中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (24): 3892-3896.doi: 10.12307/2022.572
• 干细胞培养与分化 stem cell culture and differentiation • 上一篇 下一篇
两种棘球蚴绦虫原头节与内皮祖细胞共培养后血管生成抑制蛋白1等因子的表达
俞晓凡1,姜慧娇2,谭小武2,吴向未2
- 1石河子大学医学院,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008;2石河子大学医学院第一附属医院普外科,新疆维吾尔自治区石河子市 832008
Expression of vasohibin-1 and other factors after the co-culture of two kinds of Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex and endothelial progenitor cells
Yu Xiaofan1, Jiang Huijiao2, Tan Xiaowu2, Wu Xiangwei2
- 1School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital, School of Medicine, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832008, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
棘球蚴病:是由棘球蚴绦虫引起的人畜共患寄生虫病,人体感染棘球蚴绦虫幼虫后好发于肝脏,病程缓慢,感染早期无特殊症状,感染后期对病灶周边组织器官产生影响,导致器官功能障碍。
内皮祖细胞:具有增殖和多向分化能力,是血管内皮细胞的前体细胞,可以刺激血管新生及损伤血管的修复。
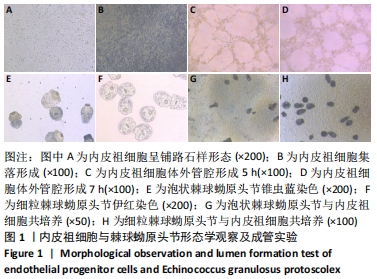
背景:泡状棘球蚴病与细粒棘球蚴病在体内的生长方式不同,泡状棘球蚴病呈浸润性生长,可侵袭组织血管、胆管;细粒棘球蚴病具有纤维性外囊壁包裹病变,对组织呈压迫性生长。两种棘球蚴病对血管侵袭、血管形成产生的作用尚不明确。
目的:探究两种棘球蚴绦虫原头节对内皮祖细胞中血管生成相关因子的影响。
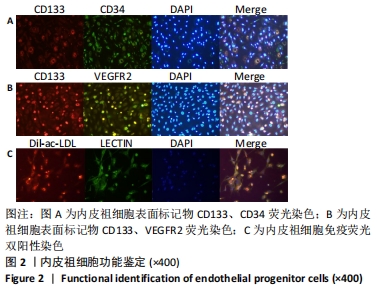
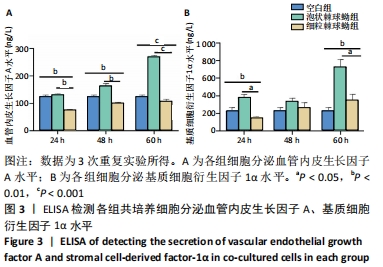
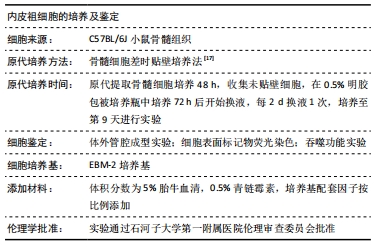
方法:提取、培养、鉴定C57BL/6小鼠骨髓来源内皮祖细胞,提取两种棘球蚴绦虫原头节;将两种棘球蚴绦虫原头节分别与内皮祖细胞共培养24,48,60 h,ELISA检测细胞共培养上清液中血管内皮生长因子A、基质细胞衍生因子1α的分泌水平;Western blot检测各组内皮祖细胞中血管生成抑制蛋白1、血管内皮生长因子A、缺氧诱导因子1α、基质细胞衍生因子1α蛋白的相对表达量。
结果与结论:①泡状棘球蚴组共培养60 h时分泌血管内皮生长因子A、基质细胞衍生因子1α水平明显高于细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);②泡状棘球蚴组共培养48,60 h时内皮祖细胞中血管生成抑制蛋白1、缺氧诱导因子1α、基质细胞衍生因子1α蛋白的相对表达量高于细粒棘球蚴组(P < 0.05);③泡状棘球蚴组与细粒棘球蚴组共培养48,60 h的血管内皮生长因子A相对表达量无显著差异(P > 0.05);④结果表明,泡状棘球蚴促进血管生成,细粒棘球蚴对血管生成影响小。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3897-6629 (吴向未)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: