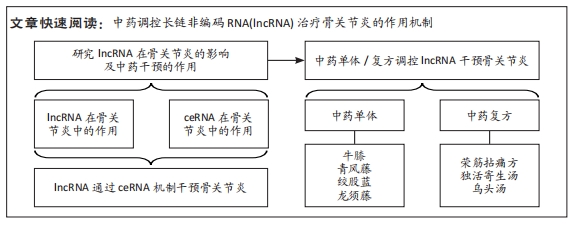
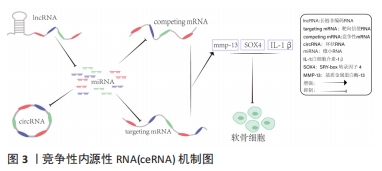
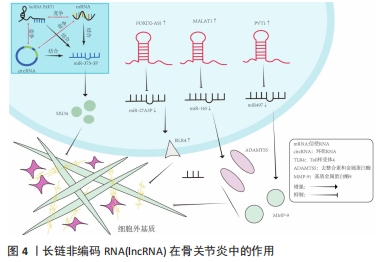
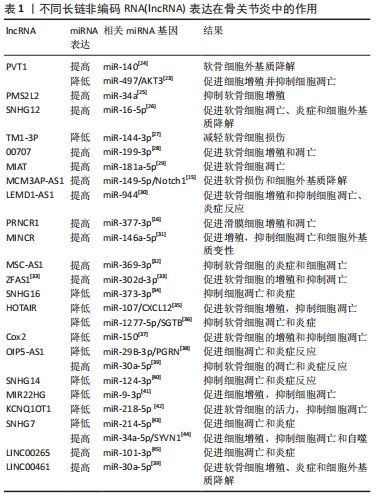
[1] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis(OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[2] GIKARO JM, XIONG H, LIN F. Activity limitation and participation restriction in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid arthritis: findings based on the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):647.
[3] GOH SL, PERSSON M, STOCKS J, et al. Relative Efficacy of Different Exercises for Pain, Function, Performance and Quality of Life in Knee and Hip Osteoarthritis: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2019;49(5):743-761.
[4] 李盛华,周明旺.规范膝骨关节炎的分期分型,倡导膝骨关节炎的中医疗法——《膝骨关节炎中医诊疗指南(2020年版)》解读[J].中医正骨,2021,33(7):1-3.
[5] ZHANG F, LAMMI MJ, TAN S, et al. Cell cycle-related lncRNAs and mRNAs in osteoarthritis chondrocytes in a Northwest Chinese Han Population. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(24):e19905.
[6] KONG H, SUN ML, ZHANG XA, et al. Crosstalk Among circRNA/lncRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Osteoarthritis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:774370.
[7] 刘莉梅,杜小正,方晓丽,等.长链非编码RNA与RA相关性及中医药干预的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(11):1700-1705.
[8] KARAGKOUNI D, KARAVANGELI A, PARASKEVOPOULOU MD, et al. Characterizing miRNA-lncRNA Interplay. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2372: 243-262.
[9] HE CP, JIANG XC, CHEN C, et al. The function of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2021;10(2):122-133.
[10] CHEN Y, ZHANG L, LI E, et al. Long-chain non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes the progression of osteoarthritis via sponging miR-20b/PTEN axis. Life Sci. 2020;253:117685.
[11] WU X, BIAN B, LIN Z, et al. Identification of exosomal mRNA, lncRNA and circRNA signatures in an osteoarthritis synovial fluid-exosomal study. Exp Cell Res. 2022;410(1):112881.
[12] REN S, LIN P, WANG J, et al. Circular RNAs: Promising Molecular Biomarkers of Human Aging-Related Diseases via Functioning as an miRNA Sponge. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;18:215-229.
[13] TEHRANI SS, EBRAHIMI R, AL-E-AHMAD A, et al. Competing Endogenous RNAs (CeRNAs): Novel Network in Neurological Disorders. Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(29):5983-6010.
[14] LIU Y, GU X, LIU H, et al. New Insight of Circular RNAs in Human Musculoskeletal Diseases. DNA Cell Biol. 2020;39(11):1938-1947.
[15] XU F, HU Q F, LI J, et al. SOX4-activated lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 aggravates osteoarthritis progression by modulating miR-149-5p/Notch1 signaling. Cytokine. 2022;152:155805.
[16] WANG G, LI C, ZHANG X, et al. Long non-coding PRNCR1 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of synoviocytes in osteoarthritis by sponging miR-377-3p. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):238.
[17] LI H, LIU Z, GUO X, et al. Circ_0128846/miR-140-3p/JAK2 Network in Osteoarthritis Development. Immunol Invest. 2022;51(6):1529-1547.
[18] LI X, XIE C, XIAO F, et al. Circular RNA circ_0000423 regulates cartilage ECM synthesis via circ_0000423/miRNA-27b-3p/MMP-13 axis in osteoarthritis. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(8):3400-3415.
[19] SUN H, PENG G, NING X, et al. Emerging roles of long noncoding RNA in chondrogenesis, osteogenesis, and osteoarthritis. Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(1):16-30.
[20] ZHU YJ, JIANG DM. LncRNA PART1 modulates chondrocyte proliferation, apoptosis, and extracellular matrix degradation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-373-3p/SOX4 axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(19): 8175-8185.
[21] WANG Y, CAO L, WANG Q, et al. LncRNA FOXD2-AS1 induces chondrocyte proliferation through sponging miR-27a-3p in osteoarthritis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019;47(1):1241-1247.
[22] LIU C, REN S, ZHAO S, et al. LncRNA MALAT1/MiR-145 Adjusts IL-1β-Induced Chondrocytes Viability and Cartilage Matrix Degradation by Regulating ADAMTS5 in Human Osteoarthritis. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(11):1081-1092.
[23] XU J, FANG X, QIN L, et al. LncRNA PVT1 regulates biological function of osteoarthritis cells by regulating miR-497/AKT3 axis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022;101(45):e31725.
[24] YAO N, PENG S, WU H, et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1 promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation by acting as a sponge for miR-140 in IL-1β-stimulated chondrocytes. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;17(1):218.
[25] YANG F, ZHAO M, SANG Q, et al. Long non-coding RNA PMS2L2 is down-regulated in osteoarthritis and inhibits chondrocyte proliferation by up-regulating miR-34a. J Immunotoxicol. 2022;19(1):74-80.
[26] YANG X, CHEN H, ZHENG H, et al. LncRNA SNHG12 Promotes Osteoarthritis Progression Through Targeted Down-Regulation of miR-16-5p. Clin Lab. 2022;68(1):210402.
[27] YI Y, YANG N, YANG Z, et al. LncRNA TM1-3P Regulates Proliferation, Apoptosis and Inflammation of Fibroblasts in Osteoarthritis through miR-144-3p/ONECUT2 Axis. Orthop Surg. 2022;14(11):3078-3091.
[28] XU Y, DUAN L, LIU S, et al. Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00707 regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation in osteoarthritis by serving as a sponge for microRNA-199-3p. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4): 11137-11145.
[29] ZENG S, TU M. The lncRNA MIAT/miR-181a-5p axis regulates osteopontin (OPN)-mediated proliferation and apoptosis of human chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. J Mol Histol. 2022;53(2):285-296.
[30] LI H, LIAN K, MAO J, et al. LncRNA LEMD1-AS1 relieves chondrocyte inflammation by targeting miR-944/PGAP1 in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(19):2038-2050.
[31] LI D, WANG X, YI T, et al. LncRNA MINCR attenuates osteoarthritis progression via sponging miR-146a-5p to promote BMPR2 expression. Cell Cycle. 2022;21(22):2417-2432.
[32] TANG Z, GONG Z, SUN X. Long non-coding RNA musculin antisense RNA 1 promotes proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in osteoarthritic chondrocytes via the microRNA-369-3p/Janus kinase-2/ signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):1554-1564.
[33] LI J, LIU M, LI X, et al. Long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 suppresses chondrocytes apoptosis via miR-302d-3p/SMAD2 in osteoarthritis. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2021;85(4):842-850.
[34] FAN H, DING L, YANG Y. lncRNA SNHG16 promotes the occurrence of osteoarthritis by sponging miR-373-3p. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(2):117.
[35] LU J, WU Z, XIONG Y. Knockdown of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR inhibits osteoarthritis chondrocyte injury by miR-107/CXCL12 axis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):410.
[36] WANG B, SUN Y, LIU N, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR modulates chondrocyte apoptosis and inflammation in osteoarthritis via regulating miR-1277-5p/SGTB axis. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(3):495-504.
[37] JIANG M, XU K, REN H, et al. Role of lincRNA-Cox2 targeting miR-150 in regulating the viability of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;22(2):800.
[38] ZHI L, ZHAO J, ZHAO H, et al. Downregulation of LncRNA OIP5-AS1 Induced by IL-1β Aggravates Osteoarthritis via Regulating miR-29b-3p/PGRN. Cartilage. 2021;13(2_suppl):1345S-1355S.
[39] ZHANG Y, MA L, WANG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00461 induced osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting miR-30a-5p. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(5):4111-4123.
[40] WANG B, LI J, TIAN F. Downregulation of lncRNA SNHG14 attenuates osteoarthritis by inhibiting FSTL-1 mediated NLRP3 and TLR4/NF-κB pathway through miR-124-3p. Life Sci. 2021;270:119143.
[41] LONG H, LI Q, XIAO Z, et al. LncRNA MIR22HG promotes osteoarthritis progression via regulating miR-9-3p/ADAMTS5 pathway. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):3148-3158.
[42] LIU Y, ZHAO D, WANG X, et al. LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 attenuates osteoarthritic chondrocyte dysfunction via the miR-218-5p/PIK3C2A axis. Cell Tissue Res. 2021;385(1):115-126.
[43] XU J, PEI Y, LU J, et al. LncRNA SNHG7 alleviates IL-1β-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting miR-214-5p-mediated PPARGC1B signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021,90:107150.
[44] TIAN F, WANG J, ZHANG Z, et al. LncRNA SNHG7/miR-34a-5p/SYVN1 axis plays a vital role in proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy in osteoarthritis. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):9.
[45] ZOU H, LU C, QIU J. Long non-coding RNA LINC00265 promotes proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis by sponging miR-101-3p[J]. Autoimmunity. 2021;54(8):526-538.
[46] LI G, LIU Y, MENG F, et al. Tanshinone IIA promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis by up-regulating lncRNA GAS5. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5): BSR20180626.
[47] ZHANG LB, YAN Y, HE J, et al. Epimedii Herba: An ancient Chinese herbal medicine in the prevention and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Chem. 2022;10:1023779.
[48] 刘芝宏,黄玉兰,姜芳,等.青藤碱的合成及构效关系研究进展[J].广州化工,2017,45(6):48-52.
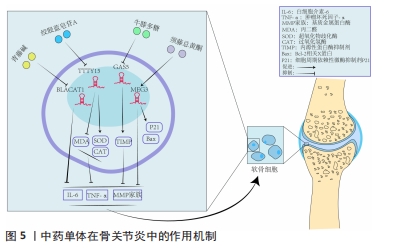
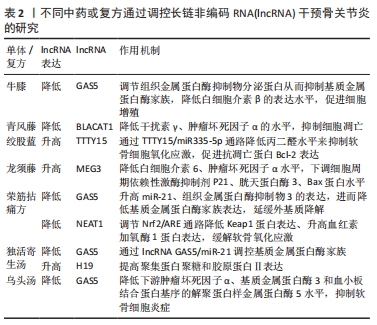
[49] 陈晨,郑润泉,李宗玉.青藤碱调控LncRNA BLACAT1对骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡的影响[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(17):2069-2073.
[50] 张子龙,李雯珊,滕菲,等.绞股蓝总苷提取物及总苷片的质量标准研究[J].中国中药杂志, 2020,45(24):5976-5981.
[51] 牛帅帅,孙卓伟,王承群.绞股蓝皂苷A调控lncRNA TTTY15/miR-335-5p通路对骨关节炎软骨细胞损伤的影响及机制[J].河北医药,2022, 44(7):981-985.
[52] 刘文斌,李艳兵,周焱涛.绞股蓝提取物通过调控lncRNA PICSAR对IL-1β诱导软骨细胞损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J].疑难病杂志,2021, 20(10):1045-1049.
[53] XU XX, ZHANG XH, DIAO Y, et al. Achyranthes bidentate saponins protect rat articular chondrocytes against interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis in vitro. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2017;33(2):62-68.
[54] FU C, QIU Z, HUANG Y, et al. Protective role of Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharides against chondrocyte extracellular matrix degeneration through lncRNA GAS5 in osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2022;24(2):532.
[55] 任安龙,季向荣,方斌.龙须藤总黄酮对膝关节炎软骨细胞增殖、凋亡的影响研究[J].新中医,2020,52(23):12-16.
[56] 付长龙,谢新宇,何俊君,等.基于PERK通路探讨荣筋拈痛方对软骨细胞内质网应激反应抑制作用[J]. 福建中医药,2022,53(4):22-24.
[57] 付长龙,谢新宇,邱志伟,等.基于lncRNA NEAT1与Nrf2/ARE通路研究荣筋拈痛方延缓膝骨关节炎软骨退变作用机制[J].康复学报,2022, 32(4):332-337.
[58] 韩玫,李贞,曹建西.温针灸联合口服独活寄生汤治疗膝骨关节炎寒湿痹阻证[J].中医正骨,2021,33(6):67-69.
[59] 李辉,李宁,谢兴文,等.中医药干预基质金属蛋白酶表达治疗膝骨性关节炎研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(1):120-123.
[60] 陈俊,郑若曦,叶锦霞,等.独活寄生汤治疗大鼠膝骨关节炎的作用机制研究[J].中医正骨,2021,33(11):6-12.
[61] 陈长兴,仲卫红,金灵璐,等.乌头汤抑制膝骨关节炎软骨细胞氧化应激反应的作用研究[J].风湿病与关节炎,2022,11(11):1-4. |