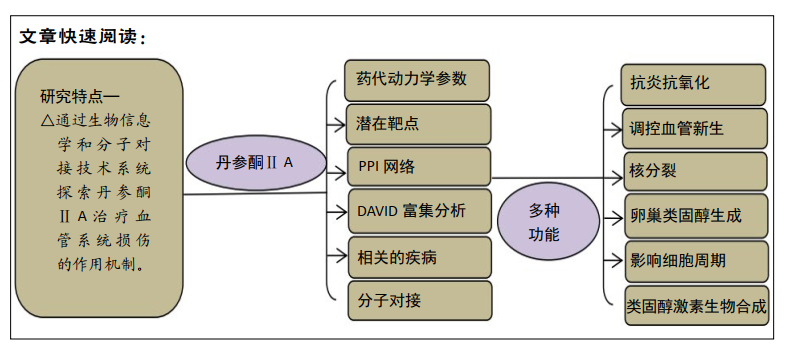
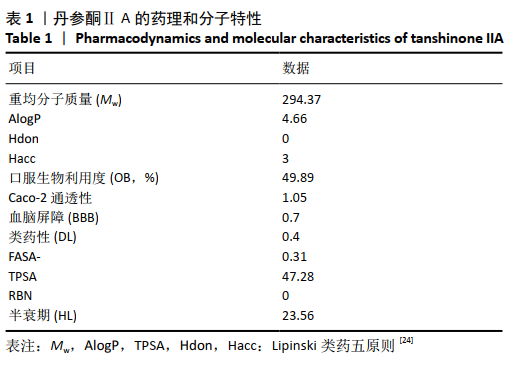
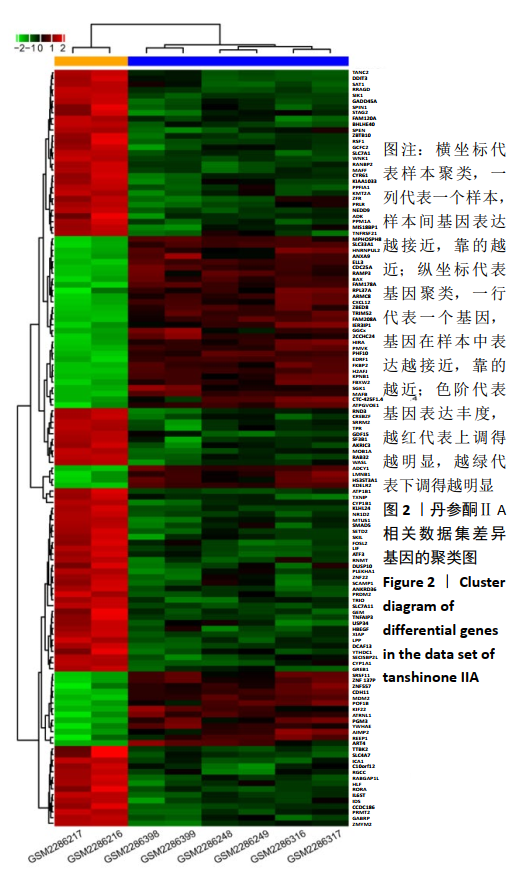
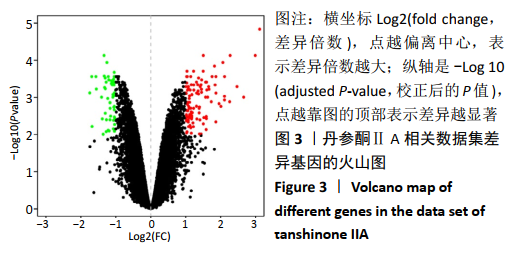
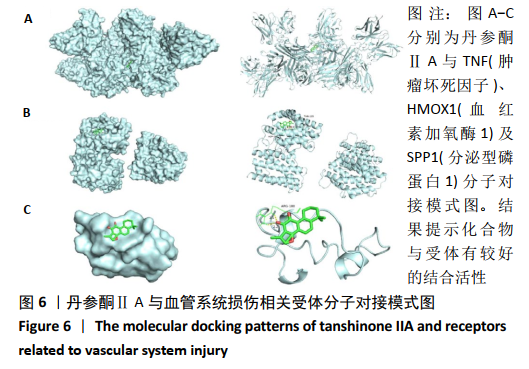
[1] 康渊强,高明宇.丹参治疗冠心病的现状及其机制研究进展 [J]. 辽宁医学杂志,2019,33(2):85-88.
[2] 徐文华,郑景辉,赵阳,等.基于网络药理学和生物信息学的丹参酮Ⅱ_A治疗冠心病的分子生物学机制分析[J]. 中草药,2019,50(5): 1131-1140.
[3] 苏梅,秦引林,娄雅静,等.丹参酮Ⅱ_A磺酸钠体内外促血管新生作用的研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2019,34(4):934-940.
[4] 宁剑,何春玲,黄健军.丹参酮ⅡA体内外抗炎作用研究[J]. 现代药物与临床,2019,34(2):292-298.
[5] 田清山.丹参酮IIA辅助治疗慢性心力衰竭的meta分析[D].南昌:南昌大学,2018.
[6] YANG YD, YU X, WANG XM, et al. Tanshinone IIA improves functional recovery in spinal cord injury-induced lower urinary tract dysfunction. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(2):267-275.
[7] 洪郭驹,何伟,魏秋实,等. 血管生长细胞因子与股骨头坏死(英文) [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2016,20(15):2197-2205.
