶[J].消化外科,2003, 2(1):72-74. [10] 谢霞,唐杰.局部止血剂的临床研究新进展[J].中国药物应用与监测, 2011,8(5):311-314. [11] 许树梧,李凡年.新型酶性止血剂—立止血[J].湖南医学,1997(1):2. [12] 蒋维连,谢丽霞.骨蜡在颅脑外科钛板固定手术中的应用[J].护士进修杂志,2011,26(6):500. [13] 黄志权,黄子贤,张大明,等.超选择性动脉栓塞联合骨蜡填充法用于儿童颌骨动静脉畸形复通的治疗[C]. 第十三次全国口腔颌面外科学术会议暨中华口腔医学会口腔颌面外科专业委员会成立30周年论文集, 沈阳,2016:500. [14] 胡小灵,郝雪梅.两种骨蜡在手术中应用效果评价[C].全国第十一届手术室护理学术交流会论文集,2007:1052. [15] 殷亚亚,王西玲.骨蜡在颅脑显微手术中的妙用[J].中华现代护理杂志, 2009,15(20):1927. [16] 邹蔼珍.骨蜡处方及制备工艺的改进[J].中国医院药学杂志,1995,15(8): 354. [17] 陈卫民.用骨蜡治疗牙龈持续性出血一例[J].临床口腔医学杂志, 1986(2):120. [18] 沈国珍,华丽荣.骨蜡的应用与制备[J].河南赤脚医生,1980(2):31. [19] DAS JM. Bone Wax in Neurosurgery: A Review. World Neurosurg. 2018;116: 72-76. [20] ZHOU H, GE J, BAI Y, et al. Translation of bone wax and its substitutes: History, clinical status and future directions. J Orthop Translat. 2019;17:64-72. [21] KUHNS CA, COOK CR, DODAM JR, et al. Injectable gelatin used as hemostatic agent to stop pedicle bleeding in long deformity surgical procedures: does it embolize? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(4):218-223. [22] LUHMANN SJ, SUCATO DJ, BACHARIER L, et al. Intraoperative anaphylaxis secondary to intraosseous gelatin administration. J Pediatr Orthop. 2013; 33(5): e58-60. [23] BUCHOWSKI JM, BRIDWELL KH, LENKE LG, et al. Epidural spinal cord compression with neurologic deficit associated with intrapedicular application of hemostatic gelatin matrix during pedicle screw insertion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(13):E473-477. [24] GUPTA G, PRESTIGIACOMO CJ. From sealing wax to bone wax: predecessors to Horsley’s development. Neurosurg Focus. 2007;23(1):E16. [25] ELLIS H. Horsley’s wax. J Perioper Pract. 2007;17(2):82-83. [26] PARKER R. Aural pyaemia successfully treated by removing putrid thrombus of jugular vein and lateral sinus. Br Med J. 1892;1:1076-1077. [27] SHERWOOD WA. Minor and operative surgery, including bandaging. Ann Surg. 1906;44(3):475-476. [28] SIMMONS CC. VI. Bone Abscess Treated with Moorhof’s Bone Wax: A Report of Five Cases. Ann Surg. 1911;53(1):67-76. [29] 武汉医学院第二附属医院手术室全体护士.用石膏制品代替骨蜡点滴经验[J].护理杂志,1959(4):162. [30] 蒋永春.骨蜡的处方改进[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2007,6(12):119. [31] 郭涛,马洪升,牟平,等.医用无菌骨蜡的研制及临床观察[J].中国药房,2002,13(5):276-277. [32] 王文涛.新型可吸收止血材料——可吸收骨蜡的研发和制备[D].上海:中国人民解放军海军军医大学,2018. [33] 傅仰攀,黄长明,王建雄.骨蜡残留致腰椎骨折内固定取出术后伤口不愈合1例[J].颈腰痛杂志,2009,30(3):286. [34] 许德荣,王海,吴志宏,等.一种具有止血功能的可吸收骨蜡及其制备方法[P].中国专利:CN109675094A,2019-04-26. [35] 张建文,曹思佳,于江,等.骨蜡致下颌角磨削术后继发脓肿2例[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(5):684-685. [36] 张臻,刘磊,王维新,等.心脏外科胸部正中切口异物反应的防治[J].医药前沿,2013(30):206-207. [37] QAYUM A, KOKA AH. Foreign body reaction to bone wax an unusual cause of persistent serous discharge from iliac crest graft donor site and the possible means to avoid such complication - a case report. Cases J. 2009;2(1):9097. [38] ALHAN C, ARıTüRK C, SENAY S, et al. Use of bone wax is related to increased postoperative sternal dehiscence. Kardiochir Torakochirurgia Pol. 2014; 11(4):385-390. [39] ALLEN-WILSON N, BEATTY R, SHARPE J. Severe bone wax foreign-body reaction causing peroneal tendon destruction. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc. 2015;105(1):74-79. [40] ATEŞ O, CAYLI SR, GüRSES I. Bone wax can cause foreign body granuloma in the medulla oblongata. Br J Neurosurg. 2004;18(5):538-540. [41] BAIRD SM, TEH BM, LIM KKM, et al. Bone wax extrusion through postauricular wounds: A case series. Laryngoscope. 2018;128(2):369-372. [42] BYRNS K, KHASGIWALA A, PATEL S. Migration of Bone Wax into the Sigmoid Sinus after Posterior Fossa Surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2016;37(11): 2129-2133. [43] CHOI BK, YANG EJ. Delayed infection after using bone wax in maxillofacial surgery: A rare complication after reduction mandibuloplasty. Wound Med 2017;17:18-23. [44] CROCKER M, NESBITT A, RICH P, et al. Symptomatic venous sinus thrombosis following bone wax application to emissary veins. Br J Neurosurg. 2008; 22(6):798-800. [45] ESER O, COSAR M, ASLAN A, et al. Bone wax as a cause of foreign body reaction after lumbar disc surgery: a case report. Adv Ther. 2007;24(3):594-597. [46] FAHRADYAN A, OHANISIAN L, TSUHA M, et al. An Unusual Complication of Bone Wax Utilization. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29(4):976-979. [47] OZERDEM G, HIDIROGLU M, KUCUKER A, et al. Bone wax as a cause of a foreign body granuloma in a resternotomy : a case report. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;8(Suppl 1):P121. [48] HILL J, LITTLE J, FORD T. Bone wax: a foreign body/giant cell reaction in the foot. Foot Ankle Spec. 2013;6(3):236-238. [49] CHUN PK, VIRMANI R, MASON TE, et al. Bone wax granuloma causing saphenous vein graft thrombosis. Am Heart J. 1988;115(6):1310-1313. [50] KAMIDE T, NAKADA M, HIROTA Y, et al. Skull osteohypertrophy as a complication of bone wax. J Clin Neurosci. 2009;16(12):1658-1660. [51] KATRE C, TRIANTAFYLLOU A, SHAW RJ, et al. Inferior alveolar nerve damage caused by bone wax in third molar surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010; 39(5):511-513. [52] KUMAR A, KALE SS, DUTTA R, et al. Post-thoracotomy paraplegia due to epidural migration of bone wax. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;35(4):734-736. [53] LOW WK, SIM CS. Bone wax foreign body granuloma in the mastoid. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2002;64(1):38-40. [54] MAKI Y, ISHIBASHI R, YAMADA D, et al. Postoperative Ptosis and Diplopia Induced by the Intraoperative Application of Bone Wax. World Neurosurg. 2017;103:951.e1-951.e3. [55] OZDEMIR N, GELAL MF, MINOGLU M, et al. Reactive changes of disc space and foreign body granuloma due to bone wax in lumbar spine. Neurol India. 2009;57(4):493-496. [56] PATEL RB, KWARTLER JA, HODOSH RM. Bone wax as a cause of foreign body granuloma in the cerebellopontine angle. Case illustration. J Neurosurg. 2000;92(2):362. [57] SPENNATO P, ENRIQUEESCAMILLA-RODRìGUEZ I, DI MARTINO G, et al. Intraventricular bone wax as cause of recurrent cerebrospinal fluid infection: a neuroradiologic pitfall. World Neurosurg. 2016;88:690.e7-690.e9. [58] SOLOMON LB, GUEVARA C, BüCHLER L, et al. Does bone wax induce a chronic inflammatory articular reaction? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012; 470(11):3207-3212. [59] WOLVIUS EB, VAN DER WAL KG. Bone wax as a cause of a foreign body granuloma in a cranial defect: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003; 32(6):656-658. [60] 周大鹏,祖启明.聚乳酸骨止血胶用于松质骨创面止血的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(5):511-514. [61] ALBERIUS P, KLINGE B, SJöGREN S. Effects of bone wax on rabbit cranial bone lesions. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 1987;15(2):63-67. [62] HOWARD TC, KELLEY RR. The effect of bone wax on the healing of experimental rat tibial lesions. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1969;63:226-232. [63] JOHNSON P, FROMM D. Effects of bone wax on bacterial clearance. Surgery. 1981;89(2):206-209. [64] 刘锐,李辉,杨俊峰,等.可吸收止血胶原海绵在心脏外科术中胸骨止血的应用体会[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014,33(5):719-721. [65] SORRENTI SJ, CUMMING WJ, MILLER D. Reaction of the human tibia to bone wax. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1984;(182):293-296. [66] KARABEKıR HS, KORKMAZ S. Residue bone wax simulating spinal tumour: a case report. Turk Neurosurg. 2010;20(4):524-526. [67] YI S, TAN J, CHEN C, et al. The use of pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(10): 1469-1476. [68] LASNE D, JUDE B, SUSEN S. From normal to pathological hemostasis. Can J Anaesth. 2006;53(6 Suppl):S2-11. [69] GANDO S. Hemostasis and thrombosis in trauma patients. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2015;41(1):26-34. [70] 汪向飞,张晓丹,周汉新.生物医用可吸收止血材料的研究与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(21):3973-3976. [71] 张少锋,洪加源.医用生物可吸收止血材料的研究现状与临床应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(21):3941-3944. [72] 魏海红.生物医用可吸收止血材料的临床应用[J].世界临床医学,2016, 10(7):80. [73] WANG MY, ARMSTRONG JK, FISHER TC, et al. A new, pluronic-based, bone hemostatic agent that does not impair osteogenesis. Neurosurgery. 2001; 49(4):962-967;discussion 8. [74] WELLISZ T, ARMSTRONG JK, CAMBRIDGE J, et al. Ostene, a new water-soluble bone hemostasis agent. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17(3):420-425. [75] WELLISZ T, AN YH, WEN X, et al. Infection rates and healing using bone wax and a soluble polymer material. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(2):481-486. [76] 张玉海,谷天祥,张光伟,等.生物蛋白胶胸骨内注射治疗老年骨质疏松冠状动脉搭桥后的胸骨出血[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(25):4735-4738. [77] 张大志,王庚.医用生物蛋白胶致严重过敏性休克一例[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2010(12):1069. [78] DIETRICH W, EBELL A, BUSLEY R, et al. Aprotinin and anaphylaxis: analysis of 12,403 exposures to aprotinin in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007; 84(4):1144-1150. [79] THAM T, ROBERTS K, SHANAHAN J, et al. Analysis of bone healing with a novel bone wax substitute compared with bone wax in a porcine bone defect model. Future Sci OA. 2018;4(8):Fso326. [80] ZHANG J, LIU W, SCHNITZLER V, et al. Calcium phosphate cements for bone substitution: chemistry, handling and mechanical properties. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(3):1035-1049. [81] MYEROFF C, ARCHDEACON M. Autogenous bone graft: donor sites and techniques. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(23):2227-2236. [82] 黄海洋,刘晋才,柳峰,等.可吸收止血成骨胶对松质骨创面止血和诱导成骨作用的实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报,2000,22(8):780-783. [83] 韦淑玲,吴珊.一种医用的骨创面止血材料及其制备方法[P].中国: CN106215225B,2021-02-12. [84] KOKOTT A, HOFFMANN B, VOLKMER E. A new biodegradable bone wax substitute with the potential to be used as a bone filling material. J Mater Chem. 2007;17(38):4028-4033. [85] 陈晨,阎作勤,郭常安.新型可止血纳米生物玻璃/壳聚糖/羧甲基纤维素复合支架修复骨缺损[C].第四届长三角地区创伤学术大会暨2014年浙江省创伤学术年会,2014. [86] MUEHRCKE DD, BARBERI P, SHIMP WM. Calcium phosphate cements to control bleeding in osteoporotic sternums. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(1):259-261. [87] MUEHRCKE DD, SHIMP WM, APONTE-LOPEZ R. Calcium phosphate cements improve bone density when used in osteoporotic sternums. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88(5):1658-1661. [88] ZHOU H, YANG M, NI X, et al. Using calcium sulfate cement-Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose/sodium alginate composites as substitutes of bone wax. Int J Appl Ceram Technol. 2018;15(4):903-909. [89] CAO W, PENG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Novel bone wax based on tricalcium silicate cement and BGs mixtures. Biomed Mater. 2018; 13(6): 065001. [90] BRÜCKNER T, SCHAMEL M, KüBLER AC, et al. Novel bone wax based on poly(ethylene glycol)-calcium phosphate cement mixtures. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:252-263. [91] 王文,蔡锦方.抗生素在骨髓炎治疗中的局部应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(17):1328-1330. [92] LEW DP, WALDVOGEL FA. Osteomyelitis. Lancet. 2004;364(9431):369-379. [93] 刘飞,崔宇韬,刘贺.局部抗生素递送系统治疗骨髓炎的优势与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):614-620. [94] RAGUSA R, FAGGIAN G, RUNGATSCHER A, et al. Use of gelatin powder added to rifamycin versus bone wax in sternal wound hemostasis after cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2007;6(1):52-55. [95] 李振宏,梁瑞德,林英,等.万古霉素骨蜡复合体体外释放研究[J].广西医学,2017,39(8):1207-1209,1214. [96] MADSBOELL TK, VESTERGAARD RF, ANDELIUS TC, et al. Gentamicin-enriched, water-soluble polymer wax reduces the burden of infection after sternotomy in pigs. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2014;45(3):476-480. [97] 杨骐宁.抗生素骨水泥的药释特性和增效思路[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2011,5(3):369-373. [98] DROGNITZ O, THORN D, KRüGER T, et al. Release of vancomycin and teicoplanin from a plasticized and resorbable gelatin sponge: in vitro investigation of a new antibiotic delivery system with glycopeptides. Infection. 2006;34(1):29-34. [99] 罗堃,范兆心,冯喆,等.铜离子对血管内皮细胞增殖与分化的影响[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2009,23(7):832-835. [100] 毕晓云,黄舒,郭杰,等.锌离子促进人骨髓间充质干细胞增殖并增强其纤黏连蛋白表达的实验研究[J]. 组织工程与重建外科杂志,2013,9(2): 81-84. [101] BOSE S, FIELDING G, TARAFDER S, et al. Understanding of dopant-induced osteogenesis and angiogenesis in calcium phosphate ceramics. Trends Biotechnol. 2013;31(10):594-605. [102] HENDERSON SJ, XIA J, WU H, et al. Zinc promotes clot stability by accelerating clot formation and modifying fibrin structure. Thromb Haemost. 2016;115(3):533-542. [103] ELTOHAMY M, KUNDU B, MOON J, et al. Anti-bacterial zinc-doped calcium silicate cements: Bone filler. Ceram Int. 2018;44(11):13031-13038. [104] YAN F, LV M, ZHANG T, et al. Copper-Loaded Biodegradable Bone Wax with Antibacterial and Angiogenic Properties in Early Bone Repair. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021;7(2):663-671. [105] PONSEN AC, PROUST R, SOAVE S, et al. A new hemostatic agent composed of Zn(2+)-enriched Ca(2+) alginate activates vascular endothelial cells in vitro and promotes tissue repair in vivo. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:368-382. [106] XU S, ZHONGLAN T, WENBO L, et al. Biomaterials and regulatory science. J Mater Sci Technol. 2022;128:221-227. [107] 缪华,张伟中,吴克勤,等.骨胶止血的临床应用[J].中国医院药学杂志,1986,6(1): 48. [108] WANG MY, ARMSTRONG JK, FISHER TC, et al. A new, pluronic-based, bone hemostatic agent that does not impair osteogenesis. Neurosurgery. 2001; 49(4):962-967;discussion 8. [109] WELLISZ T, ARMSTRONG JK, CAMBRIDGE J, et al. Ostene, a new water-soluble bone hemostasis agent. J Craniofac Surg. 2006;17(3):420-425. [110] HUAN Z, MENGMENG Y, XINYE N, et al. Using calcium sulfate cement—hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose/sodium alginate composites as substitutes of bone wax. Int J Appl Ceram Technol. 2018;15(4):903-909. [111] BRüCKNER T, SCHAMEL M, KüBLER AC, et al. Novel bone wax based on poly(ethylene glycol)–calcium phosphate cement mixtures. Acta Biomater. 2016;33(15):252-263. [112] JINTAMAI S, WARAPORN S, FAUNGCHAT T, et al. Preparation and characterization of PEG–PPG–PEG copolymer/pregelatinized starch blends for use as resorbable bone hemostatic wax. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2013; 24(12):2881-2888. [113] HUAN Z, JUN G, YANJIE B, et al. Translation of bone wax and its substitutes: history, clinical status and future directions. J Orthop Translat. 2019;17:64-72. [114] SHA S, QIU F, LIU J, et al. Physico-chemical and biological properties of novel Eu-doped carbonization modified tricalcium silicate composite bone cement. Ceram Int. 2022;48(10):13484-13493. [115] XI W, DING Z, REN H, et al. Effects of pullulan on the biomechanical and anti-collapse properties of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate bone cement. J Biomater Appl. 2021;36(5):757-771. [116] CHIANG HH, SU CY, HSU LH, et al. Improved anti-washout property of calcium sulfate/tri-calcium phosphate premixed bone substitute with glycerin and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose. Appl Sci. 2021;11(17):8136. [117] BAL-OZTURK A, CECEN B, AVCI-ADALI M, et al. Tissue Adhesives: From Research to Clinical Translation. Nano Today. 2021;36:101049. [118] MACGILLIVRAY TE. Fibrin sealants and glues. J Card Surg. 2003;18(6):480-485. [119] 陈华,左宁,南楠.透皮贴剂黏附力检测方法的简述[J].药物分析杂志, 2014,34(8):1343-1347. [120] 李玉凤,邢绍荣,左宁,等.探针法测定吲哚美辛凝胶剂粘附力的方法研究[J].药物分析杂志,2020,40(5):948-951. [121] WOKOVICH AM, PRODDUTURI S, DOUB WH, et al. Transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) adhesion as a critical safety, efficacy and quality attribute. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2006;64(1):1-8. [122] BHAGAT V, O’BRIEN E, ZHOU J, et al. Caddisfly Inspired Phosphorylated Poly(ester urea)-Based Degradable Bone Adhesives. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(9):3016-3024. [123] YANG Z, HUANG R, ZHENG B, et al. Highly Stretchable, Adhesive, Biocompatible, and Antibacterial Hydrogel Dressings for Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(8):2003627. [124] FU RM, TU LJ, ZHOU YH, et al. A Tough and Self-Powered Hydrogel for Artificial Skin. Chem Mater. 2019;31(23):9850-9860. [125] WANG Z, CHEN J, WANG L, et al. Flexible and wearable strain sensors based on tough and self-adhesive ion conducting hydrogels. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(1):24-29. [126] 葛隽.一种止血成骨一体化材料的制备方法及其应用研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2020. [127] JIN C, SONG EK, JIN QH, et al. Outcomes of simultaneous high tibial osteotomy and anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in anterior cruciate ligament deficient knee with osteoarthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):228. [128] KIM YS, KOH YG. Comparative Matched-Pair Analysis of Open-Wedge High Tibial Osteotomy With Versus Without an Injection of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Varus Knee Osteoarthritis: Clinical and Second-Look Arthroscopic Results. Am J Sports Med. 2018;46(11):2669-2677. [129] PALANISAMY JV, DAS S, MOON KH, et al. Intravenous Tranexamic Acid Reduces Postoperative Blood Loss After High Tibial Osteotomy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(11):2148-2154. [130] SABZEVARI S, EBRAHIMPOUR A, ROUDI MK, et al. High Tibial Osteotomy: A Systematic Review and Current Concept. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2016;4(3):204-212. [131] MALAHIAS MA, SHAHPARI O, KASETA MK. The clinical Outcome of One-stage High Tibial Osteotomy and Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction. A Current Concept Systematic and Comprehensive Review. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2018;6(3):161-168. [132] MOREY VM, NAG HL, CHOWDHURY B, et al. A prospective comparative study of clinical and functional outcomes between anatomic double bundle and single bundle hamstring grafts for arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Int J Surg. 2015;21:162-167. [133] HE J, XIAO S, WU Z, et al. Microendoscopic discectomy versus open discectomy for lumbar disc herniation: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(5):1373-1381. [134] KIM JE, CHOI DJ. Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Arthroscopy. Clin Orthop Surg. 2018;10(2):248-252. [135] KIM JE, CHOI DJ. Unilateral biportal endoscopic decompression by 30° endoscopy in lumbar spinal stenosis: Technical note and preliminary report. J Orthop. 2018;15(2):366-371. [136] YANG Y, ZHANG L, LIU B, et al. Hidden and overall haemorrhage following minimally invasive and open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion. J Orthop Traumatol. 2017;18(4):395-400. |
| [1] | 余伟杰, 刘爱峰, 陈继鑫, 郭天赐, 贾易臻, 冯汇川, 杨家麟. 机器学习在腰椎间盘突出症诊治中的优势和应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | 林泽玉, 徐 林. 痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [3] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [4] | 李佳琪, 黄元礼, 李 妍, 王春仁, 韩倩倩. 非交联透明质酸分子质量降解的机制及影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [5] | 徐 溶, 王豪杰, 耿梦想, 孟 凯, 王 卉, 张克勤, 赵荟菁. 多孔聚四氟乙烯人工血管制备及功能化改性研究的进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [6] | 陈小芳, 郑国爽, 李茂源, 于炜婷. 可注射海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [7] | 张 明, 王 斌, 贾 凡, 陈 杰, 唐 玮. 基于脑电图的脑机接口技术在脑卒中患者上肢运动功能康复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [8] | 何远杰, 陈宇恒, 赵永超, 王正龙. 表观遗传调控血管平滑肌细胞重塑在主动脉瘤发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 602-608. |
| [9] | 马思聪 , 陈 晶, 李云庆. 结缔组织生长因子在神经系统中的功能与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 615-620. |
| [10] | 闫炳翰, 李志超, 苏 辉, 薛海鹏, 徐展望, 谭国庆. 中药单体靶向自噬治疗骨关节炎的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
| [11] | 王欣怡, 谢宪瑞, 陈玉杰, 王晓宇, 徐小青, 沈怿弘, 莫秀梅. 软组织和硬组织再生过程中的电纺纳米纤维支架[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 426-432. |
| [12] | 龙俊东, 史业弘, 王 成, 陈世玖. 不同冷冻技术对同种异体血管移植排斥反应的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 433-438. |
| [13] | 杨 杰, 胡浩磊, 李 硕, 岳 玮, 徐 弢, 李 谊. 3D打印生物墨水在组织修复与再生医学中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(3): 445-451. |
| [14] | 代新语, 闫纪红, 华凌军, 郑晓鸿. 抗阻运动改善超重肥胖人群身体成分:一项伞形综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 267-271. |
| [15] | 孟志成, 乔卫平, 赵 阳, 刘洪飞, 李凯杰, 马 博. 免疫细胞及相关细胞因子在骨关节炎发病及治疗中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(2): 280-287. |
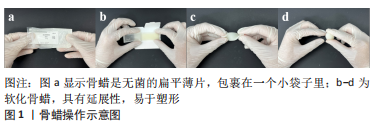
骨蜡是骨科、胸外科、神经外科、颌骨及牙科手术中用于骨止血的填塞剂[12-18],它主要是由蜂蜡和凡士林等软化剂或石蜡与棕榈酸异丙酯的混合物组成,具有较强的疏水性[19],它的最佳储存温度为21-23 ℃,使用时需在手中稍作升温后,即可任意搓揉和塑形,并可填塞到骨渗血处实现物理封堵止血(图1)[20]。市售医用骨蜡被国家药品监督管理局(NMPA)归类为第三类医疗器械,常以无菌棒或片的独立包装形式进行销售,市面一条无菌的2.5 g成品骨蜡条的价格大多在几十元人民币范围内,保质期长达5年之久[20]。目前,市面上常见的骨蜡品牌,包括正大医疗(CP Medical)、美国强生、上海三友、德国贝朗等。
