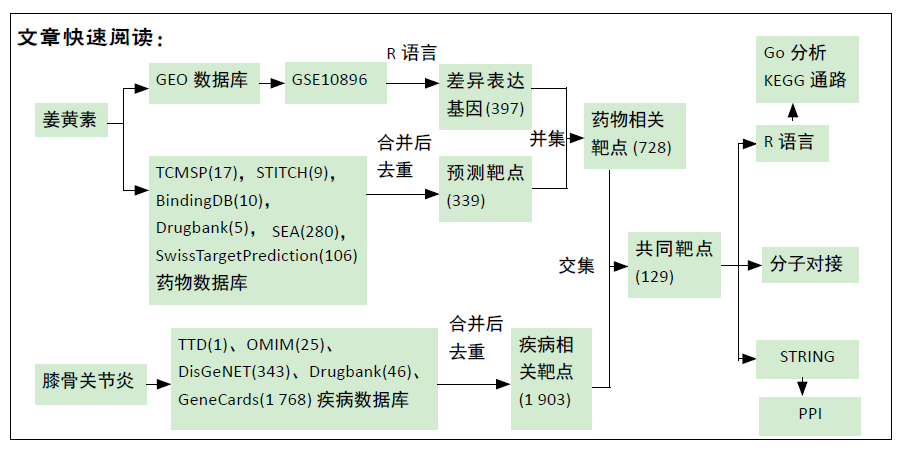
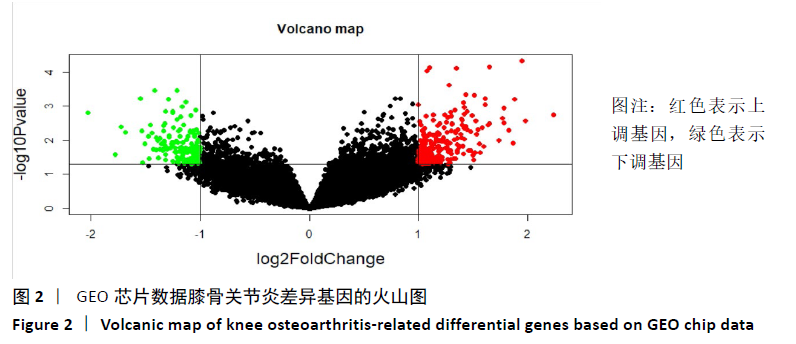
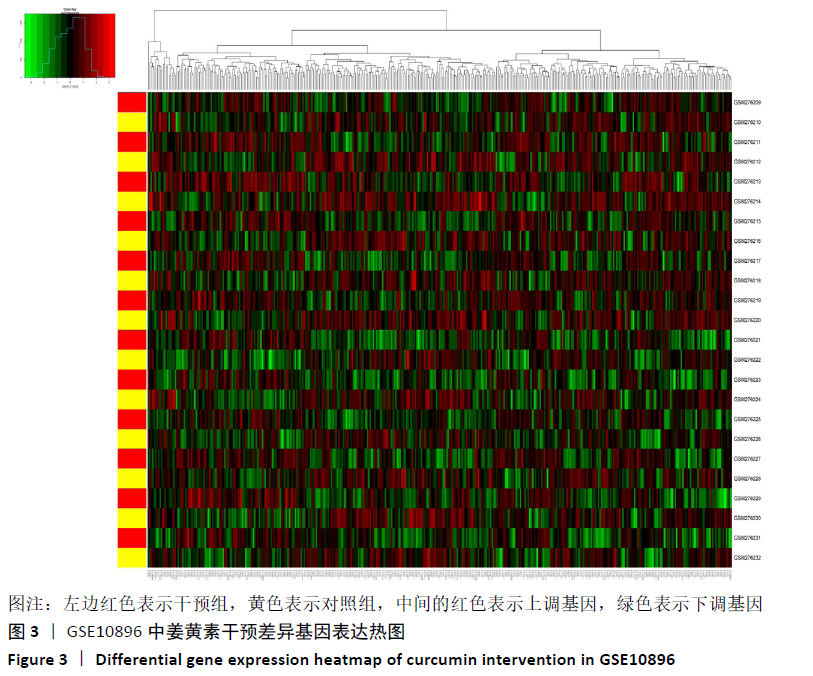
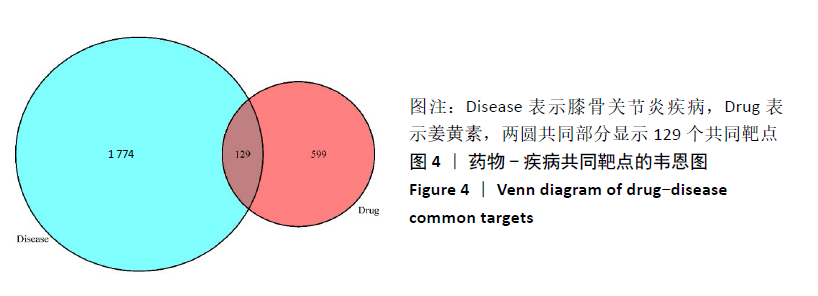
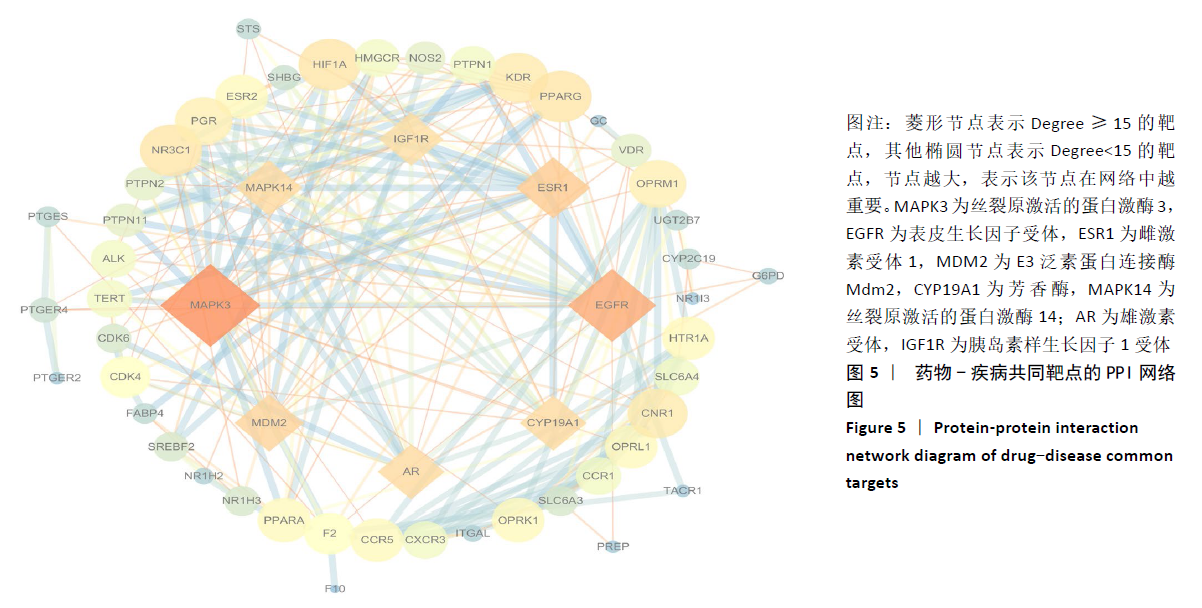
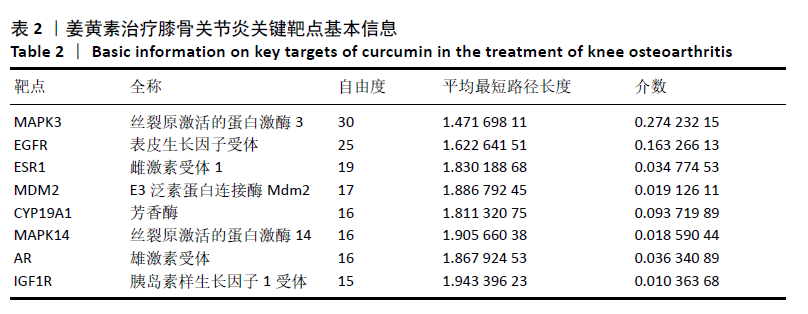
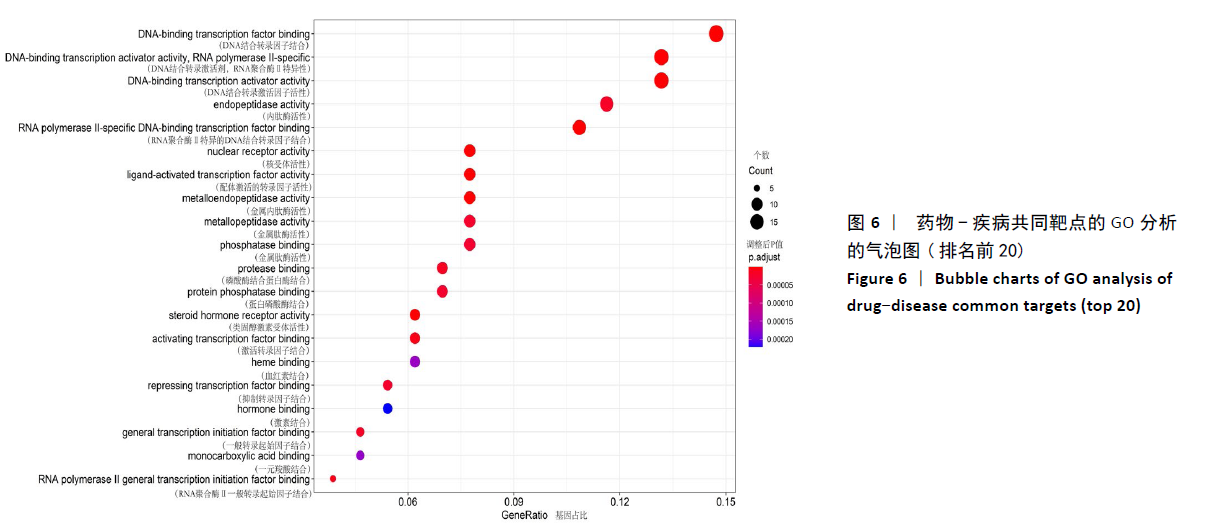
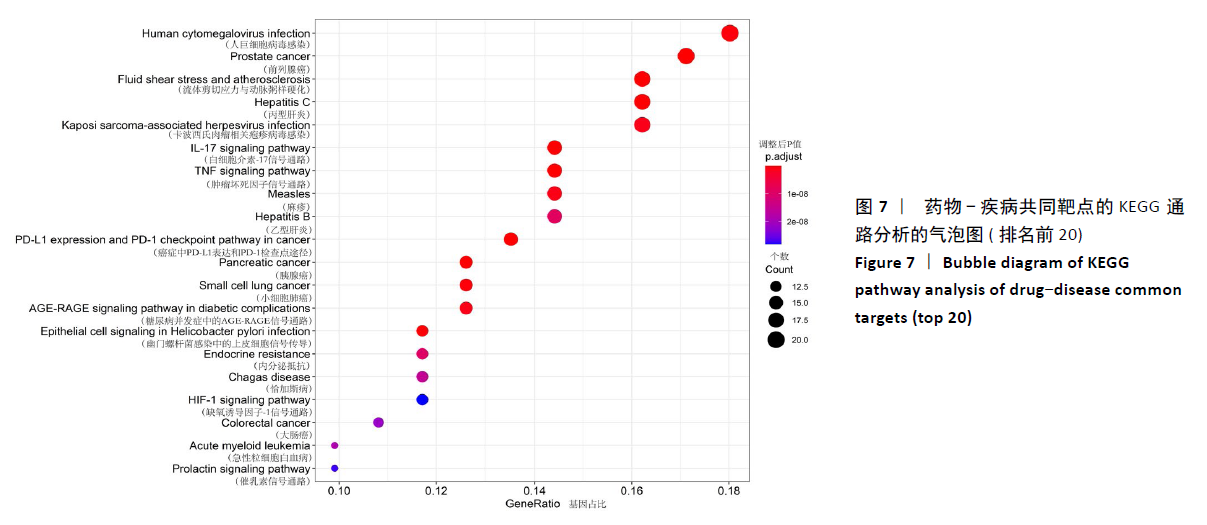
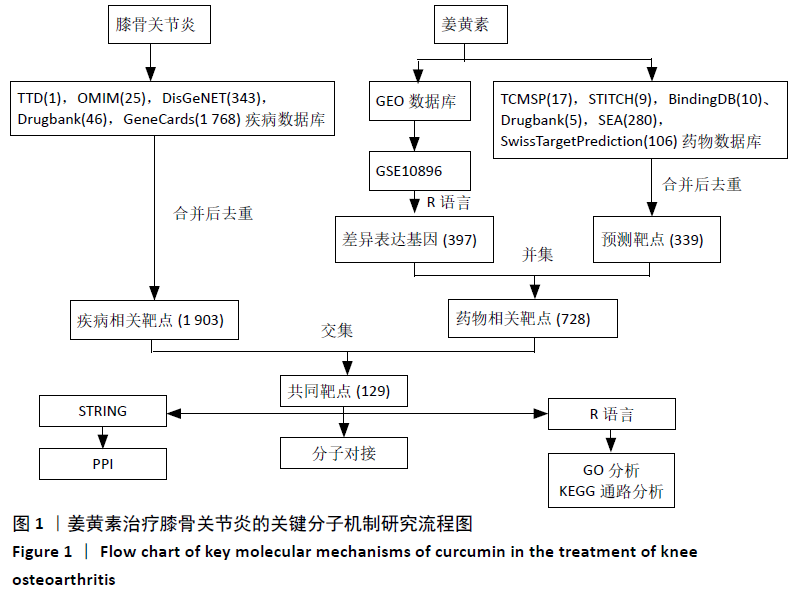
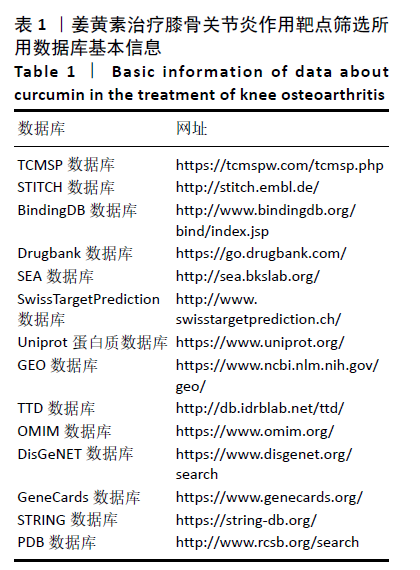
[1] GIWNEWER U, RUBIN G, ORBACH H, et al. treatment for osteoarthritis of the knee. Harefuah. 2016;155(7):403-406.
[2] URBAN H, LITTLE CB. The role of fat and inflammation in the pathogenesis and management of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2018;57(suppl_4): iv10-iv21.
[3] ISHIJIMA M, NAKAMURA T, SHIMIZU K, et al. Intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection versus oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a multi-center, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority trial. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(1):R18.
[4] ZHANG G, CAO J, YANG E, et al. Curcumin improves age-related and surgically induced osteoarthritis by promoting autophagy in mice. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(4):BSR20171691.
[5] ZHANG Z, LEONG DJ, XU L, et al. Curcumin slows osteoarthritis progression and relieves osteoarthritis-associated pain symptoms in a post-traumatic osteoarthritis mouse model. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18(1):128.
[6] ZHANG Y, ZENG Y. Curcumin reduces inflammation in knee osteoarthritis rats through blocking TLR4 /MyD88/NF-κB signal pathway. Drug Dev Res. 2019;80(3):353-359.
[7] RU J, LI P, WANG J, et al. TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform. 2014;6:13.
[8] SZKLARCZYK D, SANTOS A, VON MERING C, et al. STITCH 5: augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016; 44(D1):D380-D384.
[9] GILSON MK, LIU T, BAITALUK M, et al. BindingDB in 2015: A public database for medicinal chemistry, computational chemistry and systems pharmacology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(D1): D1045-D1053.
[10] WISHART DS, FEUNANG YD, GUO AC, et al. DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D1074-D1082.
[11] GU S, LAI LH. Associating 197 Chinese herbal medicine with drug targets and diseases using the similarity ensemble approach. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(3):432-438.
[12] DAINA A, MICHIELIN O, ZOETE V. SwissTargetPrediction: updated data and new features for efficient prediction of protein targets of small molecules. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(W1):W357-W364.
[13] UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017; 45(D1):D158-D169.
[14] LI Y, GU J, XU F, et al. Transcriptomic and functional network features of lung squamous cell carcinoma through integrative analysis of GEO and TCGA data. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15834.
[15] MEJA KK, RAJENDRASOZHAN S, ADENUGA D, et al. Curcumin restores corticosteroid function in monocytes exposed to oxidants by maintaining HDAC2. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2008;39(3):312-323.
