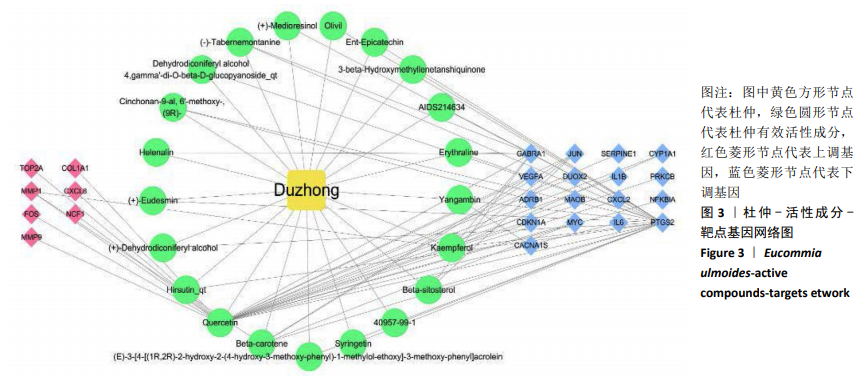
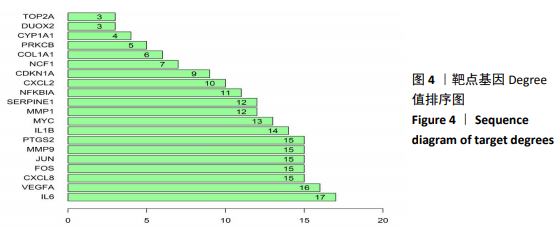
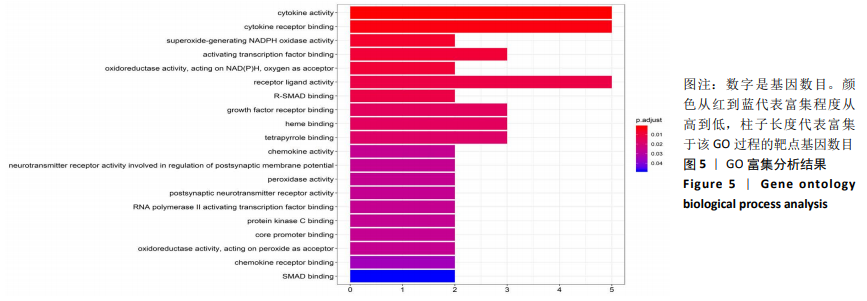
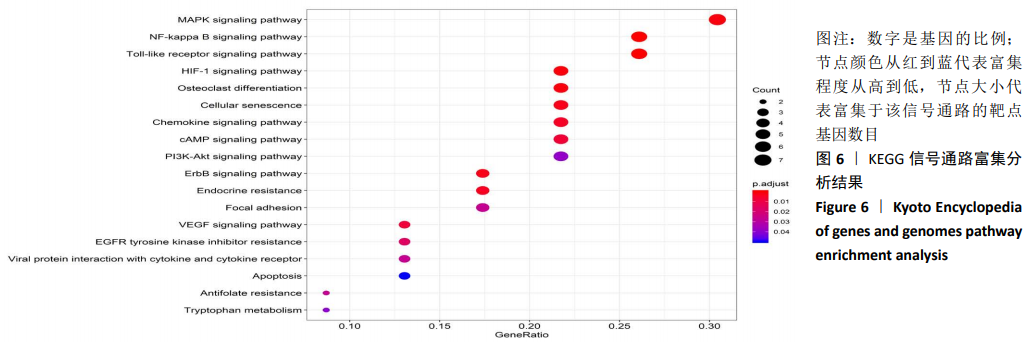
[1] CAI W, LI H, ZHANG Y, et al. Identification of key biomarkers and immune infiltration in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis by bioinformatics analysis. Peer J.2020; 8(8390):1-18
[2] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG. Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18.
[3] MIAO CG, YANG YY, HE X, et al. Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling. Cell Signal. 2013;25(10):2069-2078.
[4] LI N, XU Q, LIU Q, et al. Leonurine attenuates fibroblast-like synoviocyte-mediated synovial inflammation and joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford, England), 2017; 56(8): 1417-1427.
[5] 陈卫衡,刘献祥,童培建,等.膝骨关节炎中医诊疗专家共识(2015年版) [J].中医正骨, 2015, 27(07): 4-5.
[6] 梁子聪,易艾晶.基于文献数据挖掘调节膝骨关节炎炎症指标的中药内服方药用药规律研究[J]. 黔南民族医专学报, 2018, 31(2): 90-94.
[7] 刘磊, 张舒, 周悦悦. 复方杜仲健骨颗粒联合硫酸氨基葡萄糖治疗膝骨关节炎的临床研究[J]. 现代药物与临床, 2019, 34(11): 3343-6.
[8] 杨亚旭.蜂毒素联合杜仲黄酮治疗类风湿关节炎的实验研究[D].扬州:扬州大学, 2017.
[9] 张彦琼,李梢.网络药理学与中医药现代研究的若干进展[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2015, 29(6): 883-92.
[10] LIU H, WANG J, ZHOU W, et al. Systems approaches and polypharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines: an example using licorice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013;146(3): 773-793.
[11] XU X, ZHANG W, HUANG C, et al. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int J Mol Sci. 2012; 13(6):6964-6982.
