[1] WANG W, MENG Q, LI Q, et al. Chitosan Derivatives and Their Application in Biomedicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):487.
[2] ZOU M, SUN J, XIANG Z. Induction of M2-Type Macrophage Differentiation for Bone Defect Repair via an Interpenetration Network Hydrogel with a GO-Based Controlled Release System. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(6):e2001502.
[3] KOONS GL, DIBA M, MIKOS AG. Materials design for bone-tissue engineering. Nature Reviews Materials. 2020;5(8):584-603.
[4] REN B, CHEN X, DU S, et al. Injectable polysaccharide hydrogel embedded with hydroxyapatite and calcium carbonate for drug delivery and bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):1257-1266.
[5] BARANWAL A, KUMAR A, PRIYADHARSHINI A, et al. Chitosan: An undisputed bio-fabrication material for tissue engineering and bio-sensing applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018 ;110:110-123.
[6] NAGHIZADEH Z, KARKHANEH A, KHOJASTEH A. Self-crosslinking effect of chitosan and gelatin on alginate based hydrogels: Injectable in situ forming scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:256-264.
[7] SUKPAITA T, CHIRACHANCHAI S, SUWATTANACHAI P, et al. In Vivo Bone Regeneration Induced by a Scaffold of Chitosan/Dicarboxylic Acid Seeded with Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(19):4883.
[8] FAKHRI E, ESLAMI H, MAROUFI P, et al. Chitosan biomaterials application in dentistry. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;162:956-974.
[9] CHENG F, WU Y, LI H, et al. Biodegradable N, O-carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized regenerated cellulose composite gauze as a barrier for preventing postoperative adhesion. Carbohydr Polym. 2019;207:180-190.
[10] LU HT, LU TW, CHEN CH, et al. Development of nanocomposite scaffolds based on biomineralization of N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan/fucoidan conjugates for bone tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B): 2335-2345.
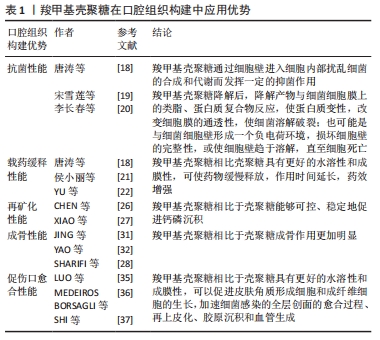
[11] VERMA NK, KAR AK, SINGH A, et al. Control Release of Adenosine Potentiate Osteogenic Differentiation within a Bone Integrative EGCG-g-NOCC/Collagen Composite Scaffold toward Guided Bone Regeneration in a Critical-Sized Calvarial Defect. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22(7):3069-3083.
[12] ARNAUD TM, DE BARROS NETO B, et al. Chitosan effect on dental enamel de-remineralization: an in vitro evaluation. J Dent. 2010;38(11):848-852.
[13] LIU H, LIN M, LIU X, et al. Doping bioactive elements into a collagen scaffold based on synchronous self-assembly/mineralization for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2020;5(4):844-858.
[14] HE J, BAO Y, LI J, et al. Nanocomplexes of carboxymethyl chitosan/amorphous calcium phosphate reduce oral bacteria adherence and biofilm formation on human enamel surface. J Dent. 2019;80:15-22.
[15] JIANG Z, CHI J, HAN B, et al. Preparation and pharmacological evaluation of norcantharidin-conjugated carboxymethyl chitosan in mice bearing hepatocellular carcinoma. Carbohydr Polym. 2017;174:282-290.
[16] SHARIATINIA Z. Carboxymethyl chitosan: Properties and biomedical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;120(Pt B):1406-1419.
[17] SULTANKULOV B, BERILLO D, SULTANKULOVA K, et al. Progress in the Development of Chitosan-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Biomolecules. 2019;9(9):470.
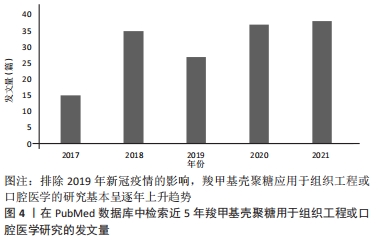
[18] 唐涛,薛毅,信玉华.羧甲基壳聚糖复合奥硝唑后对口腔重要厌氧菌增效抑菌作用的评价[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2007,23(3):451-452.
[19] 宋雪莲,孙莹莹,刘扬,等.羧甲基壳聚糖及其复合物对根管内粪肠球菌的作用评价[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(3):265-269.
[20] 李长春,许晓燕,徐全臣,等.纳米羧甲基壳聚糖氟化钠涂膜预防龋齿的实验室研究[J].中国药房,2015,26(16): 2212-2215.
[21] 侯小丽,谢光远.奥硝唑羧甲基壳聚糖联合透明质酸辅助牙周基础治疗老年慢性牙周炎效果观察[J].山东医药,2017,57(34):95-96.
[22] YU Y, SUN Y, ZHOU X, et al. Ag and peptide co-decorate polyetheretherketone to enhance antibacterial property and osteogenic differentiation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;198:111492.
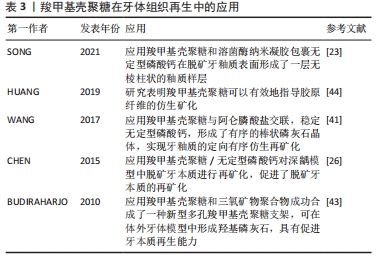
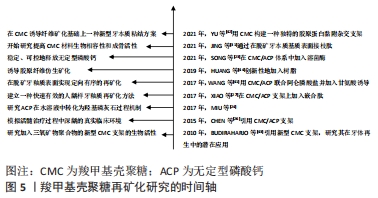
[23] SONG J, LI T, GAO J, et al. Building an aprismatic enamel-like layer on a demineralized enamel surface by using carboxymethyl chitosan and lysozyme-encapsulated amorphous calcium phosphate nanogels. J Dent. 2021;107:103599.
[24] NIU X, CHEN S, TIAN F, et al. Hydrolytic conversion of amorphous calcium phosphate into apatite accompanied by sustained calcium and orthophosphate ions release. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;70(Pt 2):1120-1124.
[25] 刘学玉,潘克清,张丽,等.羧甲基壳聚糖锌多肽复合材料局部应用对巴马小型猪龈沟液中IL-1、TNF-α和PGE-2含量的影响[J].上海口腔医学,2016,25(2):172-176.
[26] CHEN Z, CAO S, WANG H, et al. Biomimetic remineralization of demineralized dentine using scaffold of CMC/ACP nanocomplexes in an in vitro tooth model of deep caries. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116553.
[27] XIAO Z, QUE K, WANG H, et al. Rapid biomimetic remineralization of the demineralized enamel surface using nano-particles of amorphous calcium phosphate guided by chimaeric peptides. Dent Mater. 2017;33(11):1217-1228.
[28] SHARIFI F, ATYABI SM, NOROUZIAN D, et al. Polycaprolactone/carboxymethyl chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering application. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:243-248.
[29] AGARWAL T, NARAYAN R, MAJI S, et al. Gelatin/Carboxymethyl chitosan based scaffolds for dermal tissue engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(Pt B):1499-1506.
[30] HE Y, ZHAO W, DONG Z, et al. A biodegradable antibacterial alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan/Kangfuxin sponges for promoting blood coagulation and full-thickness wound healing. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;167:182-192.
[31] JING X, XIE B, LI X, et al. Peptide decorated demineralized dentin matrix with enhanced bioactivity, osteogenic differentiation via carboxymethyl chitosan. Dent Mater. 2021;37(1):19-29.
[32] YAO M, ZOU Q, ZOU W, et al. Bifunctional scaffolds of hydroxyapatite/poly(dopamine)/carboxymethyl chitosan with osteogenesis and anti-osteosarcoma effect. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(9):3319-3333.
[33] CHENG Y, LU S, HU Z, et al. Marine collagen peptide grafted carboxymethyl chitosan: Optimization preparation and coagulation evaluation. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:3953-3964.
[34] WANG YL, ZHOU YN, LI XY, et al. Continuous production of antibacterial carboxymethyl chitosan-zinc supramolecular hydrogel fiber using a double-syringe injection device. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;156:252-261.
[35] LUO P, NIE M, WEN H, et al. Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl chitosan sulfate/oxidized konjac glucomannan hydrogels. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;113:1024-1031.
[36] MEDEIROS BORSAGLI FGL, DE SOUZA AJM, Paiva AE. Ecofriendly multifunctional thiolated carboxymethyl chitosan-based 3D scaffolds with luminescent properties for skin repair and theragnostic of tissue regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;165(Pt B):3051-3064.
[37] SHI L, LIN F, ZHOU M, et al. Preparation of biocompatible wound dressings with dual release of antibiotic and platelet-rich plasma for enhancing infected wound healing. J Biomater Appl. 2021;36(2):219-236.
[38] HENKEL J, WOODRUFF MA, EPARI DR, et al. Bone Regeneration Based on Tissue Engineering Conceptions - A 21st Century Perspective. Bone Res. 20135;1(3):216-248.
[39] SUNGKHAPHAN P, THAVORNYUTIKARN B, KAEWKONG P, et al. Antibacterial and osteogenic activities of clindamycin-releasing mesoporous silica/carboxymethyl chitosan composite hydrogels. R Soc Open Sci. 2021;8(9): 210808.
[40] WANG Y, VAN MANH N, WANG H, et al. Synergistic intrafibrillar/extrafibrillar mineralization of collagen scaffolds based on a biomimetic strategy to promote the regeneration of bone defects. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016;11:2053-2067.
[41] WANG H, XIAO Z, YANG J, et al. Oriented and Ordered Biomimetic Remineralization of the Surface of Demineralized Dental Enamel Using HAP@ACP Nanoparticles Guided by Glycine. Sci Rep. 2017;7:40701.
[42] YU F, LUO ML, XU RC, et al. A novel dentin bonding scheme based on extrafibrillar demineralization combined with covalent adhesion using a dry-bonding technique. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(10):3557-3567.
[43] BUDIRAHARJO R, NEOH KG, KANG ET, et al. Bioactivity of novel carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold incorporating MTA in a tooth model. Int Endod J. 2010;43(10):930-939.
[44] HUANG Z, QI Y, ZHANG K, et al. Use of experimental-resin-based materials doped with carboxymethyl chitosan and calcium phosphate microfillers to induce biomimetic remineralization of caries-affected dentin. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2019;89:81-88.
[45] 付军权,费瑞,张桂荣,等.羧甲基壳聚糖银对实验性大鼠牙周炎的治疗作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2009,35(4):669-672.
[46] 姜明凯,曹文帅,徐全臣.羧甲基壳聚糖应用于牙周病学的研究进展[J].广东牙病防治,2014,22(5):275-278.
[47] 郭珲,潘克清,邓婧,等.羧甲基壳聚糖锌多肽复合材料对人牙周膜成纤维细胞的毒性[J].上海口腔医学,2017,26(2):162-166.
[48] 王丹,彭伟,李明珠,等.羧甲基壳聚糖温敏凝胶对NIH3T3细胞在病变牙根面附着和增殖的影响[J].郑州大学学报(医学版),2014,49(5):648-650.
[49] CHICHIRICCO PM, RIVA R, THOMASSIN JM, et al. In situ photochemical crosslinking of hydrogel membrane for Guided Tissue Regeneration. Dent Mater. 2018;34(12):1769-1782.
[50] ZHANG Y, GULATI K, LI Z, et al. Dental Implant Nano-Engineering: Advances, Limitations and Future Directions. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(10):2489.
[51] YANG M, JIANG P, GE Y, et al. Dopamine self-polymerized along with hydroxyapatite onto the preactivated titanium percutaneous implants surface to promote human gingival fibroblast behavior and antimicrobial activity for biological sealing. J Biomater Appl. 2018;32(8):1071-1082.
|