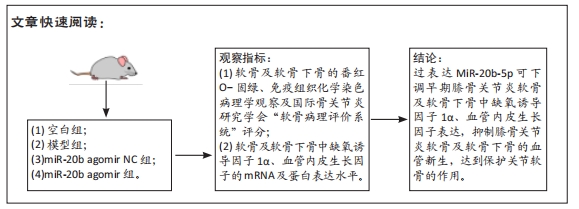
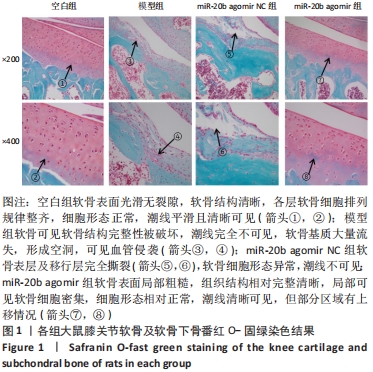
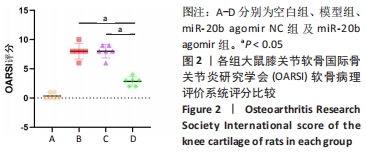
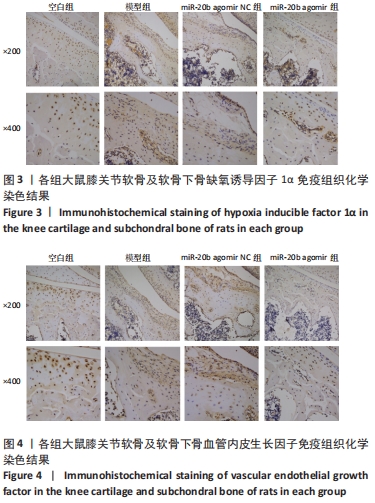
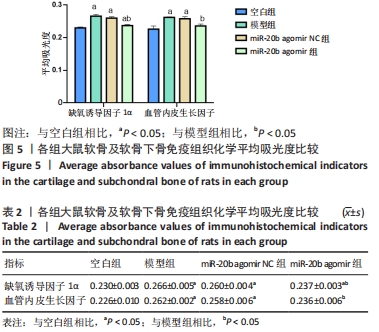
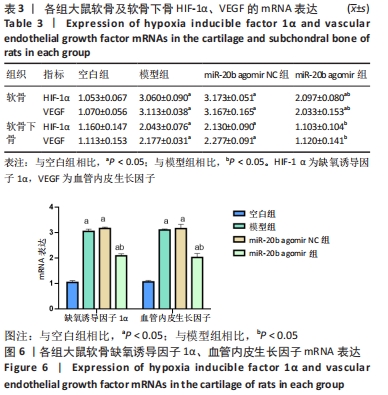
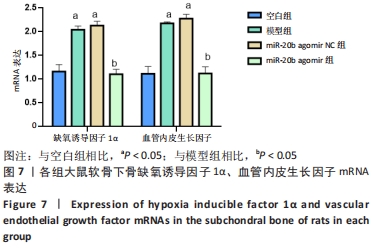
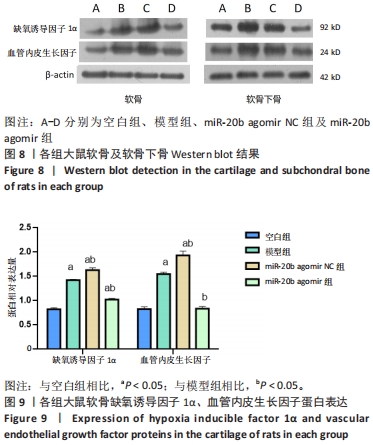
[1] VON KAEPPLER EP, WANG Q, RAGHU H, et al. Interleukin 4 promotes anti-inflammatory macrophages that clear cartilage debris and inhibits osteoclast development to protect against osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2021;229:108784.
[2] IMHOF H, BREITENSEHER M, KAINBERGER F, et al. Degenerative joint disease: cartilage or vascular disease? Skeletal Radiol. 1997;26(7):398-403.
[3] FRÖHLICH LF. Micrornas at the Interface between Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis as Targets for Bone Regeneration. Cells. 2019;8(2):121.
[4] PUGH CW, RATCLIFFE PJ. Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):677-684.
[5] LIU M, WANG D, LI N. MicroRNA-20b Downregulates HIF-1α and Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Osteosarcoma Cells. Oncol Res. 2016;23(5):257-266.
[6] 谢平金,余翔,柴生颋,等.川芎嗪干预早期膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨Ⅱ型胶原纤维α1基因与血管内皮生长因子mRNA及miR20b的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(12):1846-1851.
[7] 李飞龙,谢平金,柴生颋,等.川芎嗪对膝骨性关节炎大鼠软骨VEGF表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(7):904-909.
[8] 罗臻,李宏栩,卢启贵,等.红姜提取物保护早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠的关节软骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(32):5155-5161.
[9] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006; 14(1):13-29.
[10] LITWIC A, EDWARDS MH, DENNISON EM, et al. Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull. 2013;105:185-199.
[11] SAFIRI S, KOLAHI AA, SMITH E, et al. Global, regional and national burden of osteoarthritis 1990-2017: a systematic analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(6):819-828.
[12] WALSH DA. Angiogenesis and arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999; 38(2):103-112.
[13] BURR DB, GALLANT MA. Bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):665-673.
[14] PAN J, ZHOU X, LI W, et al. In situ measurement of transport between subchondral bone and articular cartilage. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(10): 1347-1352.
[15] ZANETTI M, BRUDER E, ROMERO J, et al. Bone marrow edema pattern in osteoarthritic knees: correlation between MR imaging and histologic findings. Radiology. 2000;215(3):835-840.
[16] HAWIGHORST H, LIBICHER M, KNOPP MV, et al. Evaluation of angiogenesis and perfusion of bone marrow lesions: role of semiquantitative and quantitative dynamic MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999;10(3):286-294.
[17] MAPP PI, WALSH DA. Mechanisms and targets of angiogenesis and nerve growth in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(7):390-398.
[18] SU W, LIU G, LIU X, et al. Angiogenesis stimulated by elevated PDGF-BB in subchondral bone contributes to osteoarthritis development. JCI Insight. 2020;5(8):e135446.
[19] MA L, ZHAO X, LIU Y, et al. Dihydroartemisinin attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting abnormal bone remodeling and angiogenesis in subchondral bone. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(3):04855.
[20] HENROTIN Y, PESESSE L, LAMBERT C. Targeting the synovial angiogenesis as a novel treatment approach to osteoarthritis. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2014;6(1):20-34.
[21] PATIL AS, SABLE RB, KOTHARI RM. Occurrence, biochemical profile of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) isoforms and their functions in endochondral ossification. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(4):1298-1308.
[22] HU K, OLSEN BR. Osteoblast-derived VEGF regulates osteoblast differentiation and bone formation during bone repair. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(2):509-526.
[23] HAMILTON JL, NAGAO M, LEVINE BR, et al. Targeting VEGF and Its Receptors for the Treatment of Osteoarthritis and Associated Pain. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(5):911-924.
[24] WALSH DA, BONNET CS, TURNER EL, et al. Angiogenesis in the synovium and at the osteochondral junction in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(7):743-751.
[25] BARRANCO C. Osteoarthritis: Animal data show VEGF blocker inhibits post-traumatic OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(11):638.
[26] GIATROMANOLAKI A, SIVRIDIS E, MALTEZOS E, et al. Upregulated hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha pathway in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003;5(4):R193-201.
[27] KATOH M. Therapeutics targeting angiogenesis: genetics and epigenetics, extracellular miRNAs and signaling networks (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2013;32(4):763-767.
[28] PRASADAM I, BATRA J, PERRY S, et al. Systematic identification, characterization and target gene analysis of microRNAs involved in osteoarthritis subchondral bone pathogenesis. Calcif Tissue Int. 2016; 99(1):43-55.
[29] BORGONIO CUADRA VM, GONZALEZ-HUERTA NC, ROMERO-CORDOBA S, et al. Altered expression of circulating microRNA in plasma of patients with primary osteoarthritis and in silico analysis of their pathways. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e97690.
[30] CHEN Y, ZHANG L, LI E, et al. Long-chain non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes the progression of osteoarthritis via sponging miR-20b/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;253:117685.
[30] QIN B, LIU J, LIU S, et al. MiR-20b targets AKT3 and modulates vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated changes in diabetic retinopathy. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016;48(8):732-740.
[32] 马玉峰,祁印泽,王庆甫,等.关节内注射药物建立骨性关节炎动物模型研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2015,28(1):90-95.
[33] JONES IA, TOGASHI R, WILSON ML, et al. Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(2):77-90.
[34] WANG H, ZHANG H, SUN Q, et al. Intra-articular Delivery of Antago-miR-483-5p Inhibits Osteoarthritis by Modulating Matrilin 3 and Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 2. Mol Ther. 2017;25(3):715-727.
|