[8] 胡敏,范建楠,赵宏斌,等. 激素性股骨头坏死模型兔血管内皮细胞生长因子表达与普伐他汀的干预[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(15):2703-2706.
[9] 胡志明,王海彬,李祖国,等.血管内皮细胞生长因子促进激素性股骨头坏死修复[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2006,14(15):1179-1181.
[10] 吴云刚,肖鲁伟,童培建,等.介入治疗激素性股骨头坏死血管内皮细胞生长因子表达的实验研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2002, 10(11):1094-1096.
[11] MONT MA, SALEM HS, PIUZZI NS, et al. Nontraumatic Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head: Where Do We Stand Today?: A 5-Year Update. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(12):1084-1099.
[12] WANG A, REN M, WANG J. The pathogenesis of steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head: A systematic review of the literature. Gene. 2018;671:103-109.
[13] 中国成人股骨头坏死临床诊疗指南(2020) [J]. 中华骨科杂志,2020, 40(20):1365-1376.
[14] 李时斌,赖渝,周毅,等. 激素性股骨头坏死发病机制及相关信号通路的靶点效应 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2020,25(6):935-941.
[15] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[16] XU X, ZHANG W, HUANG C, et al. A Novel Chemometric Method for the Prediction of Human Oral Bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(6): 6964-6982.
[17] TAO W, XU X, WANG X, et al. Network pharmacology-based prediction of the active ingredients and potential targets of Chinese herbal Radix Curcumae formula for application to cardiovascular disease.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;145(1):1-10.
[18] YANG H, ZHANG W, HUANG C, et al. A novel systems pharmacology model for herbal medicine injection: a case using reduning injection. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014;14:430.
[19] Tattersall MH, Sodergren JE, Dengupta SK, et al. Pharmacokinetics of actinoymcin D in patients with malignant melanoma. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975;17(6):701-708.
[20] DIRK W, RENE H, PETER K, et al. Identification of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis patients by transcriptome-based rule set generation. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R84.
[21] MOSTAFAVI S, RAY D, WARDE-FARLEY D, et al. GeneMANIA: a real-time multiple association network integration algorithm for predicting gene function. Genome Biol. 2008;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S4.
[22] HUANG DA W, SHERMAN BT, LEMPICKI RA. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 2009;4(1):44-57.
[23] DAVIS AP, GRONDIN CJ, JOHNSON RJ, et al. The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database: update 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1):D948-D954.
[24] LIPINSKI CA, LOMBARDO F, DOMINY BW, et al. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2001; 46(1-3):3-26.
[25] VAN DE WATERBEEMD H, GIFFORD E. ADMET in silico modelling: towards prediction paradise?. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2(3):192-204.
[26] 张媛,毛浩萍,樊官伟.丹参酮ⅡA药理作用研究进展[J]. 天津中医药大学学报,2019,38(1):15-19.
[27] 侯文书,张力.丹参酮ⅡA对心血管系统的药理作用及其新剂型研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2017,31(5):484.
[28] 陈芬燕,郭韧,张毕奎.丹参酮Ⅱ_A的心血管药理作用研究进展 [J]. 中国中药杂志,2015,40(9):1649-53.
[29] ZHANG X, MA Z, LIANG Q, et al. Tanshinone IIA exerts protective effects in a LCA-induced cholestatic liver model associated with participation of pregnane X receptor. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;164:357-367.
[30] JING L, WEIJIANG S, GUOYAN Y, et al. Compound Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) dripping pill for coronary heart disease: an overview of systematic reviews. Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(1):25-43.
[31] WING-SHING CHEUNG D, KOON CM, NG CF, et al. The roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Pueraria lobata (Gegen) inhibit atherogenic events: A study of the combination effects of the 2-herb formula.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012;143(3):859-866.
[32] XU W, YANG J, WU LM. Cardioprotective effects of tanshinone IIA on myocardial ischemia injury in rats. Pharmazie. 2009;64(5):332-336.
[33] 周丽,刘艳平,王芳,等.丹参酮Ⅱ_A对I/R大鼠脑组织NF-κB和IκB活性的影响[J].中药材,2013,36(7):1136-1139.
[34] 王炎,刘宣,周利红,等.丹参酮Ⅱ_A对裸鼠人肠癌血管新生的抑制作用[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(3):167-171.
[35] NAKAHARA H, SONG J, SUGIMOTO M, et al. Anti–interleukin‐6 receptor antibody therapy reduces vascular endothelial growth factor production in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(6): 1521-1529.
[36] BALAJI S, LESAINT M, BHATTACHARYA SS, et al. Adenoviral-mediated gene transfer of insulin-like growth factor 1 enhances wound healing and induces angiogenesis. J Surg Res. 2014;190(1):367-377.
[37] HATANPAA KJ, BURMA S, ZHAO D, et al. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Glioma: Signal Transduction, Neuropathology, Imaging, and Radioresistance. Neoplasia. 2010;12(9):675-684.
[38] 胡亮,王军海,王志烈,等.血管内皮生长因子联合突变型低氧诱导因子1α的促血管生成作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3): 378-383.
[39] 吴涛,孙瑞敏,王慧利,等. 经股动脉灌注成纤维细胞生长因子对兔股骨头缺血性坏死新生血管及骨密度的影响 [J].中国临床药理学杂志,2020,36(17):2658-2560.
[40] WAZA AA, HAMID Z, ALI S, et al. A review on heme oxygenase-1 induction: is it a necessary evil. Inflamm Res. 2018;67(7):579-588.
[41] ICER MA, GEZMEN-KARADAG M. The multiple functions and mechanisms of osteopontin. Clin Biochem. 2018;59:17-24.
|