中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 258-263.doi: 10.12307/2022.940
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
沙棘总黄酮干预兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块的消退
牛梓晗,余 扬,艾 江,卜盼盼,李文博,苏日耶·热合曼,马少林
- 新疆医科大学第一附属医院整形外科,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830054
Total flavonoids of Hippophae rhamnoides L. interfere with the regression of hypertrophic scar tissue blocks in a rabbit ear model
Niu Zihan, Yu Yang, Ai Jiang, Bu Panpan, Li Wenbo, Suriye·Reheman, Ma Shaolin
- Department of Plastic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830054, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
沙棘总黄酮:是中草药沙棘提取物中的主要活性成分,具有抗氧化、抗炎、调节免疫、促进伤口愈合的功能。
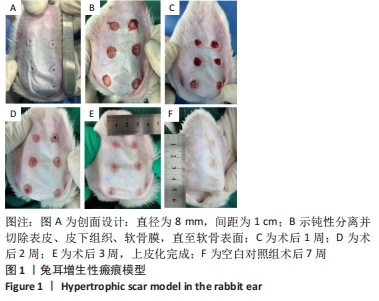
兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块:为研究增生性瘢痕常用的动物模型。在新西兰大白兔兔耳腹侧建立圆形创面,创面上皮化后,形成突出周围皮肤表面、质硬的瘢痕组织块。
背景:沙棘总黄酮可抑制肾脏、肝脏、心肌纤维化,但其对增生性瘢痕纤维化的相关疗效鲜有报道。
目的:对兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块局部注射中草药沙棘总黄酮,观察其对增生性瘢痕组织块消退的影响并探讨其作用机制。
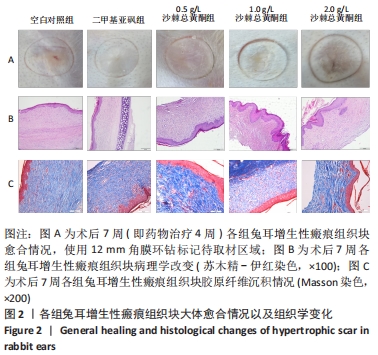
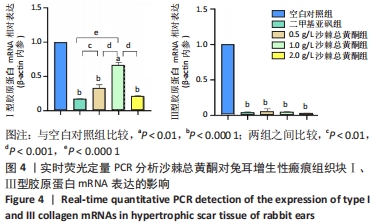
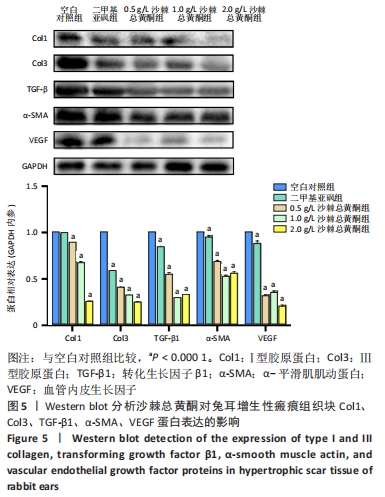
方法:选择8只新西兰大白兔,每只耳沿腹侧中线两侧各建立3个直径8 mm圆形创面,共96个创面。21 d创面上皮化后,随机分为5组:0.5,1.0,2.0 g/L沙棘总黄酮组,2只/组;二甲基亚砜组(药物溶剂对照)和空白对照组,1只/组。于组织块基底部注射相应药物,每间隔3 d注射1次,连续干预4周。通过苏木精-伊红染色和Masson染色对比各组增生性瘢痕组织块病理组织变化;实时荧光定量PCR检测各组组织块中Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原的mRNA表达;Western blot检测各组兔耳瘢痕组织块Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、血管内皮生长因子的蛋白表达。
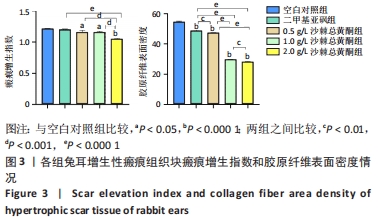
结果与结论:①大体观察:不同质量浓度的沙棘总黄酮局部注射后瘢痕组织块明显软化、变平;②空白对照组大量炎性细胞浸润、血管生成、胶原纤维不规则排列;与空白对照组相比,各沙棘总黄酮组可见整齐的束状胶原纤维分布,新生血管较少,特别是2 g/L沙棘总黄酮组改善较为明显;不同质量浓度沙棘总黄酮组间瘢痕增生指数和胶原密度均低于空白对照组和二甲基亚砜组(P < 0.05);③各沙棘总黄酮组和二甲基亚砜组瘢痕组织块的Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原mRNA表达水平均显著低于空白对照组,其中2 g/L沙棘总黄酮组的抑制作用最明显(P < 0.05);④与空白对照组相比,二甲基亚砜一定程度上可以降低组织块中Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、血管内皮生长因子蛋白表达水平;但不同质量浓度沙棘总黄酮组均可明显抑制兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原、转化生长因子β1、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、血管内皮生长因子蛋白的表达水平,且呈剂量依赖性(P < 0.05);⑤提示沙棘总黄酮可抑制瘢痕增生,使瘢痕组织块软化、变平,颜色变淡,降低兔耳增生性瘢痕组织块转化生长因子β1、Ⅰ、Ⅲ型胶原纤维的表达,抑制成纤维细胞向肌成纤维细胞转化,减少瘢痕组织内血管生成,从而达到治疗增生性瘢痕的作用。
缩略语:转化生长因子β1:transforming growth factor-β1,TGF-β1
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0675-2663 (牛梓晗)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: