中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (36): 5795-5800.doi: 10.12307/2023.732
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
骨盆倾斜对髋关节置换后站立位髋臼侧应力影响的有限元分析
闫瑞忠1,李佳慧2,林树忠1,武晓刚3,郭志坚1,刘文琦1,刘 强4
- 1山西医科大学附属太原中心医院骨科,山西省太原市 030009;2山西中医药大学,山西省晋中市 030619;3太原理工大学生物医学工程教研室,山西省太原市 030024;4山西医科大学附属山西白求恩医院骨科,山西省太原市 030032
Effect of pelvic tilt on the stress at the acetabular side in standing position after total hip arthroplasty: finite element analysis
Yan Ruizhong1, Li Jiahui2, Lin Shuzhong1, Wu Xiaogang3, Guo Zhijian1, Liu Wenqi1, Liu Qiang4
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Taiyuan Central Hospital Affiliated to Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030009, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Jinzhong 030619, Shanxi Province, China; 3Department of Biomedical Science, Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan 030024, Shanxi Province, China; 4Department of Orthopedics, Shanxi Bethune Hospital, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030032, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨盆倾斜角的调整:根据术前站立位骨盆倾斜角的值,以-10°和10°为界,若术前骨盆倾斜角> 10°,目标参考平面为站立位骨盆倾斜角减10°;如果站立位骨盆倾斜角> 10°,目标参考平面取站立位骨盆倾斜角和仰卧位骨盆倾斜角之和的1/2,其理论基础为全髋关节置换术后骨盆平均后倾10°。
功能性骨盆平面 (Functional pelvic plane,FPP):在计算机导航软件应用于髋关节置换术前计划时,计算出髋臼杯的前倾角和外展角后,此过程需选择一个平面作为参考平面,通常大多数患者选取术前仰卧位前骨盆平面作为参考平面,即三维CT重建图像前骨盆平面称之为功能性骨盆平面,也称之为目标参考平面。
骨盆前倾、后倾:指骨盆在矢状位的旋转,直接影响髋臼的方向,如果骨盆后倾增加,相伴随的是髋臼前倾角和外展角的增加;反之,骨盆后倾减少,伴随髋臼功能性前倾角和外展角的减少。后倾指骨盆相对脊柱外科医师;前倾指髋关节相对关节外科医师。背景:在髋关节置换术中,仅利用髋臼解剖放置髋臼杯会改变功能性髋臼杯的方向;计算机导航完成髋关节置换手术可提高假体放置的准确性。
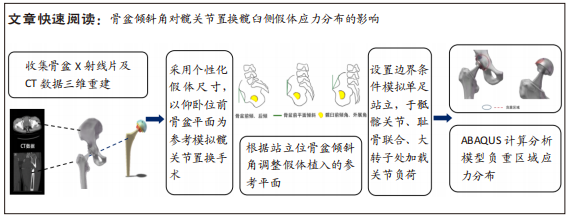
目的:应用有限元模型模拟手术,模拟髋臼杯的应力大小及区域,结合骨盆倾斜角计划髋关节置换髋臼杯放置方向,探讨骨盆倾斜角对髋关节置换术髋臼侧假体应力分布的影响。
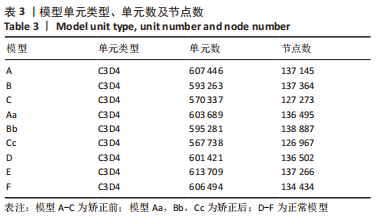
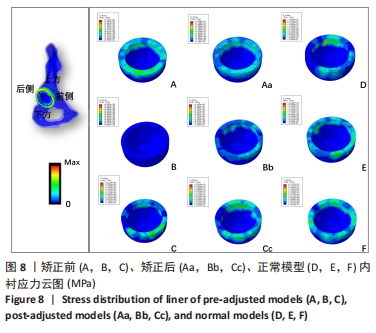
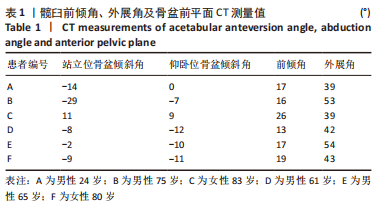
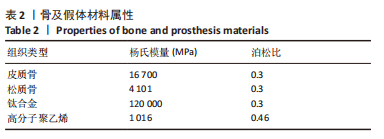
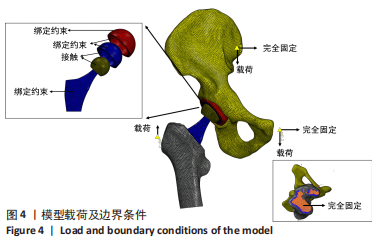
方法:收集6例(标记为A-F)骨盆X射线片及CT数据,通过有限元软件ABAQUS 6.14-4(SIMULIA 公司,法国)建立髋关节模型,以仰卧位前骨盆平面为坐标平面,模拟髋关节置换手术,建立6个模型,再根据站立位骨盆倾斜角,对骨盆倾斜角≤-10°与骨盆倾斜角 > 10°者,调整假体植入的参考平面,建立9个模型,分为矫正前模型:A(-14°),B(-29°),C(11°);矫正后模型:Aa(-7°),Bb(-18°),Cc(1°);正常模型:D(-8°),E(-2°),F(-9°)。在有限元求解软件中,约束固定模拟单足站立,于骶髂关节、耻骨联合、大转子处加载关节负荷,比较各模型髋臼、髋臼杯及内衬最大Von Mises应力分布情况。
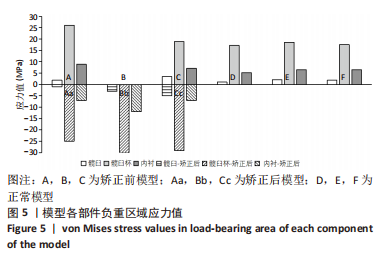
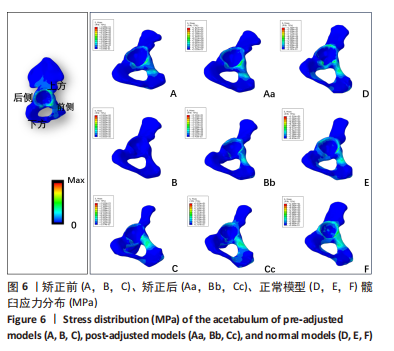
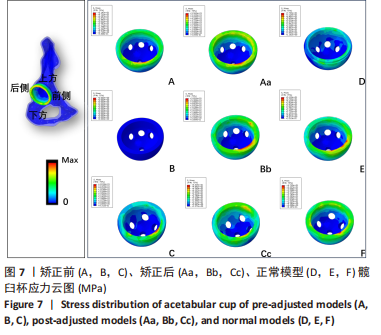
结果与结论:①运算中模型B出现不收敛,在骨盆倾斜矫正后收敛;模型A出现不收敛的趋向。9个模型中髋臼负重区最大von Mises应力(简称应力)在Cc模型,值为4.9 MPa,最低在D模型,值为1.07 MPa;髋臼杯负重区最大应力在Bb模型,值为29.87 MPa,最小在D模型,值为17.21 MPa;内衬负重区最大应力在Bb模型,值为12.45 MPa,最低应力为D模型,值为5.21 MPa,负重区域在聚乙烯内衬边缘上部靠近中部处。②站立位骨盆倾斜角-14°和-25°模型及11°模型相对-10° < 骨盆倾斜角≤10°模型表现出高的应力值,骨盆倾斜角为-14°模型矫正骨盆前平面后应力值接近-10° < 骨盆倾斜角≤10°模型之值,提示骨盆倾斜角偏离-10°至10°区域是髋关节术后磨损继发脱位的危险因素;对骨盆过度后倾者调整其骨盆前平面可降低全髋关节置换术后并发症的发生。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0016-012X (闫瑞忠)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: