中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (20): 3195-3201.doi: 10.12307/2023.405
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
荣筋拈痛方调控软骨基质代谢防治膝骨关节炎
赵忠胜1,2,郑若曦1,林 洁1,陈 俊3,叶锦霞3,付长龙3,吴广文1,3
- 1福建中医药大学中西医结合研究院,福建省福州市 350122; 2重庆市中医院骨科,重庆市 400021;3福建省中西医结合老年性疾病重点实验室,福建省福州市 350122
Rongjin Niantong Fang for treating knee osteoarthritis by regulating cartilage matrix metabolism
Zhao Zhongsheng1, 2, Zheng Ruoxi1, Lin Jie1, Chen Jun3, Ye Jinxia3, Fu Changlong3, Wu Guangwen1, 3
- 1Academy of Integrative Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chongqing 400021, China; 3Fujian Key Laboratory of Integrative Medicine on Geriatrics, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
长链非编码RNA:是全长大于200个核苷酸的非编码RNA,占非编码RNA的80%,缺乏翻译成蛋白的能力,可通过染色质重塑、竞争性内源性RNA、mRNA稳定和支架蛋白募集等多种机制影响基因的转录和转录后表达。基质金属蛋白酶:是一大类具有相似结构的蛋白酶,构成了细胞外基质降解最重要的蛋白水解系统,基质金属蛋白酶在软骨基质降解中起重要作用。
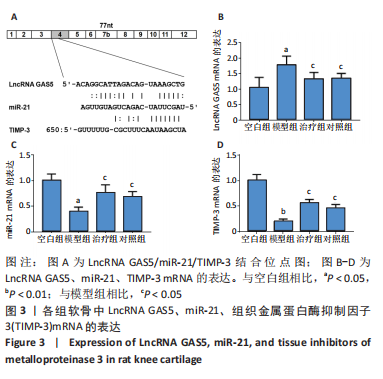
背景:前期研究发现荣筋拈痛方能有效抑制软骨基质降解。长链非编码RNA GAS5可作为竞争性内源性RNA吸附miR-21-5p调控基质金属蛋白酶的表达,进而影响关节软骨基质代谢。但荣筋拈痛方是否通过长链非编码RNA GAS5/miR-21调控软骨基质代谢,发挥防治骨关节炎的作用机制有待深入研究。
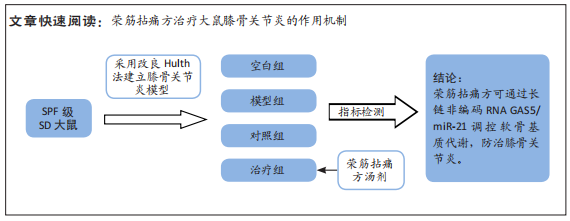
目的:从长链非编码RNA GAS5/miR-21调控软骨基质合成与分解代谢角度,探讨荣筋拈痛方治疗SD大鼠膝骨关节炎的作用机制。
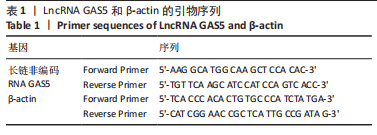
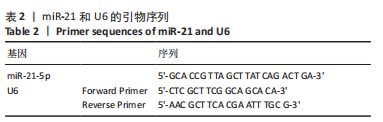
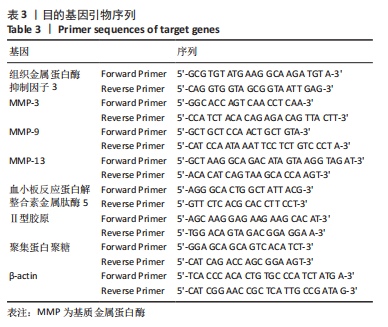
方法:SPF级8周龄雄性SD大鼠60只,随机分为4组,即空白组、模型组、治疗组及对照组,每组15只。后3组采用改良Hulth法建立大鼠膝骨关节炎模型。造模后2周,空白组和模型组予生理盐水,治疗组予荣筋拈痛方汤剂,对照组予盐酸氨基葡萄糖胶囊水溶液,每天灌胃一次,共干预12周。药物干预结束后取材,采用苏木精-伊红染色、改良番红O-固绿染色观察软骨组织显微结构形态变化,实时荧光定量PCR法检测长链非编码RNA GAS5、miR-21的表达及基质代谢因子mRNA的表达,Western blot法检测软骨组织中基质代谢因子蛋白的表达。
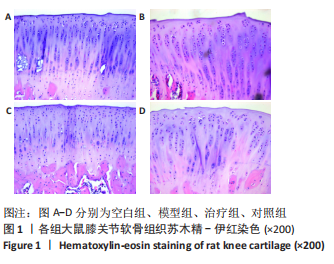
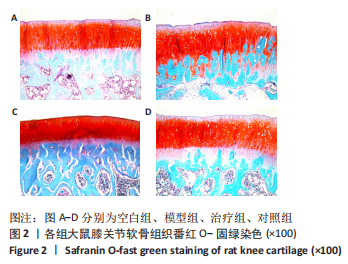
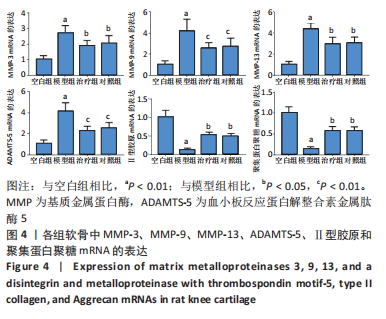
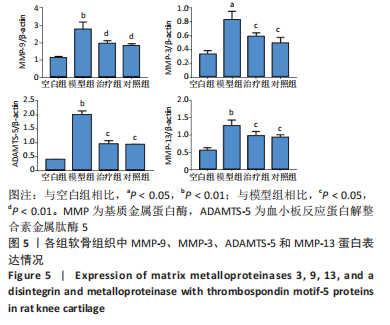
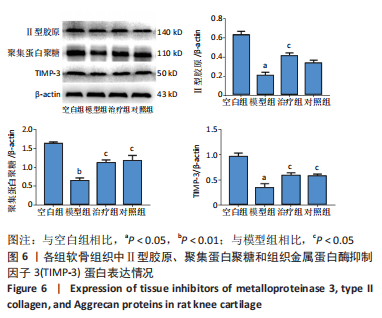
结果与结论:①软骨显微结构观察,模型组软骨4层结构紊乱,排列不规律,潮线及黏合线不规则或消失,软骨细胞增生肥大且排列紊乱,软骨下骨增生,胶原、蛋白多糖大量丢失;治疗组和对照组软骨4层结构、潮线可辨,软骨细胞排列较规律,软骨下骨结构较完整,胶原、蛋白多糖部分丢失;②与空白组相比,模型组软骨组织中长链非编码RNA GAS5及基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13、血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶5 mRNA表达量升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),治疗组、对照组与模型组相比表达量降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);模型组软骨组织中miR-21及组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3、Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖mRNA表达量降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),治疗组、对照组与模型组相比表达量升高(P < 0.05);③与空白组相比,模型组软骨组织中组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3、Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖蛋白表达降低(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),治疗组和对照组中表达升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05);模型组软骨组织中基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9、基质金属蛋白酶13、血小板反应蛋白解整合素金属肽酶5蛋白表达升高(P < 0.01或P < 0.05),治疗组和对照组中表达降低(P < 0.01或
P < 0.05);④提示荣筋拈痛方下调膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织中长链非编码RNA GAS5、基质金属蛋白酶3、基质金属蛋白酶9等的表达,上调miR-21、组织金属蛋白酶抑制因子3、Ⅱ型胶原和聚集蛋白聚糖的表达,影响软骨基质分解和合成代谢,减少软骨基质中胶原、蛋白多糖的丢失,延缓软骨基质降解,减轻软骨组织形态结构的破坏。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1470-0396(赵忠胜)
中图分类号: