[1] BRUYÈRE O, COOPER C, ARDEN N, et al. Can we identify patients with high risk of osteoarthritis progression who will respond to treatment? A focus on epidemiology and phenotype of osteoarthritis.Drugs Aging. 2015;32(3):179-187.
[2] LIU B, JI C, SHAO Y, et al. Etoricoxib decreases subchondral bone mass and attenuates biomechanical properties at the early stage of osteoarthritis in a mouse model. BiomedPharmacother. 2020;127:110144.
[3] SPITAELS D, MAMOURIS P, VAES B, et al. Epidemiology of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a registry-based study. BMJ Open. 2020;10(1):e031734.
[4] SUCHTING R, COLPO GD, ROCHA NP, et al. The Effect of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Inflammation in Older Adults With Knee Osteoarthritis: A Bayesian Residual Change Analysis. Biol Res Nurs. 2020;22(1):57-63.
[5] 汤化琪.玄胡索散成分分析及其治疗骨关节炎作用机制的网络药理学研究[D]. 北京:北京中医药大学,2017.
[6] MATSUMOTO H, HAGINO H, HAYASHI K, et al. The effect of balneotherapy on pain relief, stiffness, and physical function in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: a meta-analysis. ClinRheumatol. 2017; 36(8):1839-1847.
[7] 邓凯烽,陈日兰,朱圣旺,等.电针结合雷火灸治疗寒湿型膝骨性关节炎的临床随机对照试验[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(29):4638-4642.
[8] ZHAO J, WANG Q, WU J, et al. Therapeutic effects of low-frequency phonophoresis with a Chinese herbal medicine versus sodium diclofenac for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Tradit Chin Med. 2016;36(5):613‐617.
[9] 章晓云,张驰,宋世雷,等.基于网络药理学和蛋白模块分析淫羊藿治疗骨关节炎的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020,24(17):2660-2666.
[10] NGUYEN VS, SHI L, WANG SC, et al. Synthesis of Icaritin and β-anhydroicaritinMannich Base Derivatives and Their Cytotoxic Activities on Three Human Cancer Cell Lines. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2017; 17(1):137-142.
[11] HASSANI D, FU X, SHEN Q, et al. Parallel Transcriptional Regulation of Artemisinin and Flavonoid Biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2020;25(5):466-476.
[12] HUANG XF, CHENG WB, JIANG Y, et al. A network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting anti-inflammatory targets of ephedra in treating asthma.IntImmunopharmacol. 2020;83:106423.
[13] LI J, ZHAO P, LI Y, et al. Systems Pharmacology-Based Dissection of Mechanisms of Chinese Medicinal Formula BufeiYishen as an Effective Treatment for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15290.
[14] MONTOJO J, ZUBERI K, RODRIGUEZ H, et al. GeneMANIA: Fast gene network construction and function prediction for Cytoscape. F1000Res. 2014;3:153.
[15] 刘乐平,龙茜,曹学帅,等.基于网络药理学和分子对接法探寻麻杏薏甘汤治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎(COVID-19)活性化合物的研究[J].中草药,2020,51(7):1741-1749.
[16] 章晓云,张驰,宋世雷,等.基于网络药理学和蛋白模块探讨淫羊藿治疗股骨头坏死的机制研究[J].中药材,2019(12): 2905-2914.
[17] COWAN KJ, KLEINSCHMIDT-DÖRR K, GIGOUT A, et al. Translational strategies in drug development for knee osteoarthritis. Drug Discov Today. 2020;S1359-6446(20)30122-7.
[18] WALKER C, BIASUCCI LM. Cardiovascular safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs revisited. Postgrad Med. 2018;130(1): 55-71.
[19] 余绍涌,刘建航,章晓云,等.淫羊藿苷治疗骨性关节炎过程中对关节软骨、软骨下骨、滑膜等影响的机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(14):2243-2249.
[20] 李睿,杨信信,张小辉,等.淫羊藿苷治疗骨性关节炎的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(8):1088-1092.
[21] 段荔.吴生元辨治OA用药规律及益气养血方抗OA体外机制研究[D].昆明:云南中医药大学,2019.
[22] 赵晓燕.淫羊藿苷对人骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖凋亡的影响[J].海南医学,2018,29(1): 10-13.
[23] 汪建样,殷嫦嫦,武翠翠,等.淫羊藿素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进BMSCs成软骨分化[J].中国中药杂志,2016,41(4): 694-699.
[24] WANG ZC, SUN HJ, LI KH, et al. Icariin promotes directed chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells but not hypertrophy in vitro. ExpTherMed. 2014; 8(5):1528-1534.
[25] PARRA S, HERAS M, HERRERO P, et al. Gelsolin: a new biomarker of disease activity in SLE patients associated with HDL-c. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2020;59(3): 650-661.
[26] 陈琦.重度烧伤小鼠凝溶胶蛋白变化规律及其对T细胞免疫功能影响的研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院,2019.
[27] PIKTEL E, WNOROWSKA U, CIEŚLUK M, et al. Recombinant Human Plasma Gelsolin Stimulates Phagocytosis while Diminishing Excessive Inflammatory Responses in Mice with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sepsis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(7):2551.
[28] 曹国平. 基于FKBPs/GR/BDNF通路探讨逍遥散对抑郁模大鼠海马神经可塑性损伤修复的机制研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学,2017.
[29] 高歌.网络药理学方法探讨川续断皂苷Ⅵ诱导间充质干细胞成骨分化[D].长春:吉林大学,2019.
[30] STAMPOLIDIS P, ULLRICH A, IACOBELLI S. LGALS3BP, lectin galactoside-binding soluble 3 binding protein, promotes oncogenic cellular events impeded by antibody intervention. Oncogene. 2015;34(1)39‐52.
[31] 王丹.一个新的TPP1相互作用蛋白OTUB1参与端粒长度调节的作用研究[D].广州:中山大学,2013.
[32] MULLINS MR, RAJAVEL M, HERNANDEZ-SANCHEZ W, et al. POT1-TPP1 Binding and Unfolding of Telomere DNA Discriminates against Structural Polymorphism. J MolBiol. 2016;428(13):2695-2708.
[33] XING Y, SHEPHERD N, LAN J, et al. MMPs/TIMPs imbalances in the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid are associated with the pathogenesis of HIV-1-associated neurocognitive disorders. Brain BehavImmun. 2017;65:161-172.
[34] 陈少华,李拾林.关节腔内注射雷公藤甲素治疗胶原诱导关节炎大鼠的实验研究[J].川北医学院学报,2020,35(1):6-9.
[35] KHAN NM, HASEEB A, ANSARI MY, et al. Dataset of effect of Wogonin, a natural flavonoid, on the viability and activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in IL-1β-stimulated human OA chondrocytes. Data Brief. 2017;12: 150-155.
[36] ZUPAN J, KOMADINA R, MARC J. The relationship between osteoclastogenic and anti-osteoclastogenic pro-inflammatory cytokines differs in human osteoporotic and osteoarthritic bone tissues. Biomed Sci. 2012;19(1):28.
[37] SHI C, LI Z, WU Y, et al. Euscaphic acid and Tormentic acid protect vascular endothelial cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis via PI3K/AKT or ERK 1/2 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020;252:117666.
[38] 潘勇,祝健,卢华斌.白细胞介素-6、白细胞介素-17、白细胞介素-23与膝骨关节炎患者病情活动的相关性研究[J].中国卫生检验杂志,2018,28(11): 1395-1396, 1400.
|
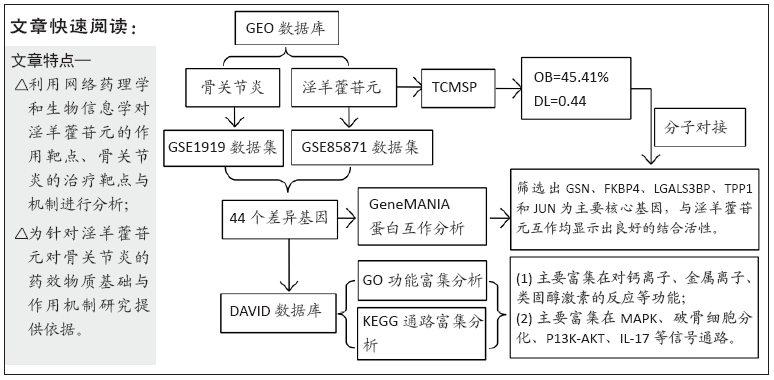
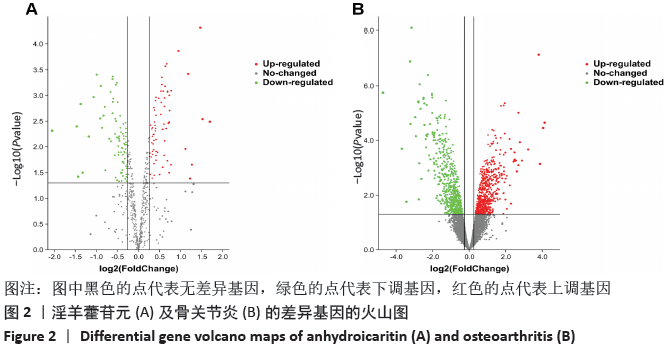
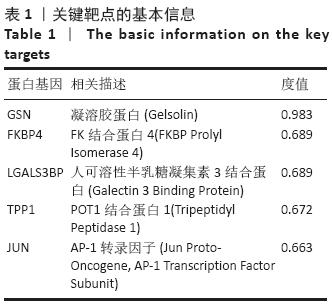
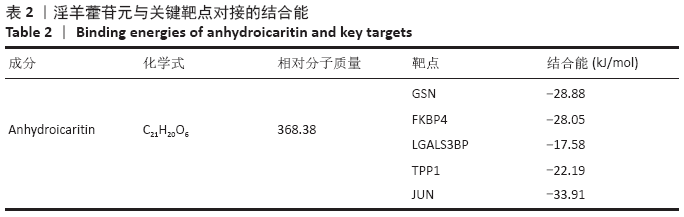
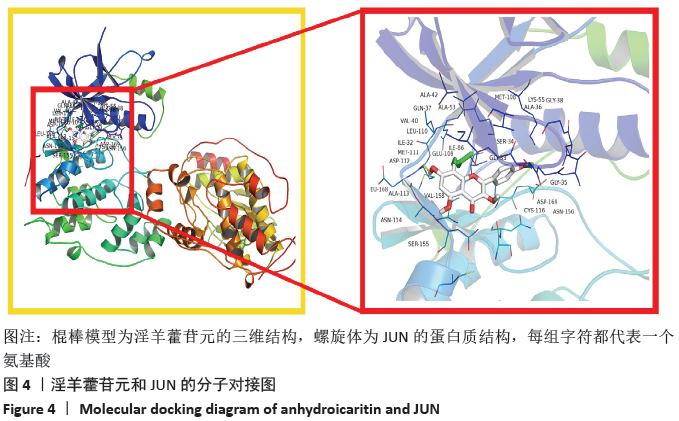
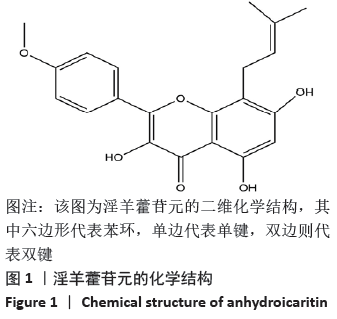 此次研究利用TCMSP数据库对淫羊藿苷元的药物动力学特性进行评估,通过GEO数据库挖掘淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎芯片,借助R语言分析差异基因,利用GeneMANIA数据库分别构建淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎差异基因的蛋白互作网络(protein-protein interaction,PPI),并将其进行合并映射获得淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的关键靶点,在淫羊藿苷元和关键靶点之间进行分子对接验证。最后利用DAVID数据库对关键基因进行基因本体(gene ontology,GO)富集分析和基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)通路分析,旨在从分子水平探讨淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的关键基因及其作用机制,为治疗骨关节炎提供新的靶点和通路。
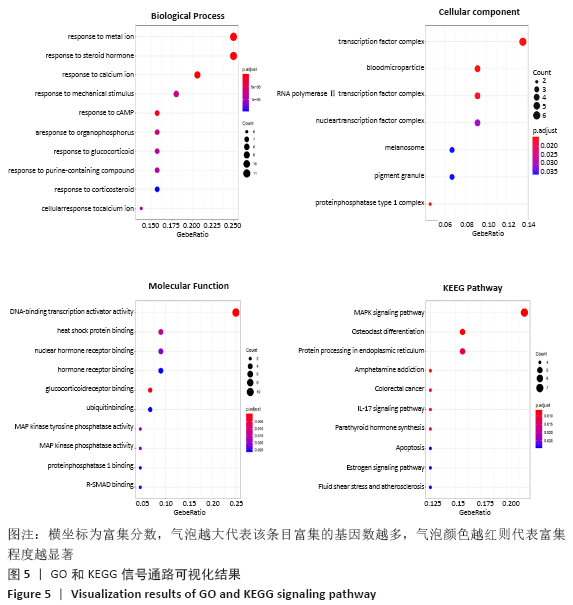
此次研究利用TCMSP数据库对淫羊藿苷元的药物动力学特性进行评估,通过GEO数据库挖掘淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎芯片,借助R语言分析差异基因,利用GeneMANIA数据库分别构建淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎差异基因的蛋白互作网络(protein-protein interaction,PPI),并将其进行合并映射获得淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的关键靶点,在淫羊藿苷元和关键靶点之间进行分子对接验证。