中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (25): 3986-3992.doi: 10.12307/2022.403
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞联合丹参酮ⅡA治疗大鼠宫腔粘连
徐炜均1,胡向丹2,余冬青2
- 1广州中医药大学第二临床医学院,广东省广州市 510000;2广东省中医院妇科,广东省广州市 510000
First-trimester human decidual mesenchymal stem cells combined with tanshinone IIA in the treatment of intrauterine adhesions in rats
Xu Weijun1, Hu Xiangdan2, Yu Dongqing2
- 1Second Clinical Medical College of Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Department of Gynecology, Guangdong Province Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
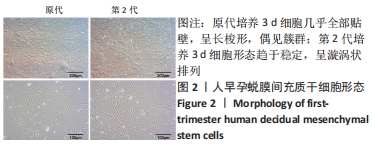
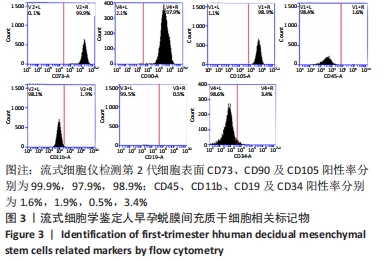
人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞:来源于正常的子宫蜕膜组织,在胎盘胎膜发育过程中可分泌多种蛋白,并随着孕周增大与绒毛膜细胞共同发育为胎盘,具有强大的增殖能力。该研究采用胶原酶消化法分离出人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞,流式细胞仪检测可表达间充质干细胞表面标志物CD90、CD73和CD105,不表达造血干细胞表面标志物CD34 和CD45。
丹参酮ⅡA:丹参酮是从中药丹参(唇形科植物丹参Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge根)中提取的具有抑菌作用的脂溶性菲醌化合物,从中分得丹参酮Ⅰ、丹参酮ⅡA、丹参酮ⅡB、隐丹参酮、异隐丹参酮等10余个丹参酮单体。丹参酮Ⅱ是丹参中脂溶性成分的代表,集中分布在丹参根的皮部,常作为肿瘤、心血管疾病、炎症、动脉粥样硬化、纤维化等疾病的治疗用药。
背景:人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞及丹参酮ⅡA具有抗粘连作用,均对宫腔粘连有一定疗效,但其具体机制待进一步研究。
目的:探索人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞联合丹参酮ⅡA治疗宫腔粘连的效果及机制。
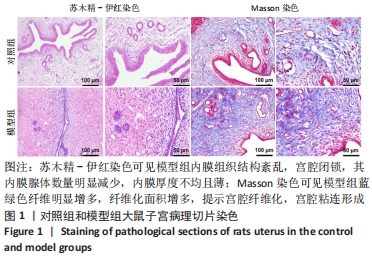
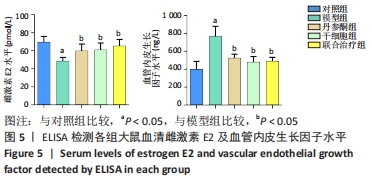
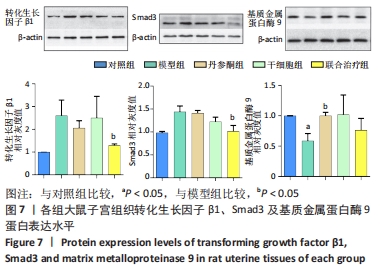
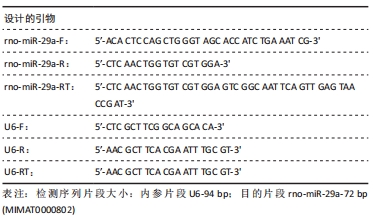
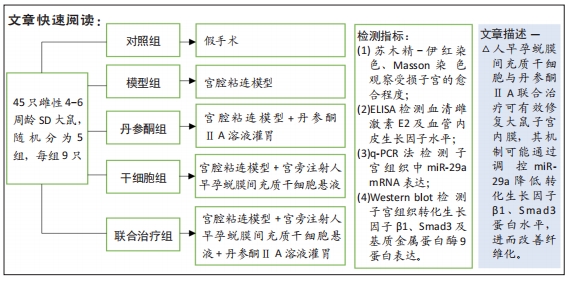
方法:采用胶原酶Ⅰ消化法分离培养人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞,选取45只雌性4-6周龄SD大鼠,随机分为5组,每组9只,分别为对照组、模型组、丹参酮组、干细胞组及联合治疗组。对照组进行假手术;模型组进行机械刮宫造模后不干预;干细胞组则在造模后7 d经宫旁注射0.2 mL人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞悬液(1×109 L-1),每隔3 d注射1次,共3次;丹参酮组在造模后7 d灌胃11 mg/(kg·d)丹参酮ⅡA溶液,持续灌胃1周;联合治疗组则为上述两种治疗方式的联合运用。对照组及模型组在术后5,10,15 d取材,各治疗组则在最后一次治疗后5,10,15 d后取材,苏木精-伊红染色、Masson染色观察受损子宫的愈合程度;ELISA检测血清雌激素E2及血管内皮生长因子水平;q-PCR法检测子宫组织中miR-29a mRNA表达;Western blot检测子宫组织转化生长因子β1、Smad3及基质金属蛋白酶9蛋白表达。
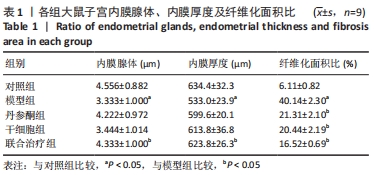
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,模型组大鼠子宫内膜纤维化面积比显著增加(P < 0.05),而内膜厚度及腺体数量显著下降(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,联合治疗组大鼠子宫内膜纤维化面积比显著下降(P < 0.05),而内膜厚度及腺体数量显著增加(P < 0.05),干细胞组及丹参酮组大鼠子宫内膜纤维化面积比也显著下降(P < 0.05);②与模型组比较,丹参酮组、干细胞组及联合治疗组血清雌激素E2水平显著升高(P < 0.05),血管内皮生长因子水平显著下降(P < 0.05),miR-29a mRNA表达显著升高(P < 0.05),联合治疗组转化生长因子β1、Smad3蛋白表达明显下降(P < 0.05),丹参酮组基质金属蛋白酶9蛋白表达明显上升(P < 0.05);③结果表明,人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞与丹参酮ⅡA联合治疗可有效修复大鼠子宫内膜,其机制可能通过调控miR-29a降低转化生长因子β1、Smad3蛋白水平,进而改善纤维化。
缩略语:人早孕蜕膜间充质干细胞:human decidual mesenchymal stem cells,hDMSCs
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8956-6622 (徐炜均)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: