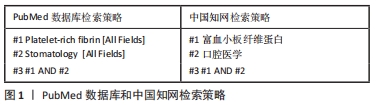
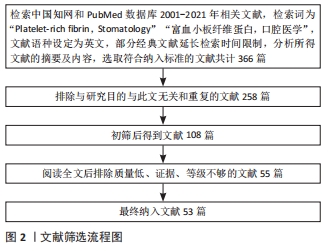
[1] MIRON RJ, FUJIOKA-KOBAYASHI M, BISHARA M, et al. Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Soft Tissue Wound Healing: A Systematic Review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2017;23:83-99.
[2] HERMIDA-NOGUEIRA L, BARRACHINA MN, MORÁN LA, et al. Deciphering the secretome of leukocyte-platelet rich fibrin: towards a better understanding of its wound healing properties. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14571.
[3] DOHAN EHRENFEST DM, DEL CORSO M, DISS A, et al. Three-dimensional architecture and cell composition of a Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin clot and membrane. J Periodontol. 2010;81:546-555
[4] HUANG Y, BORNSTEIN MM, LAMBRICHTS I, et al. Platelet-rich plasma for regeneration of neural feedback pathways around dental implants: a concise review and outlook on future possibilities. Int J Oral Sci. 2017;9:1-9.
[5] RATAJCZAK J, VANGANSEWINKEL T, GERVOIS P, et al. Angiogenic Properties of ‘Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin’. Sci Rep. 2018;8:14632.
[6] FENG M, WANG Y, ZHANG P, et al. Antibacterial effects of platelet-rich fibrin produced by horizontal centrifugation. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12:32.
[7] KOUR P, PUDAKALKATTI PS, VAS AM, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalisComparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Platelet-rich Plasma, Platelet-rich Fibrin, and Injectable Platelet-rich Fibrin on the Standard Strains of and Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Contemp Clin Dent. 2018;9:S325-S330.
[8] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part I: technological concepts and evolution. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:e37-44.
[9] Miron RJ, Chai J, Zheng S, et al. A novel method for evaluating and quantifying cell types in platelet rich fibrin and an introduction to horizontal centrifugation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107:2257-2271.
[10] MOSESSON MW, SIEBENLIST KR, MEH DA. The structure and biological features of fibrinogen and fibrin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;936:11-30.
[11] Dohan DM, MD C, Charrier JB. Cytotoxicity analyses of Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) on a wide range of human cells: The answer to a commercial controversy. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103(5):587-593.
[12] HO W, TAWIL B, DUNN JC, et al. The behavior of human mesenchymal stem cells in 3D fibrin clots: dependence on fibrinogen concentration and clot structure.Tissue Eng. 2006;12:1587-1595.
[13] HOLDERFIELD MT, HUGHES CC. Crosstalk between vascular endothelial growth factor, notch,and transforming growth factor-beta in vascular morphogenesis. Circ Res. 2008;102:637-652.
[14] MARX RE, CARLSON ER, EICHSTAEDT RM, et al. Platelet-rich plasma: Growth factor enhancement for bone grafts. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;85:638-646.
[15] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:e45-50.
[16] DOHAN DM, CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part III: leucocyte activation: a new feature for platelet concentrates?Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101:e51-55.
[17] STRAUSS FJ, STAHLI A, GRUBER R. The use of platelet-rich fibrin to enhance the outcomes of implant therapy: A systematic review. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29 Suppl 18(Suppl Suppl 18):6-19.
[18] KARGARPOUR Z, NASIRZADE J, STRAUSS FJ, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin suppresses in vitro osteoclastogenesis. J Periodontol. 2020;91:413-421.
[19] Hartlev J, Schou S, Isidor F, et al. A clinical and radiographic study of implants placed in autogenous bone grafts covered by either a platelet-rich fibrin membrane or deproteinised bovine bone mineral and a collagen membrane: a pilot randomised controlled clinical trial with a 2-year follow-up. Int J Implant Dent. 2021;7:8.
[20] Fang J, Xin X, Li W, et al. Immediate implant placement in combination with platelet rich-fibrin into extraction sites with periapical infection in the esthetic zone: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases. 2021;9:960-969.
[21] JUNG RE, IOANNIDIS A, HAMMERLE CH, et al. Alveolar ridge preservation in the esthetic zone. Periodontol 2000. 2018;77:165-175.
[22] SCHROPP L, WENZEL A, KOSTOPOULOS L, et al. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23:313-323.
[23] Ivanova V, Chenchev I, Zlatev S, et al. Comparison Study of the Histomorphometric Results after Socket Preservation with PRF and Allograft Used for Socket Preservation—Randomized Controlled Trials. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(14):7451.
[24] Zhang Y, Ruan Z, Shen M, et al. Clinical effect of platelet-rich fibrin on the preservation of the alveolar ridge following tooth extraction. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15:2277-2286.
[25] Azangookhiavi H, Ghodsi S, Jalil F, et al. Comparison of the Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin and Bone Allograft for Alveolar Ridge Preservation after Tooth Extraction: A Clinical Trial. Front Dent. 2020;17:1-6
[26] LIN CY, CHEN Z, PAN WL, et al. Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin on Ridge Preservation in Perspective of Bone Healing: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2019;34:845-854.
[27] AREEWONG K, CHANTARAMUNGKON M, KHONGKHUNTHIAN P. Platelet-rich fibrin to preserve alveolar bone sockets following tooth extraction: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21:1156-1163.
[28] PAN J, XU Q,HOU J, et al. Effect of platelet-rich fibrin on alveolar ridge preservation: A systematic review. J Am Dent Assoc. 2019;150:766-778.
[29] CHOUKROUN J, DISS A, SIMONPIERI A, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): a second-generation platelet concentrate. Part V: histologic evaluations of PRF effects on bone allograft maturation in sinus lift. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006;101:299-303.
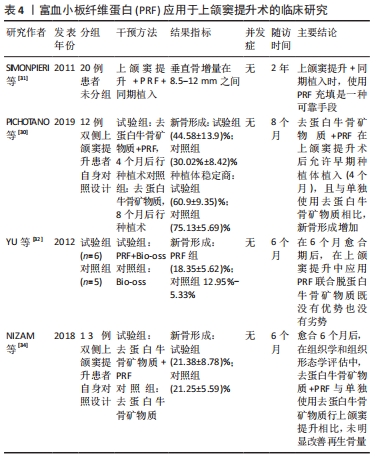
[30] PICHOTANO EC, MOLON RS, SOUZA RV, et al. Evaluation of L-PRF combined with deproteinized bovine bone mineral for early implant placement after maxillary sinus augmentation: A randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21:253-262.
[31] SIMONPIERI A, CHOUKROUN J, DEL CORSO M, et al. Simultaneous sinus-lift and implantation using microthreaded implants and leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin as sole grafting material: a six-year experience. Implant Dent. 2011;20(1):2-12.
[32] Yu Z, Tangl S, Huber CD, et al. Effects of Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin on bone regeneration in combination with deproteinized bovine bone mineral in maxillary sinus augmentation: A histological and histomorphometric study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40(4):321-328.
[33] Tatullo M, Marrelli M, Cassetta M, et al. Platelet Rich Fibrin (P.R.F.) in reconstructive surgery of atrophied maxillary bones: clinical and histological evaluations. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9:872-880.
[34] NIZAM N, EREN G, AKCALI A, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation with leukocyte and platelet-rich fibrin and deproteinized bovine bone mineral: A split-mouth histological and histomorphometric study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2018;29:67-75.
[35] Barbu HM, Iancu SA, Hancu V, et al. PRF-Solution in Large Sinus Membrane Perforation with Simultaneous Implant Placement-Micro CT and Histological Analysis. Membranes. 2021;11(6):438.
[36] Damsaz M, Castagnoli CZ, Eshghpour M, et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Efficacy of Leukocyte and Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Maxillary Sinus Floor Lift, Graft and Surgical Augmentation Procedures. Front Surg. 2020;7:537138.
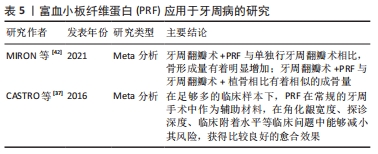
[37] CASTRO AB, MESCHI N, TEMMERMAN A, et al. Regenerative potential of leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin. Part A: intra-bony defects, furcation defects and periodontal plastic surgery. A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44:67-82.
[38] CASTRO AB, HERRERO ER, SLOMKA V, et al. Antimicrobial capacity of Leucocyte-and Platelet Rich Fibrin against periodontal pathogens. Sci Rep. 2019;9:8188.
[39] GOEL A, WINDOR LJ, GREGORY RL, et al. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin on human gingival and periodontal ligament fibroblast proliferation from chronic periodontitis versus periodontally healthy subjects. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2021;7(4): 436-442.
[40] DEBNATH K, CHATTERJEE AA. Evaluation of periosteum eversion and coronally advanced flap techniques in the treatment of isolated Miller’s Class I/II gingival recession: A comparative clinical study. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2018;22:140-149.
[41] Mijiritsky E, Assaf HD, Peleg O, et al. Use of PRP, PRF and CGF in Periodontal Regeneration and Facial Rejuvenation-A Narrative Review. Biology. 2021;10(4):317.
[42] Miron RJ, Moraschini V, Fujioka-Kobayashi M, et al. Use of platelet-rich fibrin for the treatment of periodontal intrabony defects: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Oral Investig. 2021;25:2461-2478.
[43] KORNSUTHISOPON C, PIRARAT N, OSATHANON T, et al. Autologous platelet-rich fibrin stimulates canine periodontal regeneration. Sci Rep. 2020;10:1850.
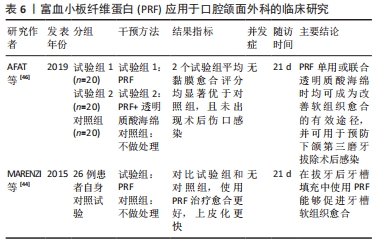
[44] Marenzi G, Riccitiello F, Tia M, et al. Influence of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) in the Healing of Simple Postextraction Sockets: A Split-Mouth Study. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:369273.
[45] Al-Hamed FS, Tawfik MA, Abdelfadil E, et al. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin After Mandibular Third Molar Extraction: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75:1124-1135.
[46] Afat IM, Akdoğan ET, Gönül O. Effects of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin alone and combined with hyaluronic acid on early soft tissue healing after surgical extraction of impacted mandibular third molars: A prospective clinical study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019;47:280-286.
[47] SINGH A, KOHLI M, GUPTA N. latelet rich fibrin: a novel approach for osseous regeneration.J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2012;11:430-434.
[48] Mauceri R, Murgia D, Cicero O, et al. Leucocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Block: Its Use for the Treatment of a Large Cyst with Implant-Based Rehabilitation. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021;57(2):180.
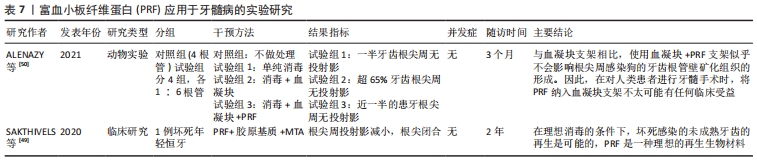
[49] Sakthivel S, Gayathri V, Anirudhan S, et al. Platelet-rich fibrin and collagen matrix for the regeneration of infected necrotic immature teeth. J Clin Transl Res. 2020;6:1-5.
[50] Alenazy MS, Al-Nazhan S, Mosadomi HA. Histologic, Radiographic, and Micro-Computed Tomography Evaluation of Experimentally Enlarged Root Apices in Dog Teeth with Apical Periodontitis after Regenerative Treatment. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 2021;94:100620.
[51] Riaz A, Shah FA. Regenerating the Pulp-Dentine Complex Using Autologous Platelet Concentrates: A Critical Appraisal of the Current Histological Evidence. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18:37-48.
[52] Temmerman A, Vandessel J, Castro A, et al. The use of leucocyte and platelet-rich fibrin in socket management and ridge preservation: a split-mouth, randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43:990-999.
[53] Afat IM, Akdoğan ET, Gönül O. Effects of Leukocyte- and Platelet-Rich Fibrin Alone and Combined With Hyaluronic Acid on Pain, Edema, and Trismus After Surgical Extraction of Impacted Mandibular Third Molars. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018;76:926-932.
|