最后利用DAVID数据库对关键基因进行基因本体(gene ontology,GO)富集分析和基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)通路分析,旨在从分子水平探讨淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的关键基因及其作用机制,为治疗骨关节炎提供新的靶点和通路。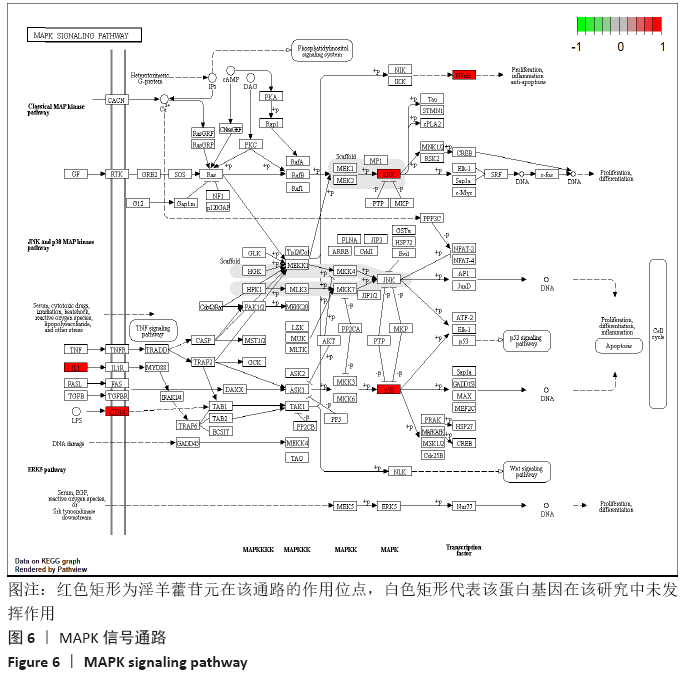 综上所述,淫羊藿苷元具有较高的口服生物利用度和良好的类药性,基于GEO数据库深入挖掘淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎的关键基因,并借助生物信息学从整体水平和分子水平深入探讨淫羊藿苷元与骨关节炎关键基因的互作关系,为研究淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎提供了切实可行的理论和方法。GO和KEGG富集分析预测淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的发病机制不仅涉及炎症反应、破骨细胞活动、成软骨细胞分化、激素水平等,更是与多靶点、多信号通路密切相关,这为后续使用淫羊藿苷元制药及进行骨关节炎的临床治疗提供了重要的理论基础。
综上所述,淫羊藿苷元具有较高的口服生物利用度和良好的类药性,基于GEO数据库深入挖掘淫羊藿苷元和骨关节炎的关键基因,并借助生物信息学从整体水平和分子水平深入探讨淫羊藿苷元与骨关节炎关键基因的互作关系,为研究淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎提供了切实可行的理论和方法。GO和KEGG富集分析预测淫羊藿苷元治疗骨关节炎的发病机制不仅涉及炎症反应、破骨细胞活动、成软骨细胞分化、激素水平等,更是与多靶点、多信号通路密切相关,这为后续使用淫羊藿苷元制药及进行骨关节炎的临床治疗提供了重要的理论基础。