 骨蜡虽被用于各个不同年龄、不同部位和不同原因所导致的骨骼断裂,颅骨钻孔或碎裂时引起的骨髓部毛细血管的渗血,但存在术中阻挡不住渗血、术后因生物相容性差和不可降解导致异物肉芽肿、阻碍骨愈合、降低组织抗感染能力和材料移位等一系列问题。因此,骨蜡代替品的研究也一直在进行,例如可注射液态明胶是一种上市的新型骨科止血材料,一般可保存较长时间,使用较为方便,与骨蜡或者类骨蜡材料相比具有较强的流动性。可注射明胶主要用于在进行脊柱手术时椎弓根螺钉植入过程出血情况的处理,但该止血材料也有许多使医生担忧的并发症,因为椎弓根为松质骨,血运极其丰富,而可注射明胶具有一定的流动性,容易移位或经血窦入血,已有报道称注射明胶止血后导致患者严重的神经受压及受损的表现;除此以外,可注射明胶还会导致过敏性休克甚至在加压注射时发生肺栓塞等严重并发症[21-23]。该文将回顾包括骨蜡和其替代材料在内的骨科止血材料的发展历程,为后续新型骨科止血材料的研究与转化提供思路。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
骨蜡虽被用于各个不同年龄、不同部位和不同原因所导致的骨骼断裂,颅骨钻孔或碎裂时引起的骨髓部毛细血管的渗血,但存在术中阻挡不住渗血、术后因生物相容性差和不可降解导致异物肉芽肿、阻碍骨愈合、降低组织抗感染能力和材料移位等一系列问题。因此,骨蜡代替品的研究也一直在进行,例如可注射液态明胶是一种上市的新型骨科止血材料,一般可保存较长时间,使用较为方便,与骨蜡或者类骨蜡材料相比具有较强的流动性。可注射明胶主要用于在进行脊柱手术时椎弓根螺钉植入过程出血情况的处理,但该止血材料也有许多使医生担忧的并发症,因为椎弓根为松质骨,血运极其丰富,而可注射明胶具有一定的流动性,容易移位或经血窦入血,已有报道称注射明胶止血后导致患者严重的神经受压及受损的表现;除此以外,可注射明胶还会导致过敏性休克甚至在加压注射时发生肺栓塞等严重并发症[21-23]。该文将回顾包括骨蜡和其替代材料在内的骨科止血材料的发展历程,为后续新型骨科止血材料的研究与转化提供思路。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者和共同第一作者在2022年7月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2022年7月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、万方数据库、中国知网及维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Bone wax,Bone wax substitute material,Orthopedic hemostatic material”;中文检索词为“骨蜡,止血材料,骨科止血材料”等。
1.1.5 检索文件类型 包括中文及英文综述、病例报告、研究原著、荟萃分析、评述等。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 暂无。
1.1.7 检索策略 见图2。
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①文章所述内容需与骨蜡、止血材料、骨科止血材料相关的文献;②文章论据、论点详实可靠;③选择近期发表或在权威杂志上发表的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①与该文内容不相关的文献;②内容较陈旧、结论重复、可信度较低的文章;③中、英文重复的文献。
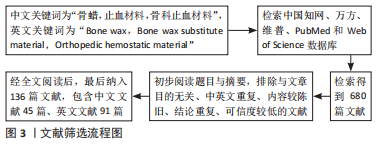
1.3 质量评估 通过计算机初检得到680篇文献,经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文献题目和相关摘要进行初步筛选;排除中、英文文献重复性研究及内容不相关的文献,最终筛选出符合标准的136篇文献进行综述,其中中文文献45篇,英文文献91篇,具体见图3。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该文从国内外骨蜡的发展历史为起点,剖析传统骨蜡材料的利弊;以骨科止血为起点,梳理在赋予骨科止血材料可降解性、成骨性、抗菌性等方面的研究进展;最后,点出骨科止血材料的发展不仅限于材料研发,建立监管机构认可的评价标准才是新的骨科止血产品转化应用的核心,并且汇总了骨科止血材料的临床前评价方法。
3.3 综述的局限性 目前止血成骨等功能性骨科止血材料的相关研究多集中于基础的理化和性能测试,缺乏系统的评价体系,同时欠缺足够的大动物实验和临床试验报道。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该文章重点总结了骨蜡在不同部位使用时会引发的并发症,以供医生综合考量骨蜡的使用情景,纵向探讨了可降解、促成骨及抗菌成血管等功能化的止血材料,横向对比了各种止血成骨一体化材料的优缺点,以期研究者的重视。此外,文章总结了骨科止血材料的相关评价标准,希望有助于新型骨科止血材料的开发,解决仍使用术后引起诸多并发症的骨蜡及国外虽有几款产品通过相关批准进入市场,但却没有后续报道的研究现状。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 目前国内的类骨科止血材料迟迟无法转化,其本质是已有材料无法适时满足临床的需求。因此,在术中止血阶段,需要材料填充渗血创面前可持续任意塑形,填充后10 min内无大体可见渗血、无材料从骨创面脱落;在术后成骨阶段,则需要材料具有一定的抗菌性能,并具有能与骨组织再生过程适配的孔隙结构、力学性能、骨传导性和生物降解性能来促进成骨和被新骨爬行替代。综上所述,未来还需要对现有止血和成骨材料的结构、组分和功能进行整合和再设计,以满足不断提高的止血与成骨需求。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
骨蜡:是骨科手术、胸外科手术及牙科手术中常用的骨科止血填塞剂。它主要是由蜂蜡和凡士林等软化剂或石蜡与棕榈酸异丙酯的混合物组成,其不可降解,具有较强的疏水性。手术中使用时,先放入手心稍作升温后,即可任意搓揉和塑形,并可填塞到骨渗血处实现物理封堵止血。骨骼:是人体运动系统的重要组成部分,含有大量的毛细血管。骨创面的出血往往为渗血,因为骨骼内部的结构松散、血运丰富,所以从表面上看没有血管断裂那样出血迅速,但并不意味出血量少,短时间内如未能有效止血,患者生命安全将难以保证。
该文系统回顾了以骨蜡为代表的骨科止血材料的需求和转化应用瓶颈。骨髓腔内毛细血管损伤造成的骨组织出血是骨科领域的常见症状,出血不仅影响患者的生命安全,也会一定程度干扰医生的手术视野。骨蜡是临床经典的骨科止血材料,但存在骨不愈合、移位、感染等众多并发症。研发新型的骨科止血材料是国内外新兴热点,但是迄今并没有获得突破性进展,新材料的临床接受度普遍不高,究其原因在于替代材料无法满足术中止血、术后成骨及不改变医生手术习惯的需求。同时,当前的骨科止血材料的产品注册转化缺少公认的评价体系,其在NMPA的注册体系中缺乏明确的定位和系统性的评价准则,这也在一定程度上给骨科止血材料的研究转化提出了挑战。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||