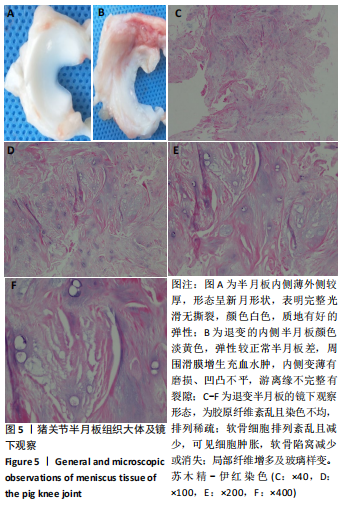
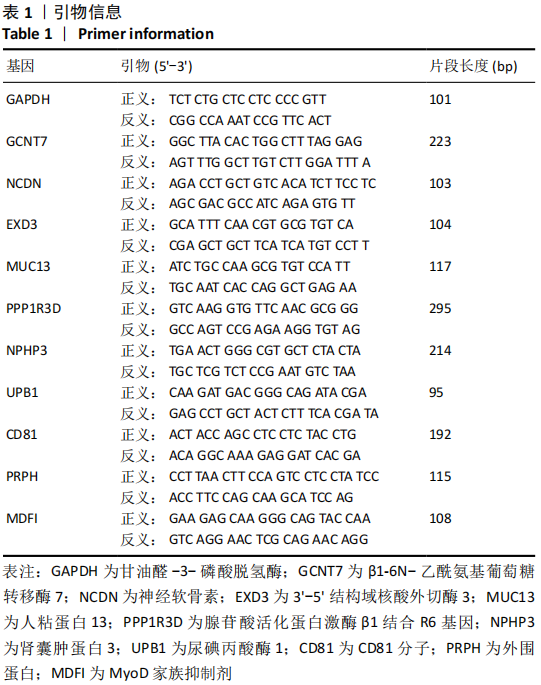
[1] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160.
[2] O NEILL TW, FELSON DT. Mechanisms of osteoarthritis (OA) pain. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(5):611-616.
[3] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5(1):1-13.
[4] WEI Y, BAI L. Recent advances in the understanding of molecular mechanisms of cartilage degeneration, synovitis and subchondral bone changes in osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(4):245-261.
[5] GOETZ JE, COLEMAN MC, FREDERICKS DC, et al. Time-dependent loss of mitochondrial function precedes progressive histologic cartilage degeneration in a rabbit meniscal destabilization model. J Orthop Res. 2016;35(3):590.
[6] YUAN X, ARKONAC DE, CHAO PG, et al. Electrical stimulation enhances cell migration and integrative repair in the meniscus. Sci Rep. 2014; 4(1):3674.
[7] LÓPEZ-FRANCO M, LÓPEZ-FRANCO O, MURCIANO-ANTÓN MA, et al. Meniscal degeneration in human knee osteoarthritis: in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry study. Orthop Trauma. 2016; 136(2):175-183.
[8] BENNETT LD, BUCKLAND WRIGHT JC. Meniscal and articular cartilage changes in knee osteoarthritis: a cross‐sectional double-contrast macroradiographic study. Rheumatol. 2002;41(8):917-923.
[9] HUNTER DJ, ZHANG YQ, NIU JB, et al. The association of meniscal pathologic changes with cartilage loss in symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(3):795-801.
[10] CHAN WP, HUANG G, HSU S, et al. Radiographic joint space narrowing in osteoarthritis of the knee: relationship to meniscal tears and duration of pain. Skeletal Radiol. 2008;37(10):917-922.
[11] AIGNER T, FUNDEL K, SAAS J, et al. Large‐scale gene expression profiling reveals major pathogenetic pathways of cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(11):3533-3544.
[12] BROPHY RH, SANDELL LJ, CHEVERUD JM, et al. Gene expression in human meniscal tears has limited association with early degenerative changes in knee articular cartilage. Connect Tissue Res. 2017;58(3-4): 295-304.
[13] TAYLOR E, COGDELL D, COOMBES K, et al. Sequence verification as quality-control step for production of cDNA microarrays. Biotechniques. 2001;31(1):62-65.
[14] 吴清洪,杨朝湘,邹华章,等.猪膝关节早期骨性关节炎模型的建立[J].动物医学进展,2018,39(6):33-37.
[15] TIEMIN P, FANZHENG M, PENG X, et al. MUC13 promotes intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma progression via EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathways. J Hepatol. 2020;72(4):761-773.
[16] SHENG YH, TRIYANA S, WANG R, et al. MUC1 and MUC13 differentially regulate epithelial inflammation in response to inflammatory and infectious stimuli. Mucosal Immunol. 2013;6(3):557-568.
[17] ZHANG B, REN J, YAN X, et al. Investigation of the porcine MUC13 gene: isolation, expression, polymorphisms and strong association with susceptibility to enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli F4ab/ac. Anim Genet. 2008;39(3):258-266.
[18] SUN Y, MAUERHAN DR, HONEYCUTT PR, et al. Analysis of meniscal degeneration and meniscal gene expression. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010;11(1):19.
[19] ROKKANEN P, PAATSAMA S, RISSANEN P. The influence of certain hormones on the meniscus of the femoro‐tibial (stifle) joint: a histological and histo‐quantitative study on young dogs. J Small Anim Pract. 1967;8(4):221-227.
[20] NOONE TJ, MILLIS DL, KORVICK DL, et al. Influence of canine recombinant somatotropin hormone on biomechanical and biochemical properties of the medial meniscus in stifles with altered stability. Am J Vet Res. 2002;63(3):419-426.
[21] HUANG H, SKELLY JD, AYERS DC, et al. Age-dependent changes in the articular cartilage and subchondral bone of C57BL/6 mice after surgical destabilization of medial meniscus. Sci Rep. 2017;7(2):42294.
[22] BLANCO FJ, OCHS RL, SCHWARZ H, et al. Chondrocyte apoptosis induced by nitric oxide. Am J Pathol. 1995;146(1):75.
[23] KIM SJ, HWANG SG, SHIN DY, et al. p38 Kinase Regulates Nitric Oxide-induced Apoptosis of Articular Chondrocytes by Accumulating p53 via NFκB-dependent Transcription and Stabilization by Serine 15 Phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(36):33501-33508.
[24] RELI B, BENTIRES-ALJ M, RIBBENS C, et al. TNF-α Protects Human Primary Articular Chondrocytes from Nitric Oxide-Induced Apoptosis Via Nuclear Factor-κB. Lab Invest. 2002;82(12):1661-1672.
[25] SURENDRAN S, KIM SH, JEE BK, et al. Anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 gene transfection of human articular chondrocytes protects against nitric oxide-induced apoptosis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006;88(12):1660.
[26] SHEN P, NGUYEN M, FUCHS M, et al. TLR1/2 signaling impairs mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in human chondrocytes via the induction of nitric oxide. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2020;28(1):S119.
[27] ZHOU Y, MING J, LI Y, et al. Ligustilide attenuates nitric oxide‐induced apoptosis in rat chondrocytes and cartilage degradation via inhibiting JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(5):3357-3368.
[28] RAMIREZ GA, COLETTO LA, SCIORATI C, et al. Ion channels and transporters in inflammation: special focus on TRP channels and TRPC6. Cells. 2018;7(7):70.
[29] 吴航宇,梁华平.TRP离子通道在炎症反应中的调控作用[J].中国急救医学,2009,29(10):944-946.
[30] KUSANO S, YOSHIMITSU M, HACHIMAN M, et al. I-mfa domain proteins specifically interact with HTLV-1 Tax and repress its transactivating functions. Virology. 2015;486(20):219-227.
[31] HUANG H, JIAXUAN Z, NINGJIANG S, et al. Identification of pathways and genes associated with synovitis in osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analyses. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):10050.
[32] DOHERTY DG, MELO AM, MORENO-OLIVERA A, et al. Activation and regulation of B cell responses by invariant natural killer T cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9(23):1360.
[33] WONDIMU EB, CULLEY KL, QUINN J, et al. Elf3 contributes to cartilage degradation in vivo in a surgical model of post-traumatic osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):6438.
[34] ADLER N, SCHOENIGER A, FUHRMANN H. Polyunsaturated fatty acids influence inflammatory markers in a cellular model for canine osteoarthritis. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2018;102(2):e623-e632.
[35] HOUSMAN G, HAVILL LM, QUILLEN EE, et al. Assessment of DNA methylation patterns in the bone and cartilage of a nonhuman primate model of osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 2019;10(3):335-345.
(责任编辑:WJ,ZN,TXY)
|