[12] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines.J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[13] WANG S, WANG H, LU Y. Tianfoshen oral liquid: a CFDA approved clinical traditional Chinese medicine, normalizes major cellular pathways disordered during colorectal carcinogenesis.Oncotarget.2017;8(9): 14549-14569.
[14] RITCHIE ME, PHIPSON B, WU D, et al. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47.
[15] SHANNON P, MARKIEL A, OZIER O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13(11):2498-2504.
[16] LI J, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Systems pharmacology-based dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Bufei Yishen as an effective treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290.
[17] SZKLARCZYK D, GABLE A L, LYON D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47(D1):D607-D613.
[18] DE SANTIAGO I, CARROLL T. Analysis of ChIP-seq Data in R/Bioconductor.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1689:195-226.
[19] DU J, YUAN Z, MA Z, et al. KEGG-PATH: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes-based pathway analysis using a path analysis model. Mol Biosyst. 2014;10(9):2441-2447.
[20] PRESS OU. Expansion of the Gene Ontology knowledgebase and resources. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D331-D338.
[21] YU G, WANG L G, HAN Y, et al. clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters]. OMICS. 2012;16(5):284-287.
[22] LUO W,BROUWER C.Pathview: an R/Bioconductor package for pathway-based data integration and visualization.Bioinformatics. 2013;29(14):1830-1831.
[23] 吕苏梅, 张瑞丽.中老年膝骨关节炎的流行病学研究进展[J].中国老年学杂志, 2016, 36(16):4133-5.
[24] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9): 1263-1267.
[25] O’NEILL TW, PARKES MJ, MARICAR N, et al. Synovial tissue volume: a treatment target in knee osteoarthritis (OA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2016;75(1):84-90.
[26] ZHAI Y, GAO GD, XU SY. Basic research progress of knee osteoarthritis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(1):83-87.
[27] 陈达,陈后煌,邵翔,等.乌头汤抑制骨关节炎炎症反应的作用机制探讨 [J]. 风湿病与关节炎, 2016, 5(8): 62-66.
[28] CENGIC T, TRKULJA V, PAVELIC SK, et al. Association of TGFB1 29C/T and IL6 -572G/C polymorphisms with developmental hip dysplasia: a case-control study in adults with severe osteoarthritis. Int Orthop. 2015;39(4): 793-798.
[29] FUJIHASHI K, KONO Y, KIYONO H. Effects of IL6 on B cells in mucosal immune response and inflammation. Res Immunol. 1992;143(7): 744-749.
[30] FRANCKHAUSER S, ELIAS I, ROTTER SOPASAKIS V, et al. Overexpression of Il6 leads to hyperinsulinaemia, liver inflammation and reduced body weight in mice. Diabetologia. 2008;51(7): 1306-1316.
[31] PEARSON MJ, HERNDLER-BRANDSTETTER D, TARIQ MA, et al. IL-6 secretion in osteoarthritis patients is mediated by chondrocyte-synovial fibroblast cross-talk and is enhanced by obesity. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3451.
[32] ZUPAN J, VRTACNIK P, COR A, et al. VEGF-A is associated with early degenerative changes in cartilage and subchondral bone. Growth Factors. 2018;36(5-6):263-273.
[33] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain.J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924.
[34] ERDEM H, PAY S, MUSABAK U, et al. Synovial angiostatic non-ELR CXC chemokines in inflammatory arthritides: does CXCL4 designate chronicity of synovitis? . Rheumatol Int. 2007;27(10):969-973.
[35] YANG CC, LIN CY, WANG HS, et al. Matrix metalloproteases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in medial plica and pannus-like tissue contribute to knee osteoarthritis progression.PLoS One. 2013;8(11):e79662.
[36] LIN J, WU G, ZHAO Z, et al. Bioinformatics analysis to identify key genes and pathways influencing synovial inflammation in osteoarthritis. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(6):5594-5602.
[37] WANG D, QIAO J, ZHAO X, et al. Thymoquinone Inhibits IL-1beta-Induced Inflammation in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes by Suppressing NF-kappaB and MAPKs Signaling Pathway.Inflammation. 2015;38(6):2235-2241.
[38] HASEEB A, HAQQI T M. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2013;146(3): 185-196.
[39] WU L, HUANG X, LI L, et al. Insights on biology and pathology of HIF-1alpha/-2alpha, TGFbeta/BMP, Wnt/beta-catenin, and NF-kappaB pathways in osteoarthritis.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(22):3293-3312.
[40] ZHANG FJ, LUO W, LEI GH. Role of HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in osteoarthritis. Joint bone spine.2015; 82(3): 144-147.
[41] FERNANDEZ-TORRES J, MARTINEZ-NAVA GA, GUTIERREZ-RUIZ MC, et al. Role of HIF-1alpha signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Rev Bras Reumatol Engl Ed. 2017;57(2):162-173.
[42] NAIR A, KANDA V, BUSH-JOSEPH C, et al. Synovial fluid from patients with early osteoarthritis modulates fibroblast-like synoviocyte responses to toll-like receptor 4 and toll-like receptor 2 ligands via soluble CD14. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(7):2268-6877.
[43] STANNUS O, JONES G, CICUTTINI F, et al. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(11):1441-1447. |