[16] LI YH, YU CY, LI XX, et al. Therapeutic target database update 2018: enriched resource for facilitating bench-to-clinic research of targeted therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D1121-D1127.
[17] AMBERGER JS, BOCCHINI CA, SCHIETTECATTE F, et al. OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43(Database issue):D789-D798.
[18] PIñERO J, BRAVO À, QUERALT-ROSINACH N, et al. DisGeNET: a comprehensive platform integrating information on human disease-associated genes and variants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D833-D839.
[19] STELZER G, ROSEN N, PLASCHKES I, et al. The genecards suite: from gene data mining to disease genome sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016;54: 1.30.1-1.30.3.
[20] SZKLARCZYK D, MORRIS JH, COOK H, et al. The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D362-D368.
[21] 黄友,杨莎莎,林夏,等.基于网络药理-分子对接研究附子理中丸治疗溃疡性结肠炎的作用机制[J].药学学报,2020, 55(8):1812-1822.
[22] HSU KC, CHEN YF, LIN SR, et al. iGEMDOCK: a graphical environment of enhancing GEMDOCK using pharmacological interactions and post-screening analysis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1):S33.
[23] BURLEY SK, BERMAN HM, KLEYWEGT GJ, et al. Protein Data Bank (PDB): the single global macromolecular structure archive. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1607:627-641.
[24] KIM S, CHEN J, CHENG T, et al. PubChem 2019 update: improved access to chemical data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47(D1): D1102-D1109.
[25] MIN S, WANG C, LU W, et al. Serum levels of the bone turnover markers dickkopf-1, osteoprotegerin, and TNF-α in knee osteoarthritis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2017;36(10):2351-2358.
[26] YUAN XL, MENG HY, WANG YC, et al. Bone-cartilage interface crosstalk in osteoarthritis: potential pathways and future therapeutic strategies. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014; 22(8):1077-1089.
[27] JO CH, LEE YG, SHIN WH, et al. Intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: a proof-of-concept clinical trial. Stem Cells. 2014;32(5):1254-1266.
[28] 葛伟韬,高云,刘珍珠,等.膝骨关节炎中医病名辨识[J].中医杂志,2016,57(23): 1989-1992.
[29] NAKAGAWA Y, MUKAI S, YAMADA S, et al. Short-term effects of highly-bioavailable curcumin for treating knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled prospective study. J Orthop Sci. 2014;19(6):933-939.
[30] CHEN Y, SHOU K, GONG C, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of geniposide on osteoarthritis by suppressing the activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8384576.
[31] DANKNER M, ROSE AAN, RAJKUMAR S, et al. Classifying BRAF alterations in cancer: new rational therapeutic strategies for actionable mutations. Oncogene. 2018;37(24): 3183-3199.
[32] 刘敏,谢巍伟,郑维,等.雌二醇与ESR1靶向结合通过ERK信号通路调控软骨细胞的增殖[J].南方医科大学学报,2019, 39(2):134-143.
[33] SASAKO T, UEKI K. Insulin/IGF-1 signaling and aging. Nihon Rinsho. 2016;74(9): 1435-1440.
[34] 吴憾,蒋凤艳,劳山,等.女性激素对骨关节炎的影响研究[J].哈尔滨医科大学学报,2017,51(6):521-523.
[35] 刘欢,李翔,刘红佶,等.补精益视片对大鼠慢性高眼压模型视神经PI3K/Akt通路MDM2、p53表达的影响[J].中医眼耳鼻喉杂志,2020,10(2):72-75.
[36] FU D, SHANG X, NI Z, et al. Shikonin inhibits inflammation and chondrocyte apoptosis by regulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(4):2735-2740.
[37] JOOS H, WILDNER A, HOGREFE C, et al. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibit migration activity of chondrogenic progenitor cells from non-fibrillated osteoarthritic cartilage. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R119.
[38] HU G, ZHAO X, WANG C, et al. MicroRNA-145 attenuates TNF-α-driven cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via direct suppression of MKK4. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3140.
[39] FERNáNDEZ-TORRES J, MARTíNEZ-NAVA GA, ZAMUDIO-CUEVAS Y, et al. Impact of the gene-gene interactions related to the HIF-1α signaling pathway with the knee osteoarthritis development. Clin Rheumatol. 2019;38(10):2897